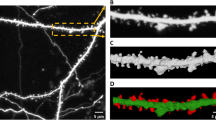
Abstract
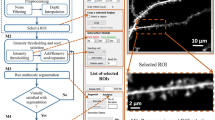
The variations in dendritic branch morphology and spine density provide insightful information about the brain function and possible treatment to neurodegenerative disease, for example investigating structural plasticity during the course of Alzheimer’s disease. Most automated image processing methods aiming at analyzing these problems are developed for in vitro data. However, in vivo neuron images provide real time information and direct observation of the dynamics of a disease process in a live animal model. This paper presents an automated approach for detecting spines and tracking spine evolution over time with in vivo image data in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. We propose an automated pipeline starting with curvilinear structure detection to determine the medial axis of the dendritic backbone and spines connected to the backbone. We, then, propose the adaptive local binary fitting (aLBF) energy level set model to accurately locate the boundary of dendritic structures using the central line of curvilinear structure as initialization. To track the growth or loss of spines, we present a maximum likelihood based technique to find the graph homomorphism between two image graph structures at different time points. We employ dynamic programming to search for the optimum solution. The pipeline enables us to extract dynamically changing information from real time in vivo data. We validate our proposed approach by comparing with manual results generated by neurologists. In addition, we discuss the performance of 3D based segmentation and conclude that our method is more accurate in identifying weak spines. Experiments show that our approach can quickly and accurately detect and quantify spines of in vivo neuron images and is able to identify spine elimination and formation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Kofahi, K. A., Lasek, S., Szarowski, D. H., Pace, C. J., Nagy, G., Turner, J. N., et al. (2002). Rapid automated three-dimensional tracing of neurons from confocal image stacks. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 6, 171–187. doi:10.1109/TITB.2002.1006304.
Bertsekas, D.P. (2000) Dynamic programming and optimal control, Vols. 1 & 2, 2nd ed. Athena Scientific.
Besl, P., & McKay, N. (1992). A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14, 239–256. doi:10.1109/34.121791.
Bourne, J. N., & Harris, K. M. (2008). Balancing structure and function at hippocampal dendritic spines. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 31, 47–67. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125646.
Bresenham, J. E. (1965). Algorithm for computer control of a digital plotter. IBM Syst., 4, 25–30.
Carsten, S. (1998). An unbiased detector of curvilinear structures. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 20, 113–125. doi:10.1109/34.659930.
Chan, T. F., & Vese, L. (2001). Active contours without edges. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 10, 266–277. doi:10.1109/83.902291.
Cheng, J., Zhou, X., Miller, E., Witt, M. R., Zhu, J., Sabatini, B. L., et al. (2007). A novel computational approach for automatic dendrite spines detection in two-photon laser scan microscopy. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 165, 122–134. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.05.020.
Gibson, S. F., & Lanni, F. (1991). Experimental test of an analytical model of aberration in an oil-immersion objective lens used in three-dimensional light microscopy. J Opt Soc Am A, 8, 1601–1613. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.8.001601.
Hell, P., & Nesetril, J.(2004) Graphs and homeomorphisms. Oxford Lecture Series in Mathematics and its Applications 28. Oxford University Press.
Jang, J. H., & Hong, K. S. (2002). Detection of curvilinear structures and reconstruction of their regions in gray-scale images. Pattern Recognition, 35, 807–824. doi:10.1016/S0031-3203(01)00073-5.
Kay, S.M. (1993) Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory. Prentice Hall.
Koh, I. Y. Y., Lindquist, W. B., Zito, K., Nimchinsky, E. A., & Svoboda, K. (2002). An image analysis algorithm for dendritic spines. Neural Computation, 14, 1283–1310. doi:10.1162/089976602753712945.
Li, C., Kao, C. Y., Gore, J. C., & Ding, Z. (2007). Implicit active contour driven by local binary fitting energy. MN: IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis Pattern Recognition. Minneapolis, Mn, 2007.
Mizrahi, A., Lu, J., Irving, R., Feng, G., & Katz, L. C. (2006). In vivo imaging of juxtaglomerular neuron turnover in the mouse olfactory bulb. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 1912–1917. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506297103.
Mosaliganti, K.P., Janoos, F., Xu, X., Machiraju, R., Huang, K., & Wong, S.T.C.(2006) Temporal matching of dendritic spines in confocal Microscopy images of neuronal tissue sections. MICCAI 2006 Proceedings. Copenhagen, Denmark. 106-113.
Otsu, N. (1979). A threshold selection method from gray-level histogram. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 9, 62–66. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076.
Peters, A., Palay, S.L., & Webster, H.(1991) The fine structure of the nervous system: neurons and their supporting cells. Oxford University Press.
Segal, M. (2005). Dendritic spines and long-term plasticity. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 6, 277–284. doi:10.1038/nrn1649.
Spires-Jones, T. L., Meyer-Luehmann, M., Osetek, J. D., Jones, P. B., Stern, E. A., Bacskai, B. J., et al. (2007). Impaired spine stability underlies plaque-related spine loss in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. American Journal of Pathology, 171, 1304–1311. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070055.
Spires, T. L., Meyer-Luehmann, M., Stern, E. A., McLean, P. J., Skoch, J., Nguyen, P. T., et al. (2005). Dendritic spine abnormalities in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice demonstrated by gene transfer and intravital multiphoton microscopy. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 7278–7287. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1879-05.2005.
Xiong, G., Zhou, X., Degterev, A., Ji, L., & Wong, S. T. C. (2006). Automated neurite labeling and analysis in fluorescence microscopy images. Cytometry Part A., 69A, 494–505.
Yang, X., Li, H., & Zhou, X. (2006). Nuclei segmentation using marker-controlled watershed, tracking using mean-shift and Kalman filter in time-lapse microscopy. IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems I., 53, 2405–2414. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2006.884469.
Zhang, Y., Zhou, X., Witt, R., Sabatini, B., Adjeroh, D., & Wong, S. T. C. (2007). Dendritic spine detection using curvilinear structure detection and LDA classifier. NeuroImage, 36, 346–360. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.044.
Zhou, W., Li, H., & Zhou, X. (2008). 3D Dendrite Reconstruction and Spine Identification. MICCAI. New York, NY, 2008.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank members of the Center for Biomedical Informatics, The Methodist Hospital Research Institute, especially Zheng Xia and former members of the HCNR Center for Bioinformatics, Harvard Medical School. We also thank Dr Tara Spires-Jones and Dr Bradley Hyman for providing sample in vivo image data. This research is partially funded by NIH R01 AG028928 and NIH R01 LM009161 and by HCNR, Harvard Medical School.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, J., Zhou, X., Dy, J.G. et al. An Automated Pipeline for Dendrite Spine Detection and Tracking of 3D Optical Microscopy Neuron Images of In Vivo Mouse Models. Neuroinform 7, 113–130 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-009-9047-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-009-9047-0