Abstract
Purpose
The aim of our study was to compare the efficacy of thyroid remnant ablation using low (1.1 GBq) and intermediate-high radioiodine (RAI) activity (1.85–3.7 GBq) in low-risk differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) and to evaluate the staging role of the whole body scan (WBS) in detection extrathyroidal disease.
Materials and methods
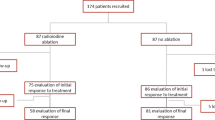
We retrospectively included 277 patients who underwent total thyroidectomy and RAI for low-risk DTC and divided them in two groups according to RAI activity at ablation: group 1 (n = 174) treated with low activity (1.1 GBq), and group 2 (n = 103) with intermediate-high activity (1.85–3.7 GBq). To evaluate the successful ablation rate, the WBS 1 year after RAI was visually interpreted using a three-point scale: score 0 in case of absence of visible RAI uptake in thyroid bed; score 1 in presence of faint uptake in the thyroid bed; and score 2 in case of significant RAI uptake in thyroid bed.
Results
The success ablation rate was significantly higher in group 2 than group 1 (p < 0.001) with the presence of a positive WBS (score 1–2) in 65% low-activity group and 33% in intermediate-high group. Considering response to therapy categories, excellent response rate was significantly higher in group 2 (p = 0.020), while indeterminate response was higher in group 1 (p value = 0.005). Post RAI imaging revealed extrathyroidal uptake in 27 cases: 17 laterocervical nodal and 10 distant metastases. In both groups similar detection rate of nodal and distant metastases were recognized without any statistical difference.
Conclusions
The ablation rate with intermediate-high RAI activity (1.85–3.7 GBq) was better than with a low activity (1.1 GBq). First WBS may help to recognize nodal and distant metastases in about 10% of cases changing clinical stage and subsequent management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.I. Sherman, Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet 361, 501–511. (2003)
B.R. Haugen, E.K. Alexander, K.C. Bible, G.M. Doherty, S.J. Mandel, Y.E. Nikiforov et al. American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2016(26), 1–133 (2015)
C.S. Bal, A.K. Padhy, Radioiodine remnant abaltion: a critical review. World J. Nucl. Med. 14, 144–155 (2015)
L.H. Duntas, D.S. Cooper, Review on the occasion of a decade of recombinant human TSH: prospects and novel uses. Thyroid 18, 509–516 (2008)
C. Bal, A.K. Padhy, S. Jana, G.S. Pant, A.K. Basu, Prospective randomized clinical trial to evaluate the optimal dose of 131I for remnant ablation in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Cancer 77, 2574–2580 (1996)
K. Watanabe, M. Uchiyama, K. Fukuda, The outcome of I-131 ablation therapy for intermediate and high-risk differentiatetd thyroid cancer using a strict definition of successful ablation. Jpn. J. Radio. 35, 505–510 (2017)
I.D. Hay, G.B. Thompson, C.S. Grant et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma managed at the Mayo Clinic during six decades (1940-1999): temporal trends in initial therapy and long-term outcome in 2444 consecutively treated patients. World J. Surg. 26, 879–885. (2002)
J. Jonklaas, D.S. Cooper, K.B. Ain et al. Radioiodine therapy in patients with stage I differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 20, 1423–1424 (2010)
E. Hindie, D. Taieb, A.M. Avram et al. Radioactive iodine ablation in low-risk thyroid cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 6, 686 (2018)
A.S. Moten, H. Zhao, A.I. Willis, The overuse of radioactive iodine in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer patients. Surg. Oncol. 29, 184–189 (2019)
A.M. Sawka, K. Thephamongkhol, M. Brouwers, L. Thabane, G. Browman, H.C. Gerstein, Clinical review 170: a systematic review and metaanalysis of the effectiveness of radioactive iodine remnant ablation for well-differentiated thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 3668–3676 (2004)
A. Hackshaw, C. Harmer, U. Mallick, M. Haq, J.A. Franklyn, 131I activity for remnant ablation in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a systematic review. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 28–38 (2007)
M. Schlumberger, B. Catargi, I. Borget, D. Deandreis, S. Zerdoud, B. Bridji et al. Strategies of radioiodine ablation in patients with low-risk thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1663–1673 (2012)
U. Mallick, C. Harmer, B. Yap, J. Wadsley, S. Clarke, L. Moss et al. Ablation with low-dose radioiodine and thyrotropin alfa in thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1674–1685 (2012)
M. Tuttle, L.F. Morris, B. Haugen, J. Shah, J.A. Sosa, E. Rohren, R.M. Subramaniam, J.L. Hunt, N.D. Perrier, Thyroid‐differentiated and anaplastic carcinoma (Chapter 73). In: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th edn. ed. by M.B. Amin, S.B. Edge, F. Greene, D. Byrd, R.K. Brookland, M.K. Washington, J.E. Gershenwald, C.C. Compton, K.R. Hess, D.C. Sullivan, J.M. Jessup, J. Brierley, L.E. Gaspar, R.L. Schilsky, C.M. Balch, D.P. Winchester, E.A. Asare, M. Madera, D.M. Gress, L.R. Meyer (Springer International Publishing, New York City, 2017)
D.S. Cooper, G.M. Doherty, B.R. Haugen, R.T. Kloos, S.L. Lee, S.J. Mandel et al. Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 19, 1167–214 (2009)
V. Zilioli, A. Peli, M.B. Panarotto, G. Magri, A. Alkraisheh, C. Wiefels et al. Differentiated thyroid carcinoma: incremental diagnosi value of 131I SPECT/CT over planar whole body scan after radioiodine therapy. Endocrine 56, 551–559 (2017)
S.C. Clement, R.P. Peeters, C.M. Ronckers, T.P. Links, M.M. van den Heuvel-Eibrink, E.J. Nieveen van Dijkum et al. Intermediate and longterm adverse effects of radioiodine therapy for differentiated thyroid carcinoma—a systematic review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 41, 925–934 (2015)
L. Agate, F. Bianchi, F. Brozzi, P. Santini, E. Molinaro, V. Bottici et al. Less than 2% of the low and intermediate risk differentiatetd thyroid cancers show distant metastases at post-ablation whole-body scan. Eur. Thyroid J. 8, 90–95 (2019)
D. Albano, M.B. Panarotto, R. Durmo, C. Rodella, F. Bertagna, R. Giubbini, Clinical and prognostic role of detection timing of distant metastases in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrine 63, 79–86 (2019)
C. Durante, N. Haddy, E. Baudin, S. Leboulleux, D. Hartl, J.P. Travagli et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 2892–2899 (2006)
A. Campenni, L. Giovanella, S.A. Pignata, A. Vento, A. Alibrandi, L. Sturiale et al. Undetectable or low (<1 ng/ml) postsurgical thyroglobulin values do not rule out metastases in early stage differentiated thyroid cancer patients. Oncotarget 9, 17491–17500 (2018)
E. Hindie, D. Melliere, F. Lange, I. Hallaj, C. de Labriolle-Vaylet, C. Jeanguillaume et al. Functioning pulmonary metastases of thyroid cancer: does radioiodine influence the prognosis? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 30, 974–981 (2003)
E. Hindie, P. Zanotti-Fregonara, I. Keller, F. Duron, J.Y. Devaux, M. Calzada-Nocaudie et al. Bone metastases of differentiated thyroid cancer: impact of early 131I-based detection on outcome. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 14, 799–807 (2007)
D. Casara, D. Rubello, G. Saladini, G. Masarotto, A. Favero, M.E. Girelli et al. Different features of pulmonary metastases in differentiated thyroid cancer: natural history and multivariate statistical analysis of prognostic variables. J. Nucl. Med. 34, 1626–1631 (1993)
Y. Orita, I. Sugitani, M. Matsuura, M. Ushijima, K. Tsukahara, Fujimoto et al. Prognostic factors and the therapeutic strategy for patients with bone metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Surgery 147, 424–431 (2010)
D. Albano, F. Bertagna, M. Bonacina, R. Durmo, E. Ceruddelli, M. Gazzilli et al. Possible delayed diagnosis and treatment of metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer by adopting the 2015 ATA guidelines. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 179, 143–151 (2018)
A. Hackshaw, C. Harmer, U. Mallick, M. Haq, J.A. Franklyn, 131Iactivity for remnant ablation in patients with differentiated thyroidcancer: a systematic review. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 28–38 (2007)
D. Peizhun, X. Jiao, Y. Zhou, Y. Li, S. Kang, D. Zhang et al. Low versus high radioiodine activity to ablate the thyroidafterthyroidectomy for cancer: a meta-analysis of randomizedcontrolled trials. Endocrine 48, 96–105 (2015)
R. Ciappuccini, J. Hardouin, N. Heutte, D. Vaur, E. Quak, J.P. Rame et al. Stimulated thyroglobulin level at ablation in differentiated thyroid cancer: the impact of treatment preparation modalities and tumor burden. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 171, 247–252 (2014)
H.J. Park, J.J. Min, H.S. Bom, J. Kim, H.C. Song, S.Y. Kwon, Early stimulated thyroglobulin for response prediction after recombinant human thyrotropin-aided radioiodine therapy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 31, 616–622 (2017)
U. Mousa, A.S. Yikilmaz, A. Nar, Stimulated thyroglobulin values above 5.6 ng/ml before radioactive iodine ablation treatment following levothyroxine withdrawal is associated with a 2.38-fold risk of relapse in Tg-ab negative subjects with differentiated thyroid cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 19, 1028–1034 (2017)
A. Piccardo, F. Arecco, M. Puntoni, L. Foppiani, M. Cabria, S. Corvisieri et al. Focus on high-risk DTC patients: high postoperative serum thyroglobulin level is a strong predictor of disease persistence and is associated to progression-free survival and overall survival. Clin. Nucl. Med. 38, 18–24 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participant included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albano, D., Bonacina, M., Durmo, R. et al. Efficacy of low radioiodine activity versus intermediate-high activity in the ablation of low-risk differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrine 68, 124–131 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02148-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02148-9