Abstract
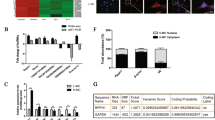
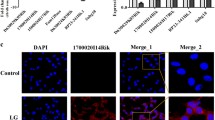
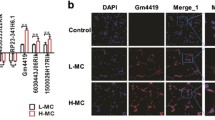
Diabetic nephropathy as the primary cause of end-stage renal disease reveals an increased incidence in patients with kidney disease as the continuous rising of type 2 diabetes. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the development of many diseases including diabetes; however, the role of lncRNAs in diabetic nephropathy is still unclear. In the present study, lncRNA microarray analysis was used to identify abnormally expressed lncRNAs and nearby mRNAs in renal cortical tissues dissected from kidney of db/db and db/m mice. After verifying the data from microarray analysis by quantitative RT-PCR, downregulated ENSMUST00000147869 associated with Cyp4a12a was selected for overexpression in mouse mesangial cells among differentially expressed lncRNAs. Cell Counting Kit-8, Western blotting, and quantitative RT-PCR showed that proliferation and fibrosis indexes were reversed in mesangial cells with ENSMUST00000147869 overexpression. Our data suggested the potential role of ENSMUST00000147869 in proliferation and fibrosis of mesangial cells, which provided a molecular biomarker and therapeutic target for diabetic nephropathy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.E. Shaw, R.A. Sicree, P.Z. Zimmet, Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 87(1), 4–14 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.007
W. Yang, J. Lu, J. Weng, W. Jia, L. Ji, J. Xiao, Z. Shan, J. Liu, H. Tian, Q. Ji, D. Zhu, J. Ge, L. Lin, L. Chen, X. Guo, Z. Zhao, Q. Li, Z. Zhou, G. Shan, J. He, Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 362(12), 1090–1101 (2010). doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0908292
R. Lehmann, E.D. Schleicher, Molecular mechanism of diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Chem. 297(1–2), 135–144 (2000)
M.K. Arora, U.K. Singh, Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: an update. Vascul. Pharmacol. 58(4), 259–271 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.vph.2013.01.001
Consortium, E.P., An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489(7414), 57–74 (2012). doi:10.1038/nature11247
C.P. Ponting, P.L. Oliver, W. Reik, Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136(4), 629–641 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006
M.C. Tsai, O. Manor, Y. Wan, N. Mosammaparast, J.K. Wang, F. Lan, Y. Shi, E. Segal, H.Y. Chang, Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 329(5992), 689–693 (2010). doi:10.1126/science.1192002
M.E. Dinger, D.K. Gascoigne, J.S. Mattick, The evolution of RNAs with multiple functions. Biochimie 93(11), 2013–2018 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.018
H. Chen, O. Charlat, L.A. Tartaglia, E.A. Woolf, X. Weng, S.J. Ellis, N.D. Lakey, J. Culpepper, K.J. Moore, R.E. Breitbart, G.M. Duyk, R.I. Tepper, J.P. Morgenstern, Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell 84(3), 491–495 (1996)
G. Fantuzzi, R. Faggioni, Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 68(4), 437–446 (2000)
L. Zhang, S. He, S. Guo, W. Xie, R. Xin, H. Yu, F. Yang, J. Qiu, D. Zhang, S. Zhou, K. Zhang, Down-regulation of miR-34a alleviates mesangial proliferation in vitro and glomerular hypertrophy in early diabetic nephropathy mice by targeting GAS1. J. Diabetes Complic 28(3), 259–264 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2014.01.002
L. Mahimainathan, F. Das, B. Venkatesan, G.G. Choudhury, Mesangial cell hypertrophy by high glucose is mediated by downregulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Diabetes 55(7), 2115–2125 (2006). doi:10.2337/db05-1326
X. Zhu, Y. Guo, S. Yao, Q. Yan, M. Xue, T. Hao, F. Zhou, J. Zhu, D. Qin, C. Lu, Synergy between Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) vIL-6 and HIV-1 Nef protein in promotion of angiogenesis and oncogenesis: role of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncogene 33(15), 1986–1996 (2014). doi:10.1038/onc.2013.136
F. Zhou, M. Xue, D. Qin, X. Zhu, C. Wang, J. Zhu, T. Hao, L. Cheng, X. Chen, Z. Bai, N. Feng, S.J. Gao, C. Lu, HIV-1 Tat promotes Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) vIL-6-induced angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by regulating PI3 K/PTEN/AKT/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 8(1), e53145 (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053145
Y. Fujii, N. Ohno, Z. Li, N. Terada, T. Baba, S. Ohno, Morphological and histochemical analyses of living mouse livers by new ‘cryobiopsy’ technique. J. Electron Microsc. 55(2), 113–122 (2006). doi:10.1093/jmicro/dfl018
R.M. Mason, N.A. Wahab, Extracellular matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 14(5), 1358–1373 (2003)
A. Sapru, S.E. Gitelman, S. Bhatia, R.F. Dubin, T.B. Newman, H. Flori, Prevalence and characteristics of type 2 diabetes mellitus in 9–18 year-old children with diabetic ketoacidosis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 18(9), 865–872 (2005)
M. Zaratiegui, D.V. Irvine, R.A. Martienssen, Noncoding RNAs and gene silencing. Cell 128(4), 763–776 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.016
M. Kato, J.T. Park, R. Natarajan, MicroRNAs and the glomerulus. Exp. Cell Res. 318(9), 993–1000 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.02.034
M.S. Cunnington, M. Santibanez Koref, B.M. Mayosi, J. Burn, B. Keavney, Chromosome 9p21 SNPs associated with multiple disease phenotypes correlate with ANRIL expression. PLoS Genet. 6(4), e1000899 (2010). doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000899
B. Yan, J. Yao, J.Y. Liu, X.M. Li, X.Q. Wang, Y.J. Li, Z.F. Tao, Y.C. Song, Q. Chen, Q. Jiang, lncRNA-MIAT regulates microvascular dysfunction by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Circ. Res. 116(7), 1143–1156 (2015). doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305510
D. Ma, J.P. Shield, W. Dean, I. Leclerc, C. Knauf, R.R. Burcelin, G.A. Rutter, G. Kelsey, Impaired glucose homeostasis in transgenic mice expressing the human transient neonatal diabetes mellitus locus, TNDM. J. Clin. Investig. 114(3), 339–348 (2004). doi:10.1172/JCI19876
R.J. Gardner, D.J. Mackay, A.J. Mungall, C. Polychronakos, R. Siebert, J.P. Shield, I.K. Temple, D.O. Robinson, An imprinted locus associated with transient neonatal diabetes mellitus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9(4), 589–596 (2000)
D.P. Caley, R.C. Pink, D. Trujillano, D.R. Carter, Long noncoding RNAs, chromatin, and development. Sci. World J. 10, 90–102 (2010). doi:10.1100/tsw.2010.7
M. Kato, S. Putta, M. Wang, H. Yuan, L. Lanting, I. Nair, A. Gunn, Y. Nakagawa, H. Shimano, I. Todorov, J.J. Rossi, R. Natarajan, TGF-beta activates Akt kinase through a microRNA-dependent amplifying circuit targeting PTEN. Nat. Cell Biol. 11(7), 881–889 (2009). doi:10.1038/ncb1897
Z. Zhang, H. Peng, J. Chen, X. Chen, F. Han, X. Xu, X. He, N. Yan, MicroRNA-21 protects from mesangial cell proliferation induced by diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. FEBS Lett. 583(12), 2009–2014 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.05.021
N. Dey, N. Ghosh-Choudhury, F. Das, X. Li, B. Venkatesan, J.L. Barnes, B.S. Kasinath, G. Ghosh Choudhury, PRAS40 acts as a nodal regulator of high glucose-induced TORC1 activation in glomerular mesangial cell hypertrophy. J. Cell. Physiol. 225(1), 27–41 (2010). doi:10.1002/jcp.22186
X. Zhao, J.D. Imig, Kidney CYP450 enzymes: biological actions beyond drug metabolism. Curr. Drug Metab. 4(1), 73–84 (2003)
J.P. Hardwick, D. Osei-Hyiaman, H. Wiland, M.A. Abdelmegeed, B.J. Song, PPAR/RXR regulation of fatty acid metabolism and fatty acid omega-hydroxylase (CYP4) isozymes: implications for prevention of lipotoxicity in fatty liver disease. PPAR Res. 2009, 952734 (2009). doi:10.1155/2009/952734
Y. Zhang, C.D. Klaassen, Hormonal regulation of Cyp4a isoforms in mouse liver and kidney. Xenobiotica 43(12), 1055–1063 (2013). doi:10.3109/00498254.2013.797622
K.M. Lukaszewicz, J.H. Lombard, Role of the CYP4A/20-HETE pathway in vascular dysfunction of the Dahl salt-sensitive rat. Clin. Sci. 124(12), 695–700 (2013). doi:10.1042/CS20120483
L. Qi, L. Meng, Y. Li, Y. Qu, Arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure influences CYP4A distribution in the rat brain. Histol. Histopathol. 27(7), 897–903 (2012)
D.N. Muller, C. Schmidt, E. Barbosa-Sicard, M. Wellner, V. Gross, H. Hercule, M. Markovic, H. Honeck, F.C. Luft, W.H. Schunck, Mouse Cyp4a isoforms: enzymatic properties, gender- and strain-specific expression, and role in renal 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid formation. Biochem. J. 403(1), 109–118 (2007). doi:10.1042/BJ20061328
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Chun Lu and Department of Microbiology, Nanjing Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Min Wang, Di Yao and Suyu Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Yao, D., Wang, S. et al. Long non-coding RNA ENSMUST00000147869 protects mesangial cells from proliferation and fibrosis induced by diabetic nephropathy. Endocrine 54, 81–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0950-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0950-5