Abstract
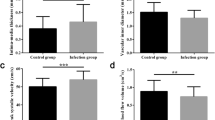
Recent studies showed that contrast agents can induce renal injury. Thus, the present study was designed to assess whether the contrast agents used during digital subtraction angiography (DSA) procedure can damage endothelium. Fow-mediated endothelium-dependent vasodilation (FMD) was measured at baseline, 1, 3, and 7 days after DSA in 198 subjects with diabetic foot. We also measured the levels of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and von Willebrand factor (vWF), interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and C-reactive protein (CRP). Compared with baseline (3.60 ± 0.47 %), FMD at 1 day decreased (2.74 ± 0.47 %), and increased significantly from 1 to 3 days (p < 0.01), and returned to baseline level at 7 days after DSA. The plasma TBARS increased at 1 day and decreased from 1 to 3 days (p < 0.01), and returned to baseline level at 7 days after DSA. CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α had similar changes before and after DSA procedure. FMD was significantly correlated to vWF, IL-6, TNF-α, CRP, and TBARS (p < 0.01). A negative correlation between contrast volume and FMD, positive correlation between contrast volume and vWF, TBARS, CRP, IL-6 at 1 or 3 days after DSA exist in diabetic group (p < 0.05). Contrast medium suppresses FMD, probably through an increased production of oxygen-derived free radicals and inflammation although adequate hydration was given in type 2 diabetes. Therefore, an effective prophylaxis should allow to prevent this complication.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jan Apelqvist, Diagnostics and treatment of the diabetic foot. Endocrine 41(3), 384–397 (2012)
P.A. McCullough, Contrast-induced acute kidney injury. JACC 51(15), 1419–1428 (2008)
M.T. James, W.A. Ghali, M. Tonelli, P. Faris, M.L. Knudtson, N. Pannu, S.W. Klarenbach, B.J. Manns, B.R. Hemmelgarn, Acute kidney injury following coronary angiography is associated with a long-term decline in kidney function. Kidney Int. 78(8), 803–809 (2010)
S.J. Kim, D. Choi, Y.G. Ko, J.S. Kim, S.H. Han, B.K. Kim, S.W. Kang, M.K. Hong, Y. Jang, K.H. Choi, T.H. Yoo, Relation of homocysteinemia to contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 108(8), 1086–1091 (2011)
P.O. Boneti, L.O. Lerman, A. Lerman, Endothelial dysfunction: a marker of atherosclerotic risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23(2), 168–175 (2003)
D.G. Armstrong, L.A. Lavery, L.B. Harkless, Validation of a diabetic wound classification system. the contribution of depth, infection, and ischemia to risk of amputation. Diabetes Care 21(5), 855–859 (1998)
Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus, Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 23(Suppl 1), S4-S19 (2000)
G.D. Xiang, Y.L. Wang, Regular aerobic exercise training improves endothelium-dependent artery dilation in patients with impaired fasting glucose. Diabetes Care 27(3), 801–802 (2004)
G.D. Xiang, Y.H. Wu, Apolipoprotein e4 allele and endothelium-dependent arterial dilation in type 2 diabetes mellitus without angiopathy. Diabetologia 46(4), 514–519 (2003)
G.D. Xiang, H.L. Sun, L.S. Zhao, Changes of osteoprotegerin before and after insulin therapy in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 76(2), 199–206 (2007)
G.D. Xiang, J.H. Pu, L. Yue, J. Hou, H.L. Sun, α-Lipoic acid can improve endothelial dysfunction in subjects with impaired fasting glucose. Metabolism 60(4), 480–485 (2011)
G.D. Xiang, J.H. Pu, H.L. Sun, L.S. Zhao, Alpha-lipoic acid improves endothelial dysfunction in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 118(9), 625–629 (2010)
P.A. McCullough, A. Adam, C.R. Becker, C. Davidson, N. Lameire, F. Stacul, J. Tumlin, CIN consensus working panel, risk prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 98(6A), 27–36 (2006)
J.Y. Cho, M.H. Jeong, S. Hwan Park, I.S. Kim, K.H. Park, D.S. Sim, N.S. Yoon, H.J. Yoon, H.W. Park, Y.J. Hong, J.H. Kim, Y. Ahn, J.G. Cho, J.C. Park, J.C. Kang, Effect of contrast-induced nephropathy on cardiac outcomes after use of nonionic isosmolar contrast media during coronary procedure. J. Cardiol. 56(3), 300–306 (2010)
C. Davidson, F. Stacul, P.A. McCullough, J. Tumlin, A. Adam, N. Lameire, C.R. Becker, CIN consensus working panel, contrast medium use. Am. J. Cardiol. 98(6A), 42–58 (2006)
A. Asif, G. Garces, R.A. Preston, D. Roth, Current trials of interventions to prevent radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Ther. 12(2), 127–132 (2005)
G. Marenzi, A.L. Bartorelli, Recent advances in the prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 10(6), 505–509 (2004)
F. Stacul, A. Adam, C.R. Becker, C. Davidson, N. Lameire, P.A. McCullough, J. Tumlin, CIN consensus working panel, strategies to reduce the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 98(6A), 59–77 (2006)
A.M. Kelly, B. Dwamena, P. Cronin, S.J. Bernstein, R.C. Carlos, Meta-analysis: effectiveness of drugs for preventing contrast-induced nephropathy. Ann. Intern. Med. 148(4), 284–294 (2008)
R. Solomon, Contrast-induced acute kidney injury: is there a risk after intravenous contrast? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 3(5), 1274–1281 (2008)
J. Tumlin, F. Stacul, A. Adam, C.R. Becker, C. Davidson, N. Lameire, P.A. McCullough, CIN consensus working panel, pathophysiology of contrast-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 98(6A), 14–20 (2006)
S. Moncada, R.M. Palmer, E.A. Higgs, Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 43(2), 109–142 (1991)
R.J. Gryglewski, R.M.J. Palmer, S. Moncada, Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-dependent vascular relaxing factor. Nature 320(6061), 454–456 (1986)
G.M. Rubanyi, P.M. Vanhoutte, Oxygen-derived free radicals, endothelium, and responsiveness of vascular smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 250(5 Pt 2), H815–H821 (1986)
G.D. Xiang, H.L. Sun, L.S. Zhao, J. Hou, L. Yue, L. Xu, The antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid improves endothelial dysfunction induced by acute hyperglycaemia during OGTT in impaired glucose tolerance. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 68(5), 716–723 (2008)
S.G. Wannamethee, A.G. Shaper, G.D. Lowe, L. Lennon, A. Rumley, P.H. Whincup, Renal function and cardiovascular mortality in elderly men: the role of inflammatory, procoagulant, and endothelial biomarkers. Eur. Heart J. 27(24), 2975–2981 (2006)
C. Ferri, G. Croce, V. Cofini, G. De Berardinis, D. Grassi, R. Casale, G. Properzi, G. Desideri, C-reactive protein: interaction with the vascular endothelium and possible role in human atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 13(16), 1631–1645 (2007)
U. Derhaschnig, B. Jilma, Assessment of platelets and the endothelium in patients presenting with acute coronary syndromes: is there a future? Thromb. Haemost. 102(6), 1144–1148 (2009)
G.Y. Lip, A. Blann, von Willebrand factor: a marker of endothelial dysfunction in vascular disorders? Cardiovasc. Res. 34(2), 255–265 (1997)
G.D. Xiang, L. Xu, L.S. Zhao, L. Yue, J. Hou, The relationship between plasma osteoprotegerin and endothelium-dependent arterial dilation in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 55(7), 2126–2131 (2006)
G.D. Xiang, J.H. Pu, L.S. Zhao, H.L. Sun, J. Hou, L. Yue, Association between plasma osteoprotegerin concentrations and urinary albumin excretion in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Med. 26(4), 397–403 (2009)
S. Beer, F. Feihl, J. Ruiz, I. Juhan-Vague, M.F. Aillaud, S.G. Wetzel, L. Liaudet, R.C. Gaillard, B. Waeber, Comparison of skin microvascular reactivity with hemostatic markers of endothelial dysfunction and damage in type 2 diabetes. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 4(6), 1449–1458 (2008)
J.S. Beckman, W.H. Koppenol, Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Am. J. Physiol. 271(5 Pt 1), C1424–C1437 (1996)
C. Gazzaruso, A. Coppola, T. Montalcini, E. Baffero, A. Garzaniti, G. Pelissero, S. Collaviti, A. Grugnetti, P. Gallotti, A. Pujia, S.B. Solerte, A. Giustina, Lipoprotein(a) and homocysteine as genetic risk factors for vascular and neuropathic diabetic foot in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 41(1), 89–95 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Nos. 2011CDA002 and 2009CDB427).
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, L., Xiang, G., Zhang, J. et al. Contrast agent suppresses endothelium-dependent arterial dilation after digital subtraction angiography procedure in patients with diabetic foot. Endocrine 46, 505–511 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0095-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0095-8