Abstract
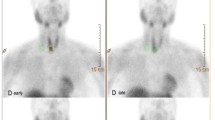
Several studies have investigated the diagnostic performance of 99mTc-MIBI scan in the evaluation of thyroid nodules suspicious for malignancy with conflicting results. The aim of our study is to meta-analyze published data on this topic. A comprehensive literature search of studies published through December 2012 regarding the diagnostic performance of 99mTc-MIBI scan in the evaluation of thyroid nodules suspicious for malignancy was carried out. Pooled sensitivity and specificity of 99mTc-MIBI scan on a per lesion-based analysis and the area under the ROC curve were calculated. Pathological reports of thyroid nodules were considered as reference standard. Twenty-one studies were included in the meta-analysis. Pooled sensitivity and specificity of 99mTc-MIBI scan in detecting malignant thyroid nodules were 85.1 % [95 % confidence interval (95 % CI): 81.1–88.5 %] and 45.7 % (95 % CI: 42.7–48.7 %), respectively, on a per lesion-based analysis, irrespective of eventual results of previous technetium pertechnetate (99mTcO4) or iodine-123 (123I) scan. The area under the ROC curve was 0.78. A sub-analysis restricted to data on hypofunctioning nodules on 99mTcO4 or 123I scans was performed: pooled sensitivity and specificity of 99mTc-MIBI scan in these nodules were 82.1 % (95 % CI: 77.2–86.3 %) and 62.8 % (95 % CI: 58.9–66.7 %), respectively, on a per lesion-based analysis. The area under the ROC curve was 0.81. 99mTc-MIBI scan is a sensitive diagnostic tool in predicting the malignancy of thyroid nodules. Therefore, this imaging method could be helpful in patients with thyroid nodules in which malignancy is suspected on the basis of conventional diagnostic techniques. Higher specificity can be reached when hypofunctioning thyroid nodules are considered.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.J. Yeung, J.W. Serpell, Management of the solitary thyroid nodule. Oncologist 13, 105–112 (2008)
S. Guth, U. Theune, J. Aberle, A. Galach, C.M. Bamberger, Very high prevalence of thyroid nodules detected by high frequency (13 MHz) ultrasound examination. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 39, 699–706 (2009)
L. Pagano, M. Caputo, M.T. Samà, V. Garbaccio, M. Zavattaro, M.G. Mauri et al., Clinical-pathological changes in differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) over time (1997–2010): data from the University Hospital “Maggiore della Carità” in Novara. Endocrine 42, 382–390 (2012)
F. Pacini, Changing natural history of differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrine 42, 229–230 (2012)
D.S. Tyler, A.R. Shaha, R.A. Udelsman, S.I. Sherman, N.W. Thompson, J.F. Moley et al., Thyroid cancer: 1999 update. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 7, 376–398 (2000)
American Thyroid Association (ATA) Guidelines Taskforce on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer, Cooper, D.S., Doherty, G.M., Haugen, B.R., Kloos, R.T., Lee, S.L., Mandel, S.J. et al. Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 19:1167–1214 (2009)
C. Caldarella, G. Treglia, A. Pontecorvi, A. Giordano, Diagnostic performance of planar scintigraphy using 99mTc-MIBI in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism: a meta-analysis. Ann. Nucl. Med. 26, 794–803 (2012)
P.F. Whiting, M.E. Weswood, A.W. Rutjes, J.B. Reitsma, P.N. Bossuyt, J. Kleijnen, Evaluation of QUADAS, a tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 6, 9 (2006)
J. Zamora, V. Abraira, A. Muriel, K. Khan, A. Coomarasamy, Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 6, 31 (2006)
G. Leidig-Bruckner, G. Cichorowski, P. Sattler, T. Bruckner, B. Sattler, Evaluation of thyroid nodules–combined use of (99m)Tc-methylisobutylnitrile scintigraphy and aspiration cytology to assess risk of malignancy and stratify patients for surgical or nonsurgical therapy: a retrospective cohort study. Clin. Endocrinol. 76, 749–758 (2012)
E.O. Onkendi, M.L. Richards, G.B. Thompson, D.R. Farley, P.J. Peller, C.S. Grant, Thyroid cancer detection with dual-isotope parathyroid scintigraphy in primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 19, 1446–1452 (2012)
J.L. Beristain Hernández, E. Servín Torres, A. Sosa Caballero, J.A. Velázquez García, R. Pozzo Bobarín, G. Delgadillo Teyer et al., Determination of the diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc sestamibi scanning in patients with thyroid nodule and a definitive histopathological report. Endocrinol. Nutr. 57, 460–466 (2010)
P. Theissen, M. Schmidt, T. Ivanova, M. Dietlein, H. Schicha, MIBI scintigraphy in hypofunctioning thyroid nodules—can it predict the dignity of the lesion? Nuklearmedizin 48, 144–152 (2009)
L. Giovanella, S. Suriano, M. Maffioli, L. Ceriani, G. Spriano, (99m)Tc-sestamibi scanning in thyroid nodules with nondiagnostic cytology. Head Neck 32, 607–611 (2010)
E. Saggiorato, T. Angusti, R. Rosas, M. Martinese, M. Finessi, F. Arecco et al., 99mTc-MIBI imaging in the presurgical characterization of thyroid follicular neoplasms: relationship to multidrug resistance protein expression. J. Nucl. Med. 50, 1785–1793 (2009)
L.M. Hurtado-López, S. Arellano-Montaño, E.M. Torres-Acosta, F.R. Zaldivar-Ramirez, R.M. Duarte-Torres, P. Alonso-De-Ruiz et al., Combined use of fine-needle aspiration biopsy, MIBI scans and frozen section biopsy offers the best diagnostic accuracy in the assessment of the hypofunctioning solitary thyroid nodule. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 31, 1273–1279 (2004)
R. Sharma, A. Mondal, L.R. Shankar, M. Sahoo, P. Bhatnagar, K. Sawroop et al., Differentiation of malignant and benign solitary thyroid nodules using 30- and 120-minute TC-99m MIBI scans. Clin. Nucl. Med. 29, 534–537 (2004)
F. Boi, M.L. Lai, C. Deias, M. Piga, A. Serra, A. Uccheddu et al., The usefulness of 99mTc-SestaMIBI scan in the diagnostic evaluation of thyroid nodules with oncocytic cytology. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 149, 493–498 (2003)
K. Demirel, O. Kapucu, C. Yücel, H. Ozdemir, G. Ayvaz, F. Taneri, A comparison of radionuclide thyroid angiography, (99m)Tc-MIBI scintigraphy and power Doppler ultrasonography in the differential diagnosis of solitary cold thyroid nodules. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 30, 642–650 (2003)
M.M. Sathekge, R.B. Mageza, M.N. Muthuphei, M.C. Modiba, R.C. Clauss, Evaluation of thyroid nodules with technetium-99m MIBI and technetium-99m pertechnetate. Head Neck 23, 305–310 (2001)
T.Y. Erdil, K. Ozker, L. Kabasakal, B. Kanmaz, K. Sönmezoglu, K.C. Atasoy et al., Correlation of technetium-99m MIBI and thallium-201 retention in solitary cold thyroid nodules with postoperative histopathology. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 27, 713–720 (2000)
E. Mezosi, L. Bajnok, F. Gyory, J. Varga, I. Sztojka, J. Szabo et al., The role of technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile scintigraphy in the differential diagnosis of cold thyroid nodules. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26, 798–803 (1999)
E. Kresnik, H.J. Gallowitsch, P. Mikosch, I. Gomez, P. Lind, Technetium-99m-MIBI scintigraphy of thyroid nodules in an endemic goiter area. J. Nucl. Med. 38, 62–65 (1997)
O. Alonso, G. Lago, F. Mut, J.C. Hermida, M. Nunez, G. De Palma et al., Thyroid imaging with Tc-99m MIBI in patients with solitary cold single nodules on pertechnetate imaging. Clin. Nucl. Med. 21, 363–363 (1996)
M. Klain, S. Maurea, A. Cuocolo, A. Colao, L. Marzano, G. Lombardi et al., Technetium-99m tetrofosmin imaging in thyroid diseases: comparison with Tc-99m-pertechnetate, thallium-201 and Tc-99m-methoxyisobutylisonitrile scans. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 23, 1568–1574 (1996)
H. Nakahara, S. Noguchi, N. Murakami, H. Hoshi, S. Jinnouchi, S. Nagamachi et al., Technetium-99m-sestamibi scintigraphy compared with thallium-201 in evaluation of thyroid tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 37, 901–904 (1996)
J.P. Wei, G.J. Burke, Characterization of the neoplastic potential of solitary solid thyroid lesions with Tc-99m-pertechnetate and Tc-99m-sestamibi scanning. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2, 233–237 (1995)
F.X. Sundram, P. Mack, Evaluation of thyroid nodules for malignancy using 99Tcm-sestamibi. Nucl. Med. Commun. 16, 687–693 (1995)
I. Földes, A. Lévay, G. Stotz, Comparative scanning of thyroid nodules with technetium-99m pertechnetate and technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 20, 330–333 (1993)
Z. Szybiński, B. Huszno, F. Gołkowski, A. Atneisha, Technetium 99m-methoxyisobutylisonitrile in early diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Endokrynol. Pol. 44, 427–433 (1993)
R.S. Bahn, M.R. Castro, Approach to the patient with nontoxic multinodular Goiter. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, 1202–1212 (2011)
P.D. Radecki, P.H. Arger, R.L. Arenson, A.S. Jennings, B.G. Coleman, M.C. Mintz et al., Thyroid imaging: comparison of high-resolution real-time ultrasound and computed tomography. Radiology 153, 145–147 (1984)
G.H. Tan, H. Gharib, Thyroid incidentalomas: management approaches to nonpalpable nodules discovered incidentally on thyroid imaging. Ann. Intern. Med. 126, 226–231 (1997)
S.A. Fish, J.E. Langer, S.J. Mandel, Sonographic imaging of thyroid nodules and cervical lymph nodes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 37, 401–417 (2008)
T. Rago, P. Vitti, L. Chiovato, S. Mazzeo, A. De Liperi, P. Miccoli et al., Role of conventional ultrasonography and color flow-doppler sonography in predicting malignancy in ‘cold’ thyroid nodules. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 138, 41–46 (1998)
F. Lumachi, L. Varotto, S. Borsato, A. Tregnaghi, P. Zucchetta, M.C. Marzola et al., Usefulness of 99mTc-pertechnetate scintigraphy and fine-needle aspiration cytology in patients with solitary thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. Anticancer Res. 24, 2531–2534 (2004)
G. Treglia, B. Muoio, L. Giovanella, M. Salvatori, The role of positron emission tomography and positron emission tomography/computed tomography in thyroid tumours: an overview. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 115(2), 237–243 (2012). doi:10.1007/s00405-012-2205-2
F. Bertagna, G. Treglia, A. Piccardo, E. Giovannini, G. Bosio, G. Biasiotto et al., F18-FDG-PET/CT thyroid incidentalomas: a wide retrospective analysis in three Italian centres on the significance of focal uptake and SUV value. Endocrine (2012). doi:10.1007/s12020-012-9837-2
G. Treglia, M.F. Villani, A. Giordano, V. Rufini, Detection rate of recurrent medullary thyroid carcinoma using fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography: a meta-analysis. Endocrine 42, 535–545 (2012)
D. Vriens, J.H. de Wilt, G.J. van der Wilt, R.T. Netea-Maier, W.J. Oyen, L.F. de Geus-Oei, The role of [18F]-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose-positron emission tomography in thyroid nodules with indeterminate fine-needle aspiration biopsy: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Cancer 117, 4582–4594 (2011)
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Giorgio Treglia and Carmelo Caldarella equally contributed to this article sharing the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Treglia, G., Caldarella, C., Saggiorato, E. et al. Diagnostic performance of 99mTc-MIBI scan in predicting the malignancy of thyroid nodules: a meta-analysis. Endocrine 44, 70–78 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-9932-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-9932-z