Abstract
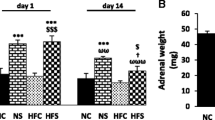
Early stressful experiences may predispose organisms to certain disorders, including those of metabolic defects. This study aimed to explore the effects of early life stress on pancreatic insulin secretion and glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) protein levels in stressed young adult male rats. Foot shock stress was induced in early life (at 2 weeks of age) and/or in young adulthood (at 8–10 weeks of age) for five consecutive days. Blood samples were taken before and after stress exposure in young adult rats. At the end of the experiment, glucose tolerance, isolated islets’ insulin secretion, and pancreatic amounts of GLUT2 protein were measured. Our results show that early life stress has no effect on basal plasma corticosterone levels and adrenal weight, either alone or combined with young adulthood stress, but that early life + young adulthood stress could prevent weight gain, and cause an increase in basal plasma glucose and insulin. The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index did not increase, when the rats were subjected to early life stress alone, but increased when combined with young adulthood stress. Moreover, glucose tolerance was impaired by the combination of early life + young adult stress. There was a decrease in islet’s insulin secretion in rats subjected to early life stress in response to 5.6 mM glucose concentration, but an increase with a concentration of 16.7 mM glucose. However, in rats subjected to early life + young adulthood stress, islet’s insulin secretion increased in response to both the levels of glucose concentrations. GLUT2 protein levels decreased in response to early life stress and early life + young adulthood stress, but there was a greater decrease in the early life stress group. In conclusion, perhaps early life stress sensitizes the body to stressors later in life, making it more susceptible to metabolic syndrome only when the two are in combination.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Zeugmann, A. Quante, L. Popova-Zeugmann, W. Kössler, I. Heuser, I. Anghelescu, Pathways linking early life stress, metabolic syndrome, and the inflammatory marker fibrinogen in depressed inpatients. Psychiatr. Danub. 24, 57–65 (2012)
M. Trombini, H. Hulshof, G. Graiani, L. Carnevali, P. Meerlo, F. Quaini et al., Early maternal separation has mild effects on cardiac autonomic balance and heart structure in adult male rats. Stress 15, 457–470 (2012)
L. Marais, S.J. Van Rensburg, J.M. Van Zyl, D.J. Stein, W.M. Daniels, Maternal separation of rat pups increases the risk of developing depressive-like behavior after subsequent chronic stress by altering corticosterone and neurotrophin levels in the hippocampus. Neurosci. Res. 61, 106–112 (2008)
Y. Chida, N. Sudo, J. Sonoda, T. Hiramoto, C. Kubo, Early-life psychological stress exacerbates adult mouse asthma via the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 175, 316–322 (2007)
P.D. Gluckman, M.A. Hanson, C. Cooper, K.L. Thornburg, Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 61–73 (2008)
A.H. Veenema, S.O. Reber, S. Selch, F. Obermeier, I.D. Neumann, Early life stress enhances the vulnerability to chronic psychosocial stress and experimental colitis in adult mice. Endocrinology 149, 2727–2736 (2008)
D.R.C. Fóscolo, R.B. Fóscolo, U. Marubayashi, A.M. Reis, C.C. Coimbra, Neonatal maternal separation affects endocrine and metabolic stress responses to ether exposure but not to restraint exposure in adult rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 23, 375–385 (2008)
R.J. McPherson, M. Mascher-Denen, S.E. Juul, Postnatal stress produces hyperglycemia in adult rats exposed to hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr. Res. 66, 278–282 (2009)
M. Nováková, V. Bruderová, Z. Sulova, J. Kopacek, L. Lacinova, R. Kvetnansky et al., Modulation of expression of the sigma receptors in the heart of rat and mouse in normal and pathological conditions. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 26, 110–117 (2007)
D. Kaufman, M.A. Banerji, I. Shorman, E.L. Smith, J.D. Coplan, L.A. Rosenblum et al., Early-life stress and the development of obesity and insulin resistance in juvenile bonnet macaques. Diabetes 56, 1382–1386 (2007)
J.W. Rich-Edwards, D. Spiegelman, E.N. Lividoti Hibert, H.-J. Jun, T.J. Todd, I. Kawachi et al., Abuse in childhood and adolescence as a predictor of type 2 diabetes in adult women. Am. J. Prev. Med. 39, 529–536 (2010)
C. Heim, D.J. Newport, S. Heit, Y.P. Graham, M. Wilcox, R. Bonsall et al., Pituitary-adrenal and autonomic responses to stress in women after sexual and physical abuse in childhood. JAMA 284, 592–597 (2000)
C. Lee, V. Tsenkova, D. Carr, Childhood trauma and metabolic syndrome in men and women. Soc. Sci. Med. 105, 122–130 (2014)
H. Zardooz, S. Zahedi Asl, M.G. Naseri, Effect of chronic psychological stress on insulin release from rat isolated pancreatic islets. Life Sci. 79, 57–62 (2006)
H. Zardooz, S. Zahediasl, F. Rostamkhani, B. Farrokhi, S. Nasiraei, B. Kazeminezhad et al., Effects of acute and chronic psychological stress on isolated islets’ insulin release. EXCLI J. 11, 163–175 (2012)
E. Farias-Silva, M.M. Sampaio-Barros, M.E. Amaral, E.M. Carneiro, A.C. Boschero, D.M. Grassi-Kassisse et al., Subsensitivity to insulin in adipocytes from rats submitted to foot-shock stress. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 80, 783–789 (2002)
A. Rafacho, L. Marroquí, S.R. Taboga, J.L. Abrantes, L.R. Silveira, A.C. Boschero et al., Glucocorticoids in vivo induce both insulin hypersecretion and enhanced glucose sensitivity of stimulus-secretion coupling in isolated rat islets. Endocrinology 151, 85–95 (2010)
J.L. Beaudry, M.C. Riddell, Effects of glucocorticoids and exercise on pancreatic β-cell function and diabetes development. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 28, 560–573 (2012)
M. Matsumoto, K. Higuchi, H. Togashi, H. Koseki, T. Yamaguchi, M. Kanno et al., Early postnatal stress alters the 5-HTergic modulation to emotional stress at postadolescent periods of rats. Hippocampus 15, 77 (2005)
F. Rostamkhani, H. Zardooz, S. Zahediasl, B. Farrokhi, Comparison of the effects of acute and chronic psychological stress on metabolic features in rats. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 13, 904–912 (2012)
M. Andersen, M. Bignotto, R. Machado, S. Tufik, Different stress modalities result in distinct steroid hormone responses by male rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 37, 791–797 (2004)
M. Fluttert, S. Dalm, M.S. Oitzl, A refined method for sequential blood sampling by tail incision in rats. Lab. Anim. 34, 372–378 (2000)
S.M. Chalkley, M. Hettiarachchi, D.J. Chisholm, E.W. Kraegen, Long-term high-fat feeding leads to severe insulin resistance but not diabetes in Wistar rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 282, E1231–E1238 (2002)
W. Oosterlinck, A. Vanderper, W. Flameng, P. Herijgers, Glucose tolerance and left ventricular pressure-volume relationships in frequently used mouse strains. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. (2011). doi:10.1155/2011/281312
X. Li, Yuan L, Wang Y, Lu C, Li X, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 deficiency aggravates glucose intolerance via impairment of islet microvascular density in mice with high-fat diet. J. Diabetes Res. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/405284
A. Hoeflich, M.M. Weber, T. Fisch, S. Nedbal, C. Fottner, M.W. Elmlinger et al., Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) separates hypertrophic and hyperplastic effects of growth hormone (GH)/IGF-I excess on adrenocortical cells in vivo. FASEB J. 16, 1721–1731 (2002)
P.E. Lacy, M. Kostianovsky, Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes 16, 35–39 (1967)
C.S. Velez-Granell, A.E. Arias, J.A. Torres-Ruiz, M. Bendayan, Molecular chaperones in pancreatic tissue: the presence of cpn10, cpn60 and hsp70 in distinct compartments along the secretory pathway of the acinar cells. J. Cell Sci. 107, 539–549 (1994)
N.J. Kruger, in The Bradford method for protein quantitation, ed. by J.M. Walker. Basic protein and peptide protocols (Humana Press, Totowa, 1994), pp. 9–15
M. Meaney, D. Aitken, S. Sharma, V. Viau, A. Sarrieau, Postnatal handling increases hippocampal type II glucocorticoid receptors and enhances adrenocortical negative-feedback efficacy in the rat. Neuroendocrinology 51, 597–604 (1989)
P.M. Plotsky, M.J. Meaney, Early, postnatal experience alters hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) mRNA, median eminence CRF content and stress-induced release in adult rats. Mol. Brain Res. 18, 195–200 (1993)
N. Uschold-Schmidt, K.D. Nyuyki, A.M. Füchsl, I.D. Neumann, S.O. Reber, Chronic psychosocial stress results in sensitization of the HPA axis to acute heterotypic stressors despite a reduction of adrenal in vitro ACTH responsiveness. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37, 1676–1687 (2012)
E.L. Rich, L.M. Romero, Exposure to chronic stress downregulates corticosterone responses to acute stressors. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 288, R1628–R1636 (2005)
C.R. Teague, F.S. Dhabhar, R.H. Barton, B. Beckwith-Hall, J. Powell, M. Cobain et al., Metabonomic studies on the physiological effects of acute and chronic psychological stress in Sprague–Dawley rats. J. Proteome Res. 6, 2080–2093 (2007)
P. Pervanidou, G.P. Chrousos, Metabolic consequences of stress during childhood and adolescence. Metabolism 61, 611–619 (2012)
M. Vallée, W. Mayo, F. Dellu, M. Le Moal, H. Simon, S. Maccari, Prenatal stress induces high anxiety and postnatal handling induces low anxiety in adult offspring: correlation with stress-induced corticosterone secretion. J. Neurosci. 17, 2626–2636 (1997)
A.S. Loria, D.M. Pollock, J.S. Pollock, Early life stress sensitizes rats to angiotensin II–induced hypertension and vascular inflammation in adult life. Hypertension 55, 494–499 (2010)
D.A. Sandoval, S.N. Davis, Leptin: metabolic control and regulation. J. Diabet. Complicat. 17, 108–113 (2003)
H. Zardooz, S. Zahedi Asl, M. Gharib Naseri, M. Hedayai, Effect of chronic restraint stress on carbohydrate metabolism in rat. Physiol. Behav. 89, 373–378 (2006)
R. Eguchi, F.R. Scarmagnani, C.A. Cunha, G.I. Souza, L.P. Pisani, E.B. Ribeiro et al., Fish oil consumption prevents glucose intolerance and hypercorticosteronemy in footshock-stressed rats. Lipids Health Dis. 10, 71 (2011)
M. Ochi, K. Tominaga, F. Tanaka, T. Tanigawa, M. Shiba, T. Watanabe et al., Effect of chronic stress on gastric emptying and plasma ghrelin levels in rats. Life Sci. 82, 862–868 (2008)
G. Wilcox, Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 26, 19 (2005)
G. Widdup, J.M. Bryson, D. Pawlak, J.L. Phuyal, G.S. Denyer, I.D. Caterson, In vivo and in vitro suppression by leptin of glucose-stimulated insulin hypersecretion in high glucose-fed rats. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 143, 431–437 (2000)
Y. Wang, M. Nishi, A. Doi, T. Shono, Y. Furukawa, T. Shimada et al., Ghrelin inhibits insulin secretion through the AMPK–UCP2 pathway in β cells. FEBS Lett. 584, 1503–1508 (2010)
S. Jacqueminet, I. Briaud, C. Rouault, G. Reach, V. Poitout, Inhibition of insulin gene expression by long-term exposure of pancreatic β cells to palmitate is dependent on the presence of a stimulatory glucose concentration. Metabolism 49, 532–536 (2000)
J-h. Fu, S-r. Xie, S-j. Kong, Y. Wang, W. Wei, Y. Shan et al., The combination of a high-fat diet and chronic stress aggravates insulin resistance in Wistar male rats. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 117, 354–360 (2009)
M.-T. Guillam, E. Hümmler, E. Schaerer, J.-Y. Wu, M.J. Birnbaum, F. Beermann et al., Early diabetes and abnormal postnatal pancreatic islet development in mice lacking Glut-2. Nat. Genet. 17, 327–330 (1997)
A. Valera, G. Solanes, J. Fernández-Alvarez, A. Pujol, J. Ferrer, G. Asins et al., Expression of GLUT-2 antisense RNA in beta cells of transgenic mice leads to diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 28543–28546 (1994)
S.D. Hughes, C. Quaade, J.H. Johnson, S. Ferber, C. Newgard, Transfection of AtT-20ins cells with GLUT-2 but not GLUT-1 confers glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Relationship to glucose metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 15205–15212 (1993)
M. Tal, B.B. Kahn, H.F. Lodish, Expression of the low Km GLUT-1 glucose transporter is turned on in perivenous hepatocytes of insulin-deficient diabetic rats. Endocrinology 129, 1933–1941 (1991)
M. Tal, Y.-J. Wu, M. Leiser, M. Surana, H. Lodish, N. Fleischer et al., [Val12] HRAS downregulates GLUT2 in beta cells of transgenic mice without affecting glucose homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89, 5744–5748 (1992)
A. De Vos, H. Heimberg, E. Quartier, P. Huypens, L. Bouwens, D. Pipeleers et al., Human and rat beta cells differ in glucose transporter but not in glucokinase gene expression. J. Clin. Investig. 96, 2489 (1995)
M.S. Patel, M. Srinivasan, Metabolic programming: causes and consequences. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1629–1632 (2002)
A. Dhar, I. Dhar, B. Jiang, K.M. Desai, L. Wu, Chronic methylglyoxal infusion by minipump causes pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and induces type 2 diabetes in Sprague-Dawley rats. Diabetes 60, 899–908 (2011)
J.R. Porter, T.G. Barrett, Monogenic syndromes of abnormal glucose homeostasis: clinical review and relevance to the understanding of the pathology of insulin resistance and β cell failure. J. Med. Genet. 42, 893–902 (2005)
M.D. Meglasson, F.M. Matschinsky, Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 2, 163–214 (1986)
K. Yasuda, Y. Yamada, N. Inagaki, H. Yano, Y. Okamoto, K. Tsuji et al., Expression of GLUT1 and GLUT2 glucose transporter isoforms in rat islets of Langerhans and their regulation by glucose. Diabetes 41, 76–81 (1992)
G.C. Weir, S. Bonner-Weir, J.L. Leahy, Islet mass and function in diabetes and transplantation. Diabetes 39, 401–405 (1990)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from Research Deputy of Faculty of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Ethical standards
All procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Neurophysiology Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is part of a PhD thesis by Forouzan Sadeghimahalli.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghimahalli, F., Karbaschi, R., Zardooz, H. et al. Effect of early life stress on pancreatic isolated islets’ insulin secretion in young adult male rats subjected to chronic stress. Endocrine 48, 493–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0337-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0337-4