Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the association between Triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) and Matsuda indices in Greek obese children and adolescents, in order to assess whether it could be used as a predictor of insulin resistance.
Methods
367 children (47.7% boys) with mean age of 9.9 ± 2.3 years, who were investigated for obesity, were included. After overnight fasting, TyG and HOMA-IR indices were calculated in all participants. In a subpopulation of 72 children Matsuda index was also calculated.
Results
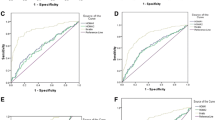
48.8% and 36.1% of the participants had insulin resistance according to HOMA-IR and Matsuda index respectively. TyG was significantly and positively correlated with BMI, ΗΟΜΑ-IR, lipid profile and Matsuda index. ROC curve analysis for TyG showed that the optimal cutoff value for the prediction of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was 7.96 with sensitivity 65% and specificity 58%. The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.65 which significantly differs from 0.5 (p < 0.001). Similarly, the optimal cutoff value of TyG index for predicting insulin resistance as evidenced by Matsuda was 7.91 with sensitivity 85% and specificity 61%. The AUC was 0.75 (p < 0.001). The odds for insulin resistance (with HOMA-IR) was 2.54 times greater for subjects with TyG higher than 7.96, while the odds for insulin resistance (with Matsuda) was 8.56 times greater for subjects with TyG more than 7.91.
Conclusions
TyG index shows a positive correlation with insulin resistance among children and adolescents, however further studies are needed to clarify its predictive ability.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CHOL:
-
Cholesterol
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- FPI:
-
Fasting plasma insulin
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
- HEC:
-
Hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Tg:
-
Triglycerides
- TSH:
-
Thyroid stimulating hormone
- TyG:
-
Triglyceride-glucose index
References
G.B.D.O. Collaborators, A. Afshin, M.H. Forouzanfar, M.B. Reitsma, P. Sur, K. Estep, A. Lee, L. Marczak, A.H. Mokdad, M. Moradi-Lakeh, M. Naghavi, J.S. Salama, T. Vos, K.H. Abate, C. Abbafati, M.B. Ahmed, Z. Al-Aly, A. Alkerwi, R. Al-Raddadi, A.T. Amare, A. Amberbir, A.K. Amegah, E. Amini, S.M. Amrock, R.M. Anjana, J. Arnlov, H. Asayesh, A. Banerjee, A. Barac, E. Baye, D.A. Bennett, A.S. Beyene, S. Biadgilign, S. Biryukov, E. Bjertness, D.J. Boneya, I. Campos-Nonato, J.J. Carrero, P. Cecilio, K. Cercy, L.G. Ciobanu, L. Cornaby, S.A. Damtew, L. Dandona, R. Dandona, S.D. Dharmaratne, B.B. Duncan, B. Eshrati, A. Esteghamati, V.L. Feigin, J.C. Fernandes, T. Furst, T.T. Gebrehiwot, A. Gold, P.N. Gona, A. Goto, T.D. Habtewold, K.T. Hadush, N. Hafezi-Nejad, S.I. Hay, M. Horino, F. Islami, R. Kamal, A. Kasaeian, S.V. Katikireddi, A.P. Kengne, C.N. Kesavachandran, Y.S. Khader, Y.H. Khang, J. Khubchandani, D. Kim, Y.J. Kim, Y. Kinfu, S. Kosen, T. Ku, B.K. Defo, G.A. Kumar, H.J. Larson, M. Leinsalu, X. Liang, S.S. Lim, P. Liu, A.D. Lopez, R. Lozano, A. Majeed, R. Malekzadeh, D.C. Malta, M. Mazidi, C. McAlinden, S.T. McGarvey, D.T. Mengistu, G.A. Mensah, G.B.M. Mensink, H.B. Mezgebe, E.M. Mirrakhimov, U.O. Mueller, J.J. Noubiap, C.M. Obermeyer, F.A. Ogbo, M.O. Owolabi, G.C. Patton, F. Pourmalek, M. Qorbani, A. Rafay, R.K. Rai, C.L. Ranabhat, N. Reinig, S. Safiri, J.A. Salomon, J.R. Sanabria, I.S. Santos, B. Sartorius, M. Sawhney, J. Schmidhuber, A.E. Schutte, M.I. Schmidt, S.G. Sepanlou, M. Shamsizadeh, S. Sheikhbahaei, M.J. Shin, R. Shiri, I. Shiue, H.S. Roba, D.A.S. Silva, J.I. Silverberg, J.A. Singh, S. Stranges, S. Swaminathan, R. Tabares-Seisdedos, F. Tadese, B.A. Tedla, B.S. Tegegne, A.S. Terkawi, J.S. Thakur, M. Tonelli, R. Topor-Madry, S. Tyrovolas, K.N. Ukwaja, O.A. Uthman, M. Vaezghasemi, T. Vasankari, V.V. Vlassov, S.E. Vollset, E. Weiderpass, A. Werdecker, J. Wesana, R. Westerman, Y. Yano, N. Yonemoto, G. Yonga, Z. Zaidi, Z.M. Zenebe, B. Zipkin, C.J.L. Murray, Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 377(1), 13–27 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1614362
J.P. Despres, I. Lemieux, Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 444(7121), 881–887 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05488
S.H. Lee, H.S. Ha, Y.J. Park, J.H. Lee, H.W. Yim, K.H. Yoon, M.I. Kang, W.C. Lee, H.Y. Son, Y.M. Park, H.S. Kwon, Identifying metabolically obese but normal-weight (MONW) individuals in a nondiabetic Korean population: the Chungju Metabolic disease Cohort (CMC) study. Clin. Endocrinol. 75(4), 475–481 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04085.x
R. Kelishadi, S.R. Cook, M.E. Motlagh, M.M. Gouya, G. Ardalan, M. Motaghian, R. Majdzadeh, M.A. Ramezani, Metabolically obese normal weight and phenotypically obese metabolically normal youths: the CASPIAN study. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 108(1), 82–90 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2007.10.013
L.E. Simental-Mendia, M. Rodriguez-Moran, F. Guerrero-Romero, The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 6(4), 299–304 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2008.0034
F. Guerrero-Romero, L.E. Simental-Mendia, M. Gonzalez-Ortiz, E. Martinez-Abundis, M.G. Ramos-Zavala, S.O. Hernandez-Gonzalez, O. Jacques-Camarena, M. Rodriguez-Moran, The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95(7), 3347–3351 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-0288
T. Du, G. Yuan, M. Zhang, X. Zhou, X. Sun, X. Yu, Clinical usefulness of lipid ratios, visceral adiposity indicators, and the triglycerides and glucose index as risk markers of insulin resistance. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 13, 146 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-014-0146-3
M.C. Espinel-Bermudez, J.A. Robles-Cervantes, L. del Sagrario Villarreal-Hernandez, J.P. Villasenor-Romero, S.O. Hernandez-Gonzalez, M. Gonzalez-Ortiz, E. Martinez-Abundis, K.G. Perez-Rubio, Insulin resistance in adult primary care patients with a surrogate index, Guadalajara, Mexico, 2012. J. Investig. Med. 63(2), 247–250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/JIM.0000000000000130
S.H. Lee, K. Han, H.K. Yang, M.K. Kim, K.H. Yoon, H.S. Kwon, Y.M. Park, Identifying subgroups of obesity using the product of triglycerides and glucose: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008-2010. Clin. Endocrinol. 82(2), 213–220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.12502
N.S. Mohd Nor, S. Lee, F. Bacha, H. Tfayli, S. Arslanian, Triglyceride glucose index as a surrogate measure of insulin sensitivity in obese adolescents with normoglycemia, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: comparison with the hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamp. Pediatr. Diabetes 17(6), 458–465 (2016)
C. Irace, C. Carallo, F.B. Scavelli, M.S. De Franceschi, T. Esposito, C. Tripolino, A. Gnasso, Markers of insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis. A comparison of the homeostasis model assessment and triglyceride glucose index. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 67(7), 665–672 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12124
S.-H. Lee, H.-S. Kwon, Y.-M. Park, H.-S. Ha, S.H. Jeong, H.K. Yang, J.-H. Lee, H.-W. Yim, M.-I. Kang, W.-C. Lee, Predicting the development of diabetes using the product of triglycerides and glucose: the Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort (CMC) study. PLoS ONE 9(2), e90430 (2014)
L.E. Simental-Mendia, G. Hernandez-Ronquillo, R. Gomez-Diaz, M. Rodriguez-Moran, F. Guerrero-Romero, The triglycerides and glucose index is associated with cardiovascular risk factors in normal-weight children and adolescents. Pediatr. Res. 82(6), 920–925 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2017.187
D.M. Styne, S.A. Arslanian, E.L. Connor, I.S. Farooqi, M.H. Murad, J.H. Silverstein, J.A. Yanovski, Pediatric obesity-assessment, treatment, and prevention: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102(3), 709–757 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-2573
D.R. Matthews, J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, B.A. Naylor, D.F. Treacher, R.C. Turner, Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7), 412–419 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00280883
B. Tresaco, G. Bueno, I. Pineda, L.A. Moreno, J.M. Garagorri, M. Bueno, Homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) index cutoff values to identify the metabolic syndrome in children. J. Physiol. Biochem. 61(2), 381–388 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03167055
M. Kostovski, V. Simeonovski, K. Mironska, V. Tasic, Z. Gucev, . Open Access Maced J. Med. Sci. 6(3), 511–518 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2018.097
E.J. Mayer-Davis, A.R. Kahkoska, C. Jefferies, D. Dabelea, N. Balde, C.X. Gong, P. Aschner, M.E. Craig, ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 19(Suppl 27), 7–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12773
M. Matsuda, R.A. DeFronzo, Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 22(9), 1462–1470 (1999)
A. Borai, C. Livingstone, I. Kaddam, G. Ferns, Selection of the appropriate method for the assessment of insulin resistance. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 11(1), 158 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-158
S. Moon, J.S. Park, Y. Ahn, The cutoff values of triglycerides and glucose index for metabolic syndrome in American and Korean adolescents. J. Korean Med. Sci. 32(3), 427–433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.427
V. Calcaterra, C. Montalbano, A. de Silvestri, G. Pelizzo, C. Regalbuto, V. Paganelli, R. Albertini, F. D. Cave, D. Larizza, H. Cena, Triglyceride glucose index as a surrogate measure of insulin sensitivity in a caucasian pediatric population. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0024
S.A. Vieira-Ribeiro, P.C.A. Fonseca, C.S. Andreoli, A.Q. Ribeiro, H.H.M. Hermsdorff, P.F. Pereira, S.E. Priore, S.C.C. Franceschini, The TyG index cutoff point and its association with body adiposity and lifestyle in children. J. Pediatr. 95(2), 217–223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jped.2017.12.012
J.C. Locateli, W.A. Lopes, C.F. Simoes, G.H. de Oliveira, K. Oltramari, R.H. Bim, V.H. de Souza Mendes, J.M. Remor, C.A. Lopera, N. Nardo Junior, Triglyceride/glucose index is a reliable alternative marker for insulin resistance in South American overweight and obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 32(10), 1163–1170 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2019-0037
G.S. Berenson, S.R. Srinivasan, W. Bao, W.P. Newman, R.E. Tracy, W.A. Wattigney, Association between multiple cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in children and young adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 338(23), 1650–1656 (1998)
Acknowledgements
Department of Endocrinology, Growth and Development, “P. & A. Kyriakou” Children’s Hospital, Athens, Greece; Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes, “Aghia Sophia” Hospital, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece; and Department of Biochemistry, P. & A. Kyriakou” Children’s Hospital, Athens, Greece are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dikaiakou, E., Vlachopapadopoulou, E.A., Paschou, S.A. et al. Τriglycerides-glucose (TyG) index is a sensitive marker of insulin resistance in Greek children and adolescents. Endocrine 70, 58–64 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02374-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02374-6