Abstract
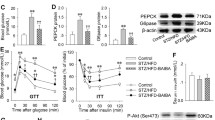
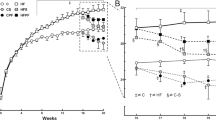
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog liraglutide can alleviate endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and insulin resistance (IR) in the liver of high-fat diet-induced insulin-resistant rats. Eighty-five male Sprague–Dawley rats were fed with normal chow or a high-fat diet for 12 weeks. The IR was evaluated using the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp technique. The rats in the HF group were further divided into four groups and were treated with or without liraglutide by subcutaneous injection. Body weight (BW), fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting insulin (FINS), and insulin sensitivity were measured. The expression of ER stress marker GRP78 and its signaling mediators, such as IRE1α, PERK, and ATF6, in the liver were examined. The ultrastructure of the ER in the liver was examined by transmission electron microscopy. The expression levels of chemerin in the liver and the serum were also measured. After 4 weeks of liraglutide treatment, the BW, FBG, and FINS levels were significantly reduced, and the insulin sensitivity was increased compared with the HF only rats. Liraglutide reduced the expression of GRP78 and chemerin in liver tissue at both the mRNA and protein levels. Interestingly, the chemerin mRNA was closely correlated with the level of GRP78 mRNA, while the level of chemerin in serum was also associated with the FINS level. As a representative GLP-1 analog, liraglutide can suppress ER stress and reduce chemerin expression in the liver of rats exposed to a high-fat diet.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Gautier, S.P. Choukem, J. Girard, Physiology of incretins (GIP and GLP-1) and abnormalities in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metabol. 34(Suppl 2), S65–S72 (2008). doi:10.1016/S1262-3636(08)73397-4
C.F. Deacon, Therapeutic strategies based on glucagon-like peptide 1. Diabetes 53(9), 2181–2189 (2004)
M. Parks, C. Rosebraugh, Weighing risks and benefits of liraglutide: the FDA’s review of a new antidiabetic therapy. New Engl. J. Med. 362(9), 774–777 (2010). doi:10.1056/NEJMp1001578
K.R. Peters, Liraglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a clinical update. Am. J. Ther. 20(2), 178–188 (2013). doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e3182204c16
M. Horowitz, A. Flint, K.L. Jones, C. Hindsberger, M.F. Rasmussen, C. Kapitza, S. Doran, T. Jax, M. Zdravkovic, I.M. Chapman, Effect of the once-daily human GLP-1 analogue liraglutide on appetite, energy intake, energy expenditure and gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 97(2), 258–266 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.02.016
Knudsen, L.B.: Liraglutide: the therapeutic promise from animal models. Int. J. Clin Pract. 64(167), 4–11 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02499.x
T. Schwasinger-Schmidt, D.C. Robbins, S.J. Williams, L. Novikova, L. Stehno-Bittel, Long-term liraglutide treatment is associated with increased insulin content and secretion in beta-cells, and a loss of alpha-cells in ZDF rats. Pharmacol. Res. 76, 58–66 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.07.005
C.W. Spellman, Incorporating glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists into clinical practice. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 112(1 suppl 1), S7–S15 (2012)
S. Chen, W.B. Melchior Jr, L. Guo, Endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug- and environmental toxicant-induced liver toxicity. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 32(1), 83–104 (2014). doi:10.1080/10590501.2014.881648
H. Malhi, R.J. Kaufman, Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 54(4), 795–809 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.005
Y. Ji, Z. Zhao, T. Cai, P. Yang, M. Cheng, Liraglutide alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy by blocking CHOP-triggered apoptosis via the inhibition of the IRE-alpha pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 9(4), 1254–1258 (2014). doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.1956
J. Liu, Y. Liu, L. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Li, Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by the inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 630537 (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/630537
L. Zhao, H. Guo, H. Chen, R.B. Petersen, L. Zheng, A. Peng, K. Huang, Effect of Liraglutide on endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 441(1), 133–138 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.026
D.Y. Jung, U. Chalasani, N. Pan, R.H. Friedline, D.A. Prosdocimo, M. Nam, Y. Azuma, R. Maganti, K. Yu, A. Velagapudi, B. O’Sullivan-Murphy, J.L. Sartoretto, M.K. Jain, M.P. Cooper, F. Urano, J.K. Kim, S. Gray, KLF15 is a molecular link between endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin resistance. PLoS One 8(10), e77851 (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077851
E. Panzhinskiy, J. Ren, S. Nair, Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and insulin resistance: role of endoplasmic reticulum stress/reactive oxygen species/nuclear factor kappa B axis. PLoS One 8(10), e77228 (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077228
Y.L. Chu, Y.D. Gong, Z.H. Su, H.N. Yu, Q. Cui, H.Y. Jiang, H.M. Qu, Relationship between tyrosine phosphorylation and protein expression of insulin receptor and insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 34(3), 393–397 (2014). doi:10.1007/s11596-014-1289-x
Z.C. Wang, J.F. Wang, Y.B. Li, C.X. Guo, Y. Liu, F. Fang, S.L. Gong, Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in apoptosis of testicular cells induced by low-dose radiation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 33(4), 551–558 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11596-013-1157-0
M. Becker, K. Rabe, C. Lebherz, J. Zugwurst, B. Goke, K.G. Parhofer, M. Lehrke, U.C. Broedl, Expression of human chemerin induces insulin resistance in the skeletal muscle but does not affect weight, lipid levels, and atherosclerosis in LDL receptor knockout mice on high-fat diet. Diabetes 59(11), 2898–2903 (2010). doi:10.2337/db10-0362
K. Bozaoglu, K. Bolton, J. McMillan, P. Zimmet, J. Jowett, G. Collier, K. Walder, D. Segal, Chemerin is a novel adipokine associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology 148(10), 4687–4694 (2007). doi:10.1210/en.2007-0175
K. Bozaoglu, D. Segal, K.A. Shields, N. Cummings, J.E. Curran, A.G. Comuzzie, M.C. Mahaney, D.L. Rainwater, J.L. VandeBerg, J.W. MacCluer, G. Collier, J. Blangero, K. Walder, J.B. Jowett, Chemerin is associated with metabolic syndrome phenotypes in a Mexican-American population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 94(8), 3085–3088 (2009). doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1833
M.C. Ernst, I.D. Haidl, L.A. Zuniga, H.J. Dranse, J.L. Rourke, B.A. Zabel, E.C. Butcher, C.J. Sinal, Disruption of the chemokine-like receptor-1 (CMKLR1) gene is associated with reduced adiposity and glucose intolerance. Endocrinology 153(2), 672–682 (2012). doi:10.1210/en.2011-1490
M.C. Ernst, M. Issa, K.B. Goralski, C.J. Sinal, Chemerin exacerbates glucose intolerance in mouse models of obesity and diabetes. Endocrinology 151(5), 1998–2007 (2010). doi:10.1210/en.2009-1098
S.S. Fatima, K. Bozaoglu, R. Rehman, F. Alam, A.S. Memon, Elevated chemerin levels in Pakistani men: an interrelation with metabolic syndrome phenotypes. PLoS One 8(2), e57113 (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057113
J.L. Rourke, H.J. Dranse, C.J. Sinal, Towards an integrative approach to understanding the role of chemerin in human health and disease. Obes. Rev. 14(3), 245–262 (2013). doi:10.1111/obr.12009
M. Takahashi, Y. Takahashi, K. Takahashi, F.N. Zolotaryov, K.S. Hong, R. Kitazawa, K. Iida, Y. Okimura, H. Kaji, S. Kitazawa, M. Kasuga, K. Chihara, Chemerin enhances insulin signaling and potentiates insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 582(5), 573–578 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.01.023
H. Malhi, G.J. Gores, Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 28(4), 360–369 (2008). doi:10.1055/s-0028-1091980
C. Owman, S.J. Lolait, S. Santen, B. Olde, Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of cDNA encoding a novel chemoattractant-like receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 241(2), 390–394 (1997). doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7822
L. Pei, J. Yang, J. Du, H. Liu, N. Ao, Y. Zhang, Downregulation of chemerin and alleviation of endoplasmic reticulum stress by metformin in adipose tissue of rats. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 97(2), 267–275 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.02.023
J. Lamontagne, E. Jalbert-Arsenault, E. Pepin, M.L. Peyot, N.B. Ruderman, C.J. Nolan, E. Joly, S.R. Madiraju, V. Poitout, M. Prentki, Pioglitazone acutely reduces energy metabolism and insulin secretion in rats. Diabetes 62(6), 2122–2129 (2013). doi:10.2337/db12-0428
Z. Luo, H. Liu, X. Sun, R. Guo, R. Cui, X. Ma, M. Yan, RNA interference against discoidin domain receptor 2 ameliorates alcoholic liver disease in rats. PLoS One 8(2), e55860 (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055860
G.S. Hotamisligil, Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140(6), 900–917 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.034
H. Li, X. Yu, Emerging role of JNK in insulin resistance. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 9(5), 422–428 (2013)
A. Bettaieb, M.A. Vazquez Prieto, C. Rodriguez Lanzi, R.M. Miatello, F.G. Haj, C.G. Fraga, P.I. Oteiza, (−)-Epicatechin mitigates high-fructose-associated insulin resistance by modulating redox signaling and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 72, 247–256 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.04.011
Y. Han, H.W. Jung, H.S. Bae, Y.K. Park, Wen-pi-tang-Hab-Wu-ling-san, a polyherbal medicine, attenuates ER stress in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by promoting the insulin signaling pathway. Evid. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 825814 (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/825814
Y.Y. Wang, S.Y. Lin, Y.H. Chuang, W.H. Sheu, K.C. Tung, C.J. Chen, Activation of hepatic inflammatory pathways by catecholamines is associated with hepatic insulin resistance in male ischemic stroke rats. Endocrinology 155(4), 1235–1246 (2014). doi:10.1210/en.2013-1593
L. Xu, G.A. Spinas, M. Niessen, ER stress in adipocytes inhibits insulin signaling, represses lipolysis, and alters the secretion of adipokines without inhibiting glucose transport. Hormone Metabol. Res. 42(9), 643–651 (2010). doi:10.1055/s-0030-1255034
P. Hu, Z. Han, A.D. Couvillon, R.J. Kaufman, J.H. Exton, Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26(8), 3071–3084 (2006). doi:10.1128/MCB.26.8.3071-3084.2006
S. Kralisch, S. Weise, G. Sommer, J. Lipfert, U. Lossner, M. Bluher, M. Stumvoll, M. Fasshauer, Interleukin-1beta induces the novel adipokine chemerin in adipocytes in vitro. Regul. Pept. 154(1–3), 102–106 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2009.02.010
D. Wang, G.Y. Yuan, X.Z. Wang, J. Jia, L.L. Di, L. Yang, X. Chen, F.F. Qian, J.J. Chen, Plasma chemerin level in metabolic syndrome. Genet. Mol. Res. 12(4), 5986–5991 (2013). doi:10.4238/2013.November.26.8
A.A. Alfadda, R.M. Sallam, M.A. Chishti, A.S. Moustafa, S. Fatma, W.S. Alomaim, M.Y. Al-Naami, A.F. Bassas, G.P. Chrousos, H. Jo, Differential patterns of serum concentration and adipose tissue expression of chemerin in obesity: adipose depot specificity and gender dimorphism. Mol. Cells 33(6), 591–596 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10059-012-0012-7
R. Chakaroun, M. Raschpichler, N. Kloting, A. Oberbach, G. Flehmig, M. Kern, M.R. Schon, E. Shang, T. Lohmann, M. Dressler, M. Fasshauer, M. Stumvoll, M. Bluher, Effects of weight loss and exercise on chemerin serum concentrations and adipose tissue expression in human obesity. Metab. Clin. Exp. 61(5), 706–714 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2011.10.008
P. Fietta, G. Delsante, Focus on adipokines. Theor. Biol. Forum 106(1–2), 103–129 (2013)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the reagents and technical support provided by the Center Laboratory of The First Affiliated Hospital and the Laboratory Animal Center of China Medical University. This work was supported by grants from the Hall Education of Liaoning (L2010597) and the Science and Technology Agency of Liaoning (2011225020).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Ao, N., Du, J. et al. Protective effect of liraglutide against ER stress in the liver of high-fat diet-induced insulin-resistant rats. Endocrine 49, 106–118 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0480-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0480-y