Abstract
Purpose
Obestatin and ghrelin are peptides encoded by the preproghrelin gene. Obestatin inhibits food intake, in addition to regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Here, we test the ability of obestatin at improving metabolic control and liver function in type 2 diabetic animals (type 2 diabetes mellitus).
Methods
The effects of chronic obestatin treatment of mice with experimentally induced type 2 diabetes mellitus on serum levels of glucose and lipids, and insulin sensitivity are characterized. In addition, alterations of hepatic lipid and glycogen contents are evaluated.
Results
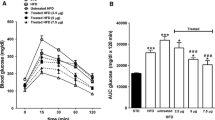
Obestatin reduced body weight and decreased serum glucose, fructosamine, and β-hydroxybutyrate levels, as well as total and low-density lipoprotein fractions of cholesterol. In addition, obestatin increased high-density lipoproteins cholesterol levels and enhanced insulin sensitivity in mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Moreover, obestatin diminished liver mass, hepatic triglycerides and cholesterol contents, while glycogen content was higher in livers of healthy and mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with obestatin. These changes were accompanied by reduction of increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and gamma glutamyl transpeptidase in T2DM mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obestatin increased adiponectin levels and reduced leptin concentration. Obestatin influenced the expression of genes involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism by increasing Fabp5 and decreasing G6pc, Pepck, Fgf21 mRNA in the liver. Obestatin increased both, AKT and AMPK phosphorylation, and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) protein levels as well as mRNA expression in the liver.
Conclusion
Obestatin improves metabolic abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus, restores hepatic lipid contents and decreases hepatic enzymes. Therefore, obestatin could potentially have a therapeutic relevance in treating of insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunctions in type 2 diabetes mellitus.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminostransferase
- AMPK:
-
5′AMP-activated protein kinase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminostransferase
- FABP1:
-
Fatty acid binding protein 1
- FABP4:
-
Fatty acid binding protein 4
- FABP5:
-
Fatty acid binding protein 5
- FAS:
-
Fatty acids synthase
- FGF-21:
-
Fibroblastic growth factor 21
- G6Pc:
-
Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit G6Pc
- GAPD:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- γGT:
-
Gamma glutamyl transferase
- GLP-1R:
-
Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor
- GLUT4:
-
Glucose transporter 4
- GOT:
-
Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase
- GPR39:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor 39
- HFD:
-
High fat diet
- IL-6:
-
interleukin 6
- IP:
-
Intraperitoneally
- OBST:
-
Obestatin
- PEPCK:
-
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
- STZ:
-
streptozotocin
- T1DM:
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
J. Zhang, P. Ren, O. Avsian-kretchmer, C. Luo, R. Rauch, Obestatin, a peptide encoded by the Ghrelin gene, opposes Ghrelin’s effects on food intake. Science (80−.) 310, 996–999 (2005)
N. Chartrel, R. Alvear-Perez, J. Leprince, X. Iturrioz, A. Reaux-Le Goazigo, V. Audinot, P. Chomarat, F. Coge, O. Nosjean, M. Rodriguez, J. Galizzi, J. Boutin, H. Vaudry, C. Llorens-Cortes, Comment on“ obestatin, a peptide encoded by the Ghrelin gene, opposes Ghrelin’s effects on food intake.” Science (80–.) 315, 766 (2007)
R. Granata, F. Settanni, D. Gallo, L. Trovato, L. Biancone, V. Cantaluppi, R. Nano, M. Annunziata, P. Campiglia, E. Arnoletti, Obestatin promotes survival of pancreatic bCells and human islets and induces expression of genes involved in the regulation of b-Cell mass and function. Diabetes 57, 967–979 (2008)
B. De Smet, T. Thijs, T.L. Peeters, I. Depoortere, Effect of peripheral obestatin on gastric emptying and intestinal contractility in rodents. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 19, 211–217 (2007)
R. Granata, M. Volante, F. Settanni, C. Gauna, C. Ghe, M. Annunziata, B. Deidda, I. Gesmundo, T. Abribat, A.J. Van Der Lely, G. Muccioli, E. Ghigo, M. Papotti, Unacylated ghrelin and obestatin increase islet cell mass and prevent diabetes in streptozotocin-treated newborn rats. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 45, 9–17 (2010)
R. Granata, D. Gallo, R.M. Luque, a Baragli, F. Scarlatti, C. Grande, I. Gesmundo, J. Cordoba-Chacon, L. Bergandi, F. Settanni, G. Togliatto, M. Volante, S. Garetto, M. Annunziata, B. Chanclon, E. Gargantini, S. Rocchietto, L. Matera, G. Datta, M. Morino, M.F. Brizzi, H. Ong, G. Camussi, J.P. Castano, M. Papotti, E. Ghigo, Obestatin regulates adipocyte function and protects against diet-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. FASEB J. 26, 3393–3411 (2012)
M. Aragno, R. Mastrocola, C. Ghé, E. Arnoletti, E. Bassino, G. Alloatti, G. Muccioli, Obestatin induced recovery of myocardial dysfunction in type 1 diabetic rats: underlying mechanisms. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 11, 129 (2012)
E. Cowan, K.J. Burch, B.D. Green, D.J. Grieve, Obestatin as a key regulator of metabolism and cardiovascular function with emerging therapeutic potential for diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 44, 2165–2181 (2016)
A. Vater, S. Sell, P. Kaczmarek, C. Maasch, K. Buchner, E. Pruszynska-Oszmalek, P. Kolodziejski, W.G. Purschke, K.W. Nowak, M.Z. Strowski, S. Klussmann, A. Mixed Mirror-image, DNA/RNA aptamer inhibits glucagon and acutely improves glucose tolerance in models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 21136–21147 (2013)
P.A. Kolodziejski, E. Pruszynska-Oszmalek, M. Sassek, P. Kaczmarek, D. Szczepankiewicz, M. Billert, P. Maćkowiak, M. Z. Strowski, W. Nowak, K. Changes, in obestatin gene and receptor-GPR39 expression in peripheral tissues of rat models of obesity, type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes 9, 353–361 (2017)
A.Z. Caron, X. He, W. Mottawea, E.L. Seifert, K. Jardine, D. Dewar-Darch, G.O. Cron, M.E. Harper, A. Stintzi, M.W. McBurney, The SIRT1 deacetylase protects mice against the symptoms of metabolic syndrome. FASEB J. 28, 1306–1316 (2014)
B. Emanuelli, S.G. Vienberg, G. Smyth, C. Cheng, K.I. Stanford, M. Arumugam, M.D. Michael, A.C. Adams, A. Kharitonenkov, C.R. Kahn, Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 515–527 (2014)
C. Allain, L. Poon, Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin. Chem. 20, 470–475 (1974)
J. Folsh, M. Less, G. Sloane Stanley, A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957)
D.R. Matthews, J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, B.A Naylor, D.F. Treacher, R.C. Turner, Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 28, 412–419 (1985)
A. Katz, S.S. Nambi, K. Mather, A. Baron, D. Follmann, G. Sullivan, M.J. Quon, Quantitative insuln sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate methof for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 2402–2410 (2000)
E. Pruszynska-Oszmalek, D. Szczepankiewicz, I. Hertig, M. Skrzypski, M. Sassek, P. Kaczmarek, P.A. Kolodziejski, P. Mackowiak, K.W. Nowak, M.Z. Strowski, T. Wojciechowicz, Obestatin inhibits lipogenesis and glucose uptake in isolated primary rat adipocytes. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 27, 23–33 (2013)
U. Gurriarán-Rodríguez, O. Al-Massadi, A. Roca-Rivada, A.B. Crujeiras, R. Gallego, M. Pardo, L.M. Seoane, Y. Pazos, F.F. Casanueva, J.P. Camiña, Obestatin as a regulator of adipocyte metabolism and adipogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 15, 1927–1940 (2011)
I. Gesmundo, D. Gallo, E. Favaro, E. Ghigo, R. Granata, Obestatin: A new metabolic player in the pancreas and white adipose tissue. IUBMB Life. 65, 976–982 (2013)
E.M. Egido, R. Hernandez, J. Marco, R.A. Silvestre, Effect of obestatin on insulin, glucagon and somatostatin secretion in the perfused rat pancreas. Regul. Pept. 152, 61–66 (2009)
B.D. Green, N. Irwin, P.R. Flatt, Direct and indirect effects of obestatin peptides on food intake and the regulation of glucose homeostasis and insulin secretion in mice. Peptides. 28, 981–987 (2007)
E. Bresciani, D. Rapetti, F. Donà, I. Bulgarelli, L. Tamiazzo, V. Locatelli, A. Torsello, Obestatin inhibits feeding but does not modulate GH and corticosterone secretion in the rat. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 29, 2–4 (2006)
G. Gourcerol, M. Million, D.W. Adelson, Y. Wang, L. Wang, J. Rivier, D.H. St-Pierre, Y. Taché, Lack of interaction between peripheral injection of CCK and obestatin in the regulation of gastric satiety signaling in rodents. Peptides. 27, 2811–2819 (2006)
P. Zizzari, R. Longchamps, J. Epelbaum, M.T. Bluet-Pajot, Obestatin partially affects ghrelin stimulation of food intake and growth hormone secretion in rodents. Endocrinology 148, 1648–1653 (2007)
K. Cusi, Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. Obes. 16, 141–149 (2009)
L. Bozzetto, A. Prinster, S. Cocozza, A.A. Rivellese, G. Annuzzi, Role of type 2 diabetes mellitus in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 41, 1368–1368 (2011)
Y. Gutierrez-Grobe, I. Villalobos-Blasquez, K. Sánchez-Lara, A.R. Villa, G. Ponciano-Rodríguez, M.H. Ramos, N.C. Chavez-Tapia, M. Uribe, N. Méndez-Sánchez, High ghrelin and obestatin levels and low risk of developing fatty liver. Ann. Hepatol. 9, 52–57 (2010)
J.M. Clark, F.L. Brancati, A.M. Diehl, The prevalence and etiology of elevated aminotransferase levels in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 98, 960–967 (2003)
S.S. Abiru, K. Migita, Y. Maeda, M. Daikoku, M. Ito, K. Ohata, S. Nagaoka, T. Matsumoto, Y. Takii, K. Kusumoto, M. Nakamura, A. Komori, K. Yano, H. Yatsuhashi, K. Eguchi, H. Ishibashi, Serum cytokine and soluble cytokine receptor levels in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 26, 39–45 (2006)
J.W. Haukeland, J.K. Damas, Z. Konopski, E.M. Løberg, T. Haaland, I. Goverud, P.A. Torjesen, K. Birkeland, K. Bjøro, P. Aukrust, Systemic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by elevated levels of CCL2 *. J. Hepatol. 44, 1167–1174 (2006)
J. Crespo, A. Cayón, P. Fernández-Gil, M. Hernández-Guerra, M. Mayorga, A. Domínguez-Díez, J. Fernández-Escalante, F. Pons-Romero, Gene Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor α and TNF-Receptors, p55 and p75, in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Patients. Hepatology 34, 1158–1163 (2000)
A. Wieckowska, B. Papouchado, Z. Li, R. Lopez, N. Zein, A. Feldstein, Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 103, 1372–1379 (2008)
A.J. Wigg, I.C. Roberts-Thomson, R.B. Dymock, P.J. McCarthy, R.H. Grose, A.G. Cummins, The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal permeability, endotoxaemia, and tumour necrosis factor α in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut. 48, 206–211 (2001)
Y. Wang, L.M. Ausman, R.M. Russell, A.S. Greenberg, X.-D. Wang, Increased apoptosis in high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats is associated with c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation and elevated proapoptotic bax. J. Nutr. 138, 1866–1871 (2008)
K. Uysal, S. Wiesbrock, M. Marino, G. Hotamisligil, Protection from obesity- induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF- alpha function. Nature 389, 610–614 (1997)
P.J. Klover, A.H. Clementi, R.A. Mooney, Interleukin-6 depletion selectively Improves hepatic insulin action in obesity. Endocrinology. 146, 3417–3427 (2016)
M. Maffei, J. Halaas, E. Ravussin, R.E. Pratley, G.H. Lee, Y. Zhang, H. Fei, S. Kim, R. Lallone, S. Ranganathan, Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1, 1155–1161 (1995)
K. Hotta, T. Funahashi, Y. Arita, M. Takahashi, M. Matsuda, Y. Okamoto, H. Iwahashi, H. Kuriyama, N. Ouchi, K. Maeda, M. Nishida, S. Kihara, N. Sakai, T. Nakajima, K. Hasegawa, M. Muraguchi, Y. Ohmoto, T. Nakamura, S. Yamashita, Adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20, 1595–1599 (2000)
M. Matsubara, S. Maruoka, S. Katayose, Inverse relationship between plasma adiponectin and leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese women. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 147, 173–180 (2002)
T. Yamauchi, J. Kamon, Y. Minokoshi, Y. Ito, H. Waki, S. Uchida, S. Yamashita, M. Noda, S. Kita, K. Ueki, K. Eto, Y. Akanuma, P. Froguel, F. Foufelle, P. Ferre, D. Carling, S. Kimura, R. Nagai, B.B. Kahn, T. Kadowaki, Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 8, 1288–1295 (2002)
K. Hotta, T. Funahashi, Y. Arita, M. Takahashi, M. Matsuda, Y. Okamoto, H. Iwahashi, H. Kuriyama, N. Ouchi, K. Maeda, M. Nishida, S. Kihara, N. Sakai, T. Nakajima, K. Hasegawa, M. Muraguchi, Y. Ohmoto, T. Nakamura, S. Yamashita, Adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. 20, 1595–1599 (2000)
S. Fischer, M. Hanefeld, S.M. Haffner, C. Fusch, U. Schwanebeck, C. Kohler, K. Fucker, U. Julius, Insulin-resistant patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have higher serum leptin levels independently of body fat mass. Acta Diabetol. 39, 105–110 (2002)
S. Zhang, Q. Zhang, L. Zhang, C. Li, H. Jiang, Expression of ghrelin and leptin during the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rat model. Mol. Med. Rep. 7, 223–228 (2013)
B.P. Cummings, Leptin therapy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 15, 607–612 (2013)
A. Wren, L. Seal, M. Cohen, A. Brynes, G. Frost, K. Murphy, W. Dhillo, M. Ghatei, S. Bloom, Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5992–5995 (2001)
R. Barazzoni, A. Bosutti, M. Stebel, M.R. Cattin, E. Roder, L. Visintin, L. Cattin, G. Biolo, M. Zanetti, G. Guarnieri, Ghrelin regulates mitochondrial-lipid metabolism gene expression and tissue fat distribution in liver and skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 288, 228–235 (2005)
E.T. Vestergaard, L.C. Gormsen, N. Jessen, S. Lund, T.K. Hansen, N. Moller, J. Otto, L. Jorgensen, Ghrelin infusion in humans induces acute insulin resistance and lipolysis independent of growth hormone signaling. Diabetes 57, 3205–3210 (2008)
S.S. Damjanovic, N.M. Lalic, P.M. Pesko, M.S. Petakov, A. Jotic, D. Miljic, K.S. Lalic, L. Lukic, M. Djurovic, V.B. Djukic, Acute effects of Ghrelin on insulin secretion and glucose disposal rate in Gastrectomized patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 2574–2581 (2016)
A. Agnew, D. Calderwood, O.P. Chevallier, B. Greer, D.J. Grieve, B.D. Green, Chronic treatment with a stable obestatin analog significantly alters plasma triglyceride levels but fails to influence food intake; fluid intake; body weight; or body composition in rats. Peptides. 32, 755–762 (2011)
G. Ren, Z. He, P. Cong, H. Chen, Y. Guo, J. Yu, Z. Liu, Q. Ji, Z. Song, Y. Chen, Peripheral administration of TAT-obestatin can influence the expression of liporegulatory genes but fails to affect food intake in mice. Peptides. 42, 8–14 (2013)
S. El Sawy, R. El-Sherbiny, M. El-Saka, R. El-Shaer, Effect of obestatin on normal, diabetic, and obese male albino rats. Tanta Med. J. 44, 16 (2016)
C. Wang, J. Dai, M. Yang, G. Deng, S. Xu, Y. Jia, Silencing of FGF-21 expression promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis by regulation of the. FEBS J. 281, 2136–2147 (2014)
M. Kitada, D. Koya, SIRT1 in type 2 diabetes: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Diabetes Metab. J 37, 315–325 (2013)
K. Coughlan, R. Valentine, N. Ruderman, A. Saha, AMPK activation: A therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes? Diabetes, Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 7, 241–253 (2014)
B.K. Smith, K. Marcinko, E.M. Desjardins, J.S. Lally, R.J. Ford, G.R. Steinberg, Treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease : role of AMPK. Am. J. Physiol. 311(4), 730–740 (2016)
C.J.P. Alvarez, M. Lodeiro, M. Theodoropoulou, J.P. Camiña, F.F. Casanueva, Y. Pazos, Obestatin stimulates Akt signalling in gastric cancer cells through beta-arrestin-mediated epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 16, 599–611 (2009)
A.S. Banks, N. Kon, C. Knight, M. Matsumoto, R. Gutierrez-Juarez, L. Rossetti, W. Gu, D. Accili, SirT1 gain of function increases energy efficiency and prevents diabetes in mice. Cell Metab. 8, 333–341 (2008)
C. Sun, F. Zhang, X. Ge, T. Yan, X. Chen, X. Shi, Q. Zhai, SIRT1 improves insulin sensitivity under insulin-resistant conditions by repressing PTP1B. Cell Metab. 6, 307–319 (2007)
B. Viollet, M. Foretz, B. Guigas, S. Horman, R. Dentin, L. Bertrand, L. Hue, F. Andreelli, Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver: a new strategy for the management of metabolic hepatic disorders. J. Physiol. 1, 41–53 (2006)
W.J. Schnedl, S. Ferber, J.H. Johnson, C.B. Newgard, STZ transport and cytotoxicity: specific enhancement in GLUT2-expressing cells. Diabetes. 43, 1326–1333 (1994)
T. Szkudelski, The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol. Res. 50, 537–546 (2001)
L. Pozzo, A. Vornoli, I. Coppola, C.M. Croce, Della, L. Giorgetti, P.G. Gervasi, V. Longo, Effect of HFD/STZ on expression of genes involved in lipid, cholesterol and glucose metabolism in rats. Life Sci. 166, 149–156 (2016)
A. Teufel, T. Itzel, W. Erhart, M. Brosch, X.Y. Wang, Y.O. Kim, W. von Schönfels, A. Herrmann, S. Brückner, F. Stickel, J.-F. Dufour, T. Chavakis, C. Hellerbrand, R. Spang, T. Maass, T. Becker, S. Schreiber, C. Schafmayer, D. Schuppan, J. Hampe, Comparison of gene expression patterns between mouse models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver tissues from patients. Gastroenterology 151, 513–525 (2016)
H. Nakagawa, Recent advances in mouse models of obesity- and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. World J. Hepatol. 7, 2110–2118 (2015)
Acknowledgements
P.A.K. is the recipient of a 2013 fellowship program UE Human Capital. This study forms part of the PhD thesis of P.A.K. This study was partially supported by the National Science Centre, Poland 2015/19/N/NZ4/00572 PRELUDIUM grant. M.Z.S. was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Deutsche Diabetes Stiftung.
Author contributions
P.A.K. designed the study, obtained the data and wrote the manuscript. E.P.O., contributed to the study design, experiment performing, edited, supported and critically revised the manuscript and contributed to the discussion. M.Z.S., K.W.N., contributed to the study design, edited, supported and critically revised the manuscript and contributed to the discussion. All authors have given final approval to the current version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kołodziejski, P.A., Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, E., Strowski, M.Z. et al. Long-term obestatin treatment of mice type 2 diabetes increases insulin sensitivity and improves liver function. Endocrine 56, 538–550 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1309-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1309-2