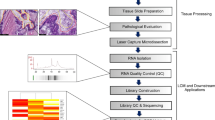
Abstract
Results from investigations of human genomics which utilize intact tissue biopsy specimens maybe compromised due to a host of uncontrolled variables including cellular heterogeneity of a sample collected under diverse conditions, then processed and stored using different protocols. To determine the cellular origin and assess relationships of mRNA expression of two genes reported to be co-expressed in human breast carcinoma (estrogen receptor-α, ESR1 and X-box binding protein 1, XBP1), gene expression analyses were performed with intact tissue sections and compared with those of laser capture microdissection (LCM)-procured carcinoma and stromal cells from serial sections of the same tissue. Frozen sections of human breast carcinomas were first evaluated for structural integrity and pathology after hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Total RNA preparations from intact tissue sections and LCM-procured carcinoma and stromal cells were reverse transcribed for measurements of ESR1 and XBP1 expression by quantitative PCR (qPCR). These results were compared with those obtained from microarray analyses of LCM-procured carcinoma cells. Levels of ESR1 and XBP1 were detected in the intact breast cancer tissue sections suggesting coordinate gene expression. Although coordinate expression of these genes was observed in the LCM-procured carcinoma cells, it was not discerned in LCM-procured stromal cells. The origin of coordinate expression of ESR1 and XBP1 observed in whole tissue sections of human breast cancer biopsies is due principally to their co-expression in carcinoma cells and not in the surrounding stromal cells as substantiated using LCM-procured cells. Collectively, a microgenomic process was established from human tissue preparation to RNA characterization and analysis to identify molecular signatures of specific cell types predicting clinical behavior.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Chalabi, L. Delort, C.L. Le, S. Satih, Y.J. Bignon, D. Bernard-Gallon, Gene signature of breast cancer cell lines treated with lycopene. Pharmacogenomics 7, 663–672 (2006)
C.P. Giacomini, S.Y. Leung, X. Chen, S.T. Yuen, Y.H. Kim, E. Bair, J.R. Pollack, A gene expression signature of genetic instability in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 65, 9200–9205 (2005)
S. Nanni, C. Priolo, A. Grasselli, M. D’Eletto, R. Merola, F. Moretti, M. Gallucci, C.P. De, S. Sentinelli, A.M. Cianciulli, M. Mottolese, P. Carlini, D. Arcelli, M. Helmer-Citterich, C. Gaetano, M. Loda, A. Pontecorvi, S. Bacchetti, A. Sacchi, A. Farsetti, Epithelial-restricted gene profile of primary cultures from human prostate tumors: a molecular approach to predict clinical behavior of prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 4, 79–92 (2006)
D.T. Ross, U. Scherf, M.B. Eisen, C.M. Perou, C. Rees, P. Spellman, V. Iyer, S.S. Jeffrey, M. van de Rijn, M. Waltham, A. Pergamenschikov, J.C. Lee, D. Lashkari, D. Shalon, T.G. Myers, J.N. Weinstein, D. Botstein, P.O. Brown, Systematic variation in gene expression patterns in human cancer cell lines. Nat. Genet. 24, 227–235 (2000)
T. Sorlie, C.M. Perou, R. Tibshirani, T. Aas, S. Geisler, H. Johnsen, T. Hastie, M.B. Eisen, M. van de Rijn, S.S. Jeffrey, T. Thorsen, H. Quist, J.C. Matese, P.O. Brown, D. Botstein, L.P. Eystein, A.L. Borresen-Dale, Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 10869–10874 (2001)
C. Sotiriou, S.Y. Neo, L.M. McShane, E.L. Korn, P.M. Long, A. Jazaeri, P. Martiat, S.B. Fox, A.L. Harris, E.T. Liu, Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 10393–10398 (2003)
L.J. Van’t Veer, H. Dai, M.J. van de Vijver, Y.D. He, A.A. Hart, M. Mao, H.L. Peterse, K. van der Kooy, M.J. Marton, A.T. Witteveen, G.J. Schreiber, R.M. Kerkhoven, C. Roberts, P.S. Linsley, R. Bernards, S.H. Friend, Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415, 530–536 (2002)
M.J. van de Vijver, Y.D. He, L.J. van’t Veer, H. Dai, A.A. Hart, D.W. Voskuil, G.J. Schreiber, J.L. Peterse, C. Roberts, M.J. Marton, M. Parrish, D. Atsma, A. Witteveen, A. Glas, L. Delahaye, T. van der Velde, H. Bartelink, S. Rodenhuis, E.T. Rutgers, S.H. Friend, R. Bernards, A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 1999–2009 (2002)
K.A. Cole, D.B. Krizman, M.R. Emmert-Buck, The genetics of cancer—a 3D model. Nat. Genet. 21, 38–41 (1999)
M.R. Emmert-Buck, R.F. Bonner, P.D. Smith, R.F. Chuaqui, Z. Zhuang, S.R. Goldstein, R.A. Weiss, L.A. Liotta, Laser capture microdissection. Science 274, 998–1001 (1996)
J.L. Wittliff, S.T. Kunitake, S.S. Chu, J.C. Travis, Applications of laser capture microdissection in genomics and proteomics. J. Clin. Ligand Assay 23, 66 (2000)
J.L. Wittliff, M.G. Erlander, Laser capture microdissection and its applications in genomics and proteomics. Methods Enzymol. 356, 12–25 (2002)
R.F. Bonner, M. Emmert-Buck, K. Cole, T. Pohida, R. Chuaqui, S. Goldstein, L.A. Liotta, Laser capture microdissection: molecular analysis of tissue. Science 278, 1481–1483 (1997)
M.R. Emmert-Buck, J.W. Gillespie, C.P. Paweletz, D.K. Ornstein, V. Basrur, E. Appella, Q.H. Wang, J. Huang, N. Hu, P. Taylor, E.F. Petricoin III, An approach to proteomic analysis of human tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 27, 158–165 (2000)
X.J. Ma, R. Salunga, J.T. Tuggle, J. Gaudet, E. Enright, P. McQuary, T. Payette, M. Pistone, K. Stecker, B.M. Zhang, Y.X. Zhou, H. Varnholt, B. Smith, M. Gadd, E. Chatfield, J. Kessler, T.M. Baer, M.G. Erlander, D.C. Sgroi, Gene expression profiles of human breast cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5974–5979 (2003)
J.L. Wittliff, Laser capture microdissection and its applications in genomics and proteomics, in Techniques in Confocal Microscopy, ed. by P.M. Conn (Elsevier, Oxford, 2010), pp. 463–478
J.L. Wittliff, W. Raffelsberger, Mechanisms of signal transduction: sex hormones, their receptors and clinical utility. J. Clin. Ligand Assay 18, 211–235 (1995)
J.L. Wittliff, R. Pasic, K.I. Bland, Steroid and peptide hormone receptors: methods, quality control, and clinical use, in The Breast: Comprehensive Management of Benign and Malignant Diseases, ed. by K. Bland, E.M. Copeland (W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1998), pp. 458–498
S.J. Santner, R.J. Pauley, L. Tait, J. Kaseta, R.J. Santen, Aromatase activity and expression in breast cancer and benign breast tissue stromal cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 200–208 (1997)
R.J. Santen, S.J. Santner, R.J. Pauley, L. Tait, J. Kaseta, L.M. Demers, C. Hamilton, W. Yue, J.P. Wang, Estrogen production via the aromatase enzyme in breast carcinoma: Which cell type is responsible? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 61, 267–271 (1997)
R.A. Smith, R.A. Lea, S.R. Weinstein, L.R. Griffiths, Progesterone, glucocorticoid, but not estrogen receptor mRNA is altered in breast cancer stroma. Cancer Lett. 255, 77–84 (2007)
B.P. Gomez, R.B. Riggins, A.N. Shajahan, U. Klimach, A. Wang, A.C. Crawford, Y. Zhu, A. Zwart, M. Wang, R. Clarke, Human X-box binding protein-1 confers both estrogen independence and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer cell lines. FASEB J. 21, 4013–4027 (2007)
M. Lacroix, G. Leclercq, About GATA3, HNF3A, and XBP1, three genes co-expressed with the oestrogen receptor-alpha gene (ESR1) in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 219, 1–7 (2004)
M.P. Davies, D.L. Barraclough, C. Stewart, K.A. Joyce, R.M. Eccles, R. Barraclough, P.S. Rudland, D.R. Sibson, Expression and splicing of the unfolded protein response gene XBP-1 are significantly associated with clinical outcome of endocrine-treated breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 123, 85–88 (2008)
S. Sengupta, C.G. Sharma, V.C. Jordan, Estrogen regulation of X-box binding protein-1 and its role in estrogen induced growth of breast and endometrial cancer cells. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2, 235–243 (2010)
D.Y. Wang, R. Fulthorpe, S.N. Liss, E.A. Edwards, Identification of estrogen-responsive genes by complementary deoxyribonucleic acid microarray and characterization of a novel early estrogen-induced gene: EEIG1. Mol. Endocrinol. 18, 402–411 (2004)
L. Ding, J. Yan, J. Zhu, H. Zhong, Q. Lu, Z. Wang, C. Huang, Q. Ye, Ligand-independent activation of estrogen receptor alpha by XBP-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 5266–5274 (2003)
Y. Fang, J. Yan, L. Ding, Y. Liu, J. Zhu, C. Huang, H. Zhao, Q. Lu, X. Zhang, X. Yang, Q. Ye, XBP-1 increases ERalpha transcriptional activity through regulation of large-scale chromatin unfolding. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 323, 269–274 (2004)
F. Bertucci, V. Nasser, S. Granjeaud, F. Eisinger, J. Adelaide, R. Tagett, B. Loriod, A. Giaconia, A. Benziane, E. Devilard, J. Jacquemier, P. Viens, C. Nguyen, D. Birnbaum, R. Houlgatte, Gene expression profiles of poor-prognosis primary breast cancer correlate with survival. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 863–872 (2002)
T. Fujimoto, M. Onda, H. Nagai, T. Nagahata, K. Ogawa, M. Emi, Upregulation and overexpression of human X-box binding protein 1 (hXBP-1) gene in primary breast cancers. Breast Cancer 10, 301–306 (2003)
D.A. Kerr II, J.F. Eliason, J.L. Wittliff, Steroid receptor and growth factor receptor expression in human nonsmall cell lung cancers using cells procured by laser-capture microdissection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 617, 377–384 (2008)
N.L. Simone, R.F. Bonner, J.W. Gillespie, M.R. Emmert-Buck, L.A. Liotta, Laser-capture microdissection: opening the microscopic frontier to molecular analysis. Trends Genet. 14, 272–276 (1998)
N.L. Simone, A.T. Remaley, L. Charboneau, E.F. Petricoin III, J.W. Glickman, M.R. Emmert-Buck, T.A. Fleisher, L.A. Liotta, Sensitive immunoassay of tissue cell proteins procured by laser capture microdissection. Am. J. Pathol. 156, 445–452 (2000)
M. Fleisher, A.M. Dnistrian, C.M. Sturgeon, J.L. Wittliff, Practice guidelines and recommendations for use of tumor markers in the clinic, in Tumor Markers: Physiology, Pathobiology, Technology, and Clinical Applications, ed. by D.P. Diamandis, H.A. Fritsche, H. Lilja, D.W. Chan, M.K. Schwartz (AACC Press, Washington, 2002), pp. 33–63
M. Srinivasan, D. Sedmak, S. Jewell, Effect of fixatives and tissue processing on the content and integrity of nucleic acids. Am. J. Pathol. 161, 1961–1971 (2002)
M.W. Pfaffl, A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, e45 (2001)
X.J. Ma, W. Wang, R. Salunga, J.T. Tuggle, K. Stecker, T.M. Baer, M.G. Erlander, J.L. Wittliff, Gene expression associated with clinical outcome in breast cancer via laser capture microdissection. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 82 (2003)
J.L. Wittliff, X.J. Ma, K.K. Stecker, R.C. Salunga, J.T. Tuggle, Y.K. Tran, K.N. Mesina, T.R. Payette, P.R. McQuary, M.P. Pistone, B.M. Zhang, D.D. Hartwig, T.H. Wittliff, W. Wang, M.G. Erlander, Gene expression profiles and tumor marker signatures of human breast carcinoma cells procured by laser capture microdissection. Endocr. Soc. Abs. 538 (2002)
J.L. Wittliff, X.J. Ma, W. Wang, R. Salunga, J.T. Tuggle, K. Stecker, T.H. Wittliff, M.G. Erlander, Expression of estrogen receptor-associated genes in breast cancer cells procured by laser capture microdissection. Jensen Symp. Abs. 81 (2003)
A.L. Bookout, C.L. Cummins, D.J. Mangelsdorf, J.M. Pesola, M.F. Kramer, High-throughput real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. Chapter 15, Unit 15.8 (2006)
H.J. Motulsky, Prism 4 Statistics Guide—Statistical Analyses for Laboratory and Clinical Researchers, 4th edn. (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, 2003), pp. 71–73
A. Casabianca, C. Orlandi, A. Fraternale, M. Magnani, Development of a real-time PCR assay using SYBR Green I for provirus load quantification in a murine model of AIDS. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 4361–4364 (2004)
M.W. Pfaffl, G.W. Horgan, L. Dempfle, Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, e36 (2002)
E. Zini, M. Franchini, M. Osto, A. Vogtlin, F. Guscetti, P. Linscheid, K. Kaufmann, B. Sigrist, M. Ackermann, T.A. Lutz, C.E. Reusch, Quantitative real-time PCR detection of insulin signalling-related genes in pancreatic islets isolated from healthy cats. Vet. J. 183, 287–293 (2008)
S.Z. Haslam, K.A. Nummy, The ontogeny and cellular distribution of estrogen receptors in normal mouse mammary gland. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 42, 589–595 (1992)
S.Z. Haslam, T.L. Woodward, Host microenvironment in breast cancer development: epithelial-cell-stromal-cell interactions and steroid hormone action in normal and cancerous mammary gland. Breast Cancer Res. 5, 208–215 (2003)
R. Judd, Advantages of an immunohistochemical estrogen receptor assay. South. Med. J. 84, 853–856, 861 (1991)
T. Suzuki, P.J. Higgins, D.R. Crawford, Control selection for RNA quantitation. Biotechniques 29, 332–337 (2000)
S.L. Hembruff, D.J. Villeneuve, A.M. Parissenti, The optimization of quantitative reverse transcription PCR for verification of cDNA microarray data. Anal. Biochem. 345, 237–249 (2005)
J. Vandesompele, P.K. De, F. Pattyn, B. Poppe, R.N. Van, P.A. De, F. Speleman, Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3, RESEARCH0034 (2002)
P. Scriven, S. Coulson, R. Haines, S. Balasubramanian, S. Cross, L. Wyld, Activation and clinical significance of the unfolded protein response in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 101, 1692–1698 (2009)
S. Myhre, H. Mohammed, T. Tramm, J. Alsner, G. Finak, M. Park, J. Overgaard, A.L. Borresen-Dale, A. Frigessi, T. Sorlie, In silico ascription of gene expression differences to tumor and stromal cells in a model to study impact on breast cancer outcome. PLoS. ONE. 5, e14002 (2010)
V.R. Grann, A.B. Troxel, N.J. Zojwalla, J.S. Jacobson, D. Hershman, A.I. Neugut, Hormone receptor status and survival in a population-based cohort of patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 103, 2241–2251 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. D. Alan Kerr II for providing technical advice and Dr. Irina A. Smolenkova for technical assistance in the conduct of this study. Supported in part by grants from the Phi Beta Psi Sorority Charity Trust, the University of Louisville, Office of the Executive Vice President for Research and a CTSP Award from the Commonwealth of Kentucky. SAA was a recipient of a Graduate Fellowship from the Integrated Programs in Biomedical Sciences, University of Louisville, and an AACR Scholar-in-Training Award funded by Susan G. Komen for the Cure™. The experiments outlined in this manuscript comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andres, S.A., Wittliff, J.L. Relationships of ESR1 and XBP1 expression in human breast carcinoma and stromal cells isolated by laser capture microdissection compared to intact breast cancer tissue. Endocrine 40, 212–221 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9522-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9522-x