Abstract
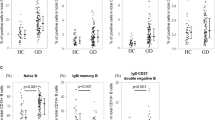
Regulatory T (Treg) cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid disorders (AITD). New subsets of CD4+CD69+ and CD4+NKG2D+ T lymphocytes that behave as regulatory cells have been recently reported. The role of these immunoregulatory lymphocytes has not been previously explored in AITD. We analyzed by multi-parametric flow cytometry different Treg cell subsets in peripheral blood from 32 patients with AITD and 19 controls, and in thyroid tissue from seven patients. The suppressive activity was measured by an assay of inhibition of lymphocyte activation. We found a significant increased percentage of CD4+CD69+IL-10+, CD4+CD69+NKG2D+, and CD4+CD69+IL-10+NKG2D+ cells, in peripheral blood from GD patients compared to controls. The increase in CD4+CD69+IL-10+ and CD4+CD69+IL-10+NKG2D+ T cells was especially remarkable in patients with active Graves’ ophthalmopathy (GO), and a significant positive correlation between GO activity and CD4+CD69+IL-10+ or CD4+CD69+IL-10+NKG2D+ cells was also found. In addition, these cells were increased in patients with a more severe and/or prolonged disease. Thyroid from AITD patients showed an increased proportion of CD69+ regulatory T cells subpopulations compared to autologous peripheral blood. The presence of CD69+, NKG2D+, and IL-10+ cells was confirmed by immunofluorescence microscopy. In vitro functional assays showed that CD69+ Treg cells exerted an important suppressive effect on the activation of T effector cells in controls, but not in AITD patients. Our findings suggest that the levels of CD69+ regulatory lymphocytes are increased in AITD patients, but they are apparently unable to down-modulate the autoimmune response and tissue damage.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P. Weetman, Autoimmune thyroid disease. Autoimmunity 37(4), 337–340 (2004). doi:10.1080/08916930410001705394
G. Stassi, R. De Maria, Autoimmune thyroid disease: new models of cell death in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2(3), 195–204 (2002). doi:10.1038/nri750
S.Z. Josefowicz, L.F. Lu, A.Y. Rudensky, Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 30, 531–564 (2012). doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141623
A. Schmidt, N. Oberle, P.H. Krammer, Molecular mechanisms of treg-mediated T cell suppression. Front. Immunol. 3, 51 (2012). doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00051
E.M. Shevach, A.M. Thornton, tTregs, pTregs, and iTregs: similarities and differences. Immunol. Rev. 259(1), 88–102 (2014). doi:10.1111/imr.12160
S. Sakaguchi, K. Wing, Y. Onishi, P. Prieto-Martin, T. Yamaguchi, Regulatory T cells: how do they suppress immune responses? Int. Immunol. 21(10), 1105–1111 (2009). doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp095
S. Sakaguchi, K. Wing, M. Miyara, Regulatory T cells - a brief history and perspective. Eur. J. Immunol. 37(Suppl 1), S116–S123 (2007). doi:10.1002/eji.200737593
L.W. Collison, V. Chaturvedi, A.L. Henderson, P.R. Giacomin, C. Guy, J. Bankoti, D. Finkelstein, K. Forbes, C.J. Workman, S.A. Brown, J.E. Rehg, M.L. Jones, H.T. Ni, D. Artis, M.J. Turk, D.A. Vignali, IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population. Nat. Immunol. 11(12), 1093–1101 (2010). doi:10.1038/ni.1952
M. Battaglia, S. Gregori, R. Bacchetta, M.G. Roncarolo, Tr1 cells: from discovery to their clinical application. Semin. Immunol. 18(2), 120–127 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.smim.2006.01.007
R.K. Dinesh, B.J. Skaggs, A. La Cava, B.H. Hahn, R.P. Singh, CD8 + Tregs in lupus, autoimmunity, and beyond. Autoimmun. Rev. 9(8), 560–568 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2010.03.006
R.A. Peterson, Regulatory T-cells: diverse phenotypes integral to immune homeostasis and suppression. Toxicol. Pathol. 40(2), 186–204 (2012). doi:10.1177/0192623311430693
Y. Han, Q. Guo, M. Zhang, Z. Chen, X. Cao, CD69 + CD4 + CD25- T cells, a new subset of regulatory T cells, suppress T cell proliferation through membrane-bound TGF-beta 1. J. Immunol. 182(1), 111–120 (2009). doi:10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.111
J. Zhu, A. Feng, J. Sun, Z. Jiang, G. Zhang, K. Wang, S. Hu, X. Qu, Increased CD4(+) CD69(+) CD25(-) T cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma are associated with tumor progression. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 26(10), 1519–1526 (2011). doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06765.x
S. Bauer, V. Groh, J. Wu, A. Steinle, J.H. Phillips, L.L. Lanier, T. Spies, Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 285(5428), 727–729 (1999). doi:10.1126/science.285.5428.727
Z. Dai, C.J. Turtle, G.C. Booth, S.R. Riddell, T.A. Gooley, A.M. Stevens, T. Spies, V. Groh, Normally occurring NKG2D + CD4 + T cells are immunosuppressive and inversely correlated with disease activity in juvenile-onset lupus. J. Exp. Med. 206(4), 793–805 (2009). doi:10.1084/jem.20081648
M. Vitales-Noyola, L. Doníz-Padilla, C. Álvarez-Quiroga, A. Monsiváis-Urenda, H. Portillo-Salazar, R. González-Amaro, Quantitative and functional analysis of CD69 + NKG2D + T regulatory cells in healthy subjects. Hum. Immunol. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2015.06.003
S. Bhattacharyya, S. Ghosh, P.L. Jhonson, S.K. Bhattacharya, S. Majumdar, Immunomodulatory role of interleukin-10 in visceral leishmaniasis: defective activation of protein kinase C-mediated signal transduction events. Infect. Immun. 69(3), 1499–1507 (2001). doi:10.1128/IAI.69.3.1499-1507.2001
K. Asadullah, R. Sabat, M. Friedrich, H.D. Volk, W. Sterry, Interleukin-10: an important immunoregulatory cytokine with major impact on psoriasis. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 3(2), 185–192 (2004). doi:10.2174/1568010043343886
E. Niesen, J. Schmidt, T. Flecken, R. Thimme, Suppressive effect of interleukin 10 on priming of naive hepatitis C virus-specific CD8 + T cells. J. Infect. Dis. 211(5), 821–826 (2015). doi:10.1093/infdis/jiu541
R. de Waal Malefyt, J. Abrams, B. Bennett, C.G. Figdor, J.E. de Vries, Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 174(5), 1209-1220 (1991). doi:10.1084/jem.174.5.1209
Yssel, H., De Waal Malefyt, R., Roncarolo, M.G., Abrams, J.S., Lahesmaa, R., Spits, H., de Vries, J.E.: IL-10 is produced by subsets of human CD4 + T cell clones and peripheral blood T cells. J Immunol 149(7), 2378-2384 (1992)
G. Del Prete, M. De Carli, F. Almerigogna, M.G. Giudizi, R. Biagiotti, S. Romagnani, Human IL-10 is produced by both type 1 helper (Th1) and type 2 helper (Th2) T cell clones and inhibits their antigen-specific proliferation and cytokine production. J Immunol 150(2), 353–360 (1993)
D.F. Fiorentino, M.W. Bond, T.R. Mosmann, Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J. Exp. Med. 170(6), 2081–2095 (1989). doi:10.1084/jem.170.6.2081
P.L. Vieira, J.R. Christensen, S. Minaee, E.J. O’Neill, F.J. Barrat, A. Boonstra, T. Barthlott, B. Stockinger, D.C. Wraith, A. O’Garra, IL-10-secreting regulatory T cells do not express Foxp3 but have comparable regulatory function to naturally occurring CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 172(10), 5986–5993 (2004). doi:10.4049/jimmunol.172.10.5986
M. Asano, M. Toda, N. Sakaguchi, S. Sakaguchi, Autoimmune disease as a consequence of developmental abnormality of a T cell subpopulation. J. Exp. Med. 184(2), 387–396 (1996). doi:10.1084/jem.184.2.387
A. Kojima, Y. Tanaka-Kojima, T. Sakakura, Y. Nishizuka, Spontaneous development of autoimmune thyroiditis in neonatally thymectomized mice. Lab. Invest. 34(6), 550–557 (1976)
H. Xue, X. Yu, L. Ma, S. Song, Y. Li, L. Zhang, T. Yang, H. Liu, The possible role of CD4CD25 Foxp3/CD4 IL-17A cell imbalance in the autoimmunity of patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Endocrine (2015). doi:10.1007/s12020-015-0569-y
N. Figueroa-Vega, M. Alfonso-Perez, I. Benedicto, F. Sanchez-Madrid, R. Gonzalez-Amaro, M. Marazuela, Increased circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and Th17 lymphocytes in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95(2), 953–962 (2010). doi:10.1210/jc.2009-1719
M. Marazuela, M.A. Garcia-Lopez, N. Figueroa-Vega, H. de la Fuente, B. Alvarado-Sanchez, A. Monsivais-Urenda, F. Sanchez-Madrid, R. Gonzalez-Amaro, Regulatory T cells in human autoimmune thyroid disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91(9), 3639–3646 (2006). doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2337
L. Bartalena, L. Baldeschi, A. Dickinson, A. Eckstein, P. Kendall-Taylor, C. Marcocci, M. Mourits, P. Perros, K. Boboridis, A. Boschi, N. Curro, C. Daumerie, G.J. Kahaly, G.E. Krassas, C.M. Lane, J.H. Lazarus, M. Marino, M. Nardi, C. Neoh, J. Orgiazzi, S. Pearce, A. Pinchera, S. Pitz, M. Salvi, P. Sivelli, M. Stahl, G. von Arx, W.M. Wiersinga, Consensus statement of the European Group on Graves’ orbitopathy (EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 158(3), 273–285 (2008). doi:10.1530/EJE-07-0666
N. Figueroa-Vega, P. Sanz-Cameno, R. Moreno-Otero, F. Sanchez-Madrid, R. Gonzalez-Amaro, M. Marazuela, Serum levels of angiogenic molecules in autoimmune thyroid diseases and their correlation with laboratory and clinical features. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94(4), 1145–1153 (2009). doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1571
S. Leskela, A. Rodriguez-Munoz, H. de la Fuente, N. Figueroa-Vega, P. Bonay, P. Martin, A. Serrano, F. Sanchez-Madrid, R. Gonzalez-Amaro, M. Marazuela, Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98(7), 2822–2833 (2013). doi:10.1210/jc.2013-1273
J.B. Canavan, B. Afzali, C. Scotta, H. Fazekasova, F.C. Edozie, T.T. Macdonald, M.P. Hernandez-Fuentes, G. Lombardi, G.M. Lord, A rapid diagnostic test for human regulatory T-cell function to enable regulatory T-cell therapy. Blood 119(8), e57–e66 (2012). doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-380048
P.K. Chattopadhyay, J. Yu, M. Roederer, A live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4 + T cells with diverse cytokine profiles. Nat. Med. 11(10), 1113–1117 (2005). doi:10.1038/nm1293
A.P. Weetman, A.M. McGregor, Autoimmune thyroid disease: further developments in our understanding. Endocr. Rev. 15(6), 788–830 (1994)
S. Sakaguchi, Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell 101(5), 455–458 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80856-9
K. Otsubo, H. Kanegane, I. Kobayashi, T. Miyawaki, IPEX syndrome and human Treg cells. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 33(4), 196–206 (2010). doi:10.2177/jsci.33.196
P. Castro-Sanchez, J.M. Martin-Villa, Gut immune system and oral tolerance. Br. J. Nutr. 109(Suppl 2), S3–11 (2013). doi:10.1017/S0007114512005223
D. Sancho, M. Gomez, F. Viedma, E. Esplugues, M. Gordon-Alonso, M.A. Garcia-Lopez, H. de la Fuente, A.C. Martinez, P. Lauzurica, F. Sanchez-Madrid, CD69 downregulates autoimmune reactivity through active transforming growth factor-beta production in collagen-induced arthritis. J Clin Invest 112(6), 872–882 (2003). doi:10.1172/JCI19112112/6/872
R. Gandhi, M.F. Farez, Y. Wang, D. Kozoriz, F.J. Quintana, H.L. Weiner, Cutting edge: human latency-associated peptide + T cells: a novel regulatory T cell subset. J Immunol 184(9), 4620–4624 (2010). doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903329
M. Bonelli, A. Savitskaya, K. von Dalwigk, C.W. Steiner, D. Aletaha, J.S. Smolen, C. Scheinecker, Quantitative and qualitative deficiencies of regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Int. Immunol. 20(7), 861–868 (2008). doi:10.1093/intimm/dxn044
M.H. Garcia-Hernandez, B. Alvarado-Sanchez, M.Z. Calvo-Turrubiartes, M. Salgado-Bustamante, C.Y. Rodriguez-Pinal, L.R. Gamez-Lopez, R. Gonzalez-Amaro, D.P. Portales-Perez, Regulatory T Cells in children with intestinal parasite infection. Parasite Immunol. 31(10), 597–603 (2009). doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01149.x
A. Saez-Borderias, M. Guma, A. Angulo, B. Bellosillo, D. Pende, M. Lopez-Botet, Expression and function of NKG2D in CD4 + T cells specific for human cytomegalovirus. Eur. J. Immunol. 36(12), 3198–3206 (2006). doi:10.1002/eji.200636682
V. Groh, A. Bruhl, H. El-Gabalawy, J.L. Nelson, T. Spies, Stimulation of T cell autoreactivity by anomalous expression of NKG2D and its MIC ligands in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(16), 9452–9457 (2003). doi:10.1073/pnas.16328071001632807100
M. Allez, V. Tieng, A. Nakazawa, X. Treton, V. Pacault, N. Dulphy, S. Caillat-Zucman, P. Paul, J.M. Gornet, C. Douay, S. Ravet, R. Tamouza, D. Charron, M. Lemann, L. Mayer, A. Toubert, CD4 + NKG2D + T cells in Crohn’s disease mediate inflammatory and cytotoxic responses through MICA interactions. Gastroenterology 132(7), 2346–2358 (2007). doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.025
R. Gonzalez-Amaro, F. Sanchez-Madrid, Cell adhesion molecules: selectins and integrins. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 19(5–6), 389–429 (1999)
D. Cao, V. Malmstrom, C. Baecher-Allan, D. Hafler, L. Klareskog, C. Trollmo, Isolation and functional characterization of regulatory CD25brightCD4 + T cells from the target organ of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 33(1), 215–223 (2003). doi:10.1002/immu.200390024
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work has received the following Grants: Proyectos de Investigación en Salud (FIS) PI13-01414, PIE-0041 (funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III) and S2011/BMD-2328 TIRONET (funded by Comunidad de Madrid) (to Mónica Marazuela). Ayuda Predoctoral de Formación en Investigación en Salud (PFIS) FI11/00668 (funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III) (to Ana Rodríguez-Muñoz).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Muñoz, A., Vitales-Noyola, M., Ramos-Levi, A. et al. Levels of regulatory T cells CD69+NKG2D+IL-10+ are increased in patients with autoimmune thyroid disorders. Endocrine 51, 478–489 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0662-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0662-2