Abstract
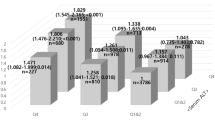
The aim of this article is to prospectively investigate the association of the liver enzyme γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT) with the development of diabetes and impaired glucose regulation (IGR) in a Chinese population. Seven hundred and sixty normoglycaemic subjects aged 40 years or older randomly selected from an urban community of Shanghai received a baseline investigation in May 2005. The participants were invited to receive a standard 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in November 2008. Incident diabetes and IGR were determined according to the 1999 WHO criteria. Serum GGT levels were significantly associated with incident diabetes or combined diabetes and IGR prospectively. After extensive adjustment, the diabetes risk was significantly increased with incrementing serum GGT quartiles (P value for trend = 0.0027). As compared with the lowest quartile of GGT, the highest quartile had an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.30 (95% CI 1.03–1.65) for developing combined diabetes and IGR. Furthermore, a high serum GGT level at baseline was independently associated with an increase in the index of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) at follow-up. Serum GGT concentration, even within its normal range, is a risk marker for developing impaired glucose metabolism in middle-aged and elderly Chinese.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Marchesini, M. Brizi, G. Bianchi, S. Tomassetti, E. Bugianesi, M. Lenzi, A.J. McCullough, S. Natale, G. Forlani, N. Melchionda, Diabetes 50, 1844–1850 (2001)
J.M. Clark, F.L. Brancati, A.M. Diehl, Am. J. Gastroenterol. 98, 960–967 (2003)
R. Teschke, A. Brand, G. Strohmeyer, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 75, 718–724 (1977)
D.J. Kim, J.H. Noh, N.H. Cho, B.W. Lee, Y.H. Choi, J.H. Jung, Y.K. Min, M.S. Lee, M.K. Lee, K.W. Kim, Diabet. Med. 22, 1134–1140 (2005)
A. Fraser, S. Ebrahim, G.D. Smith, D.A. Lawlor, Hepatology 46, 158–165 (2007)
I.J. Perry, S.G. Wannamethee, A.G. Shaper, Diabetes Care 21, 732–737 (1998)
Y. Doi, M. Kubo, K. Yonemoto, T. Ninomiya, M. Iwase, Y. Tanizaki, K. Shikata, M. Iida, Y. Kiyohara, Obesity Res. 15, 1841–1850 (2007)
E.S. Ford, M.B. Schulze, M.M. Bergmann, C. Thamer, H.G. Joost, H. Boeing, Diabetes Care 31, 1138–1143 (2008)
A. Fraser, R. Harris, N. Sattar, S. Ebrahim, G. Davey Smith, D.A. Lawlor, Diabetes Care 32, 741–750 (2009)
M. Nannipieri, C. Gonzales, S. Baldi, R. Posadas, K. Williams, S.M. Haffner, M.P. Stern, E. Ferrannini, Diabetes Care 28, 1757–1762 (2005)
P. André, B. Balkau, S. Vol, M.A. Charles, E. Eschwège, DESIR Study Group, Diabetes Care 30, 2355–2361 (2007)
D.S. Lee, J.C. Evans, S.J. Robins, P.W. Wilson, I. Albano, C.S. Fox, T.J. Wang, E.J. Benjamin, R.B. D’Agostino, R.S. Vasan, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27, 127–133 (2007)
J. Xiang, X.Y. Li, M. Xu, J. Hong, Y. Huang, J.R. Tan, X. Lu, M. Dai, B. Yu, G. Ning, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 4107–4112 (2008)
M. Xu, X.Y. Li, J.G. Wang, X.J. Wang, Y. Huang, Q. Cheng, H.E. Huang, R. Li, J. Xiang, J.R. Tan, M. Dai, G. Ning, Diabetologia 52, 1511–1519 (2009)
M. Rosell, U. De Faire, M.L. Hellénius, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 57, 227–234 (2003)
M.A. Abdul-Ghani, R.A. DeFronzo, Curr. Diab. Rep. 9, 193–199 (2009)
T.P. Whitehead, D. Robinson, S.L. Allaway, Ann. Clin. Biochem. 33, 530–535 (1996)
T.M. Wallace, J.C. Levy, D.R. Matthews, Diabetes Care 27, 1487–1495 (2004)
M. Emdin, C. Passino, C. Michelassi, F. Titta, A. L’abbate, L. Donato, A. Pompella, A. Paolicchi, Eur. Heart J. 22, 1802–1807 (2001)
M. Emdin, C. Passino, L. Donato, A. Paolicchi, A. Pompella, Stroke 33, 1163–1164 (2002)
E. Ruttmann, L.J. Brant, H. Concin, G. Diem, K. Rapp, H. Ulmer, Circulation 112, 2130–2137 (2005)
H.J. Forman, R.M. Liu, L. Tian, Lung Biol. Health Dis. 105, 99–121 (1997)
A. Paolicchi, M. Emdin, E. Ghliozeni, E. Ciancia, C. Passino, G. Popoff, A. Pompella, Circulation 109, 1440 (2004)
D.H. Lee, M.D. Gross, D.R. Jacobs Jr., Clin. Chem. 50, 582–588 (2004)
D.H. Lee, L.M. Steffen, D.R. Jacobs, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 79, 600–605 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The present study would not have been possible without the participation of the participants. This research was supported by the grants from the National Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program (No. 2008ZX09312/019), the National Key Technologies Research and Development Program (No. 2008BAI52B03), and Shanghai Committee for Science and Technology (No. 09XD1403400).
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to be disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Xu, M., Huang, Y. et al. Elevated serum γ-glutamyltransferase predicts the development of impaired glucose metabolism in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Endocrine 40, 265–272 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9468-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9468-z