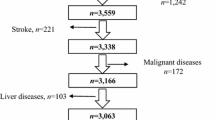
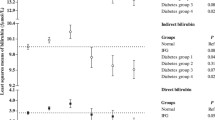
Abstract
Total bilirubin, not direct or indirect bilirubin, has been reported to associate inversely with metabolic syndrome. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the association between bilirubin subtypes and metabolic syndrome among the Korean population. This study included 5,231 Koreans (3,008 men, 2,223 women) aged 30–87 years, who visited the Health promotion centers in Seoul from April, 2006 to June, 2007. The associations of direct, indirect, and total bilirubin classified in quartiles with metabolic syndrome were measured by logistic regression analyses in men and women. Odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) of the lowest, 2nd and 3rd quartiles of direct serum bilirubin compared with the highest quartile (reference) were 2.3 (1.6–3.2), 1.8 (1.3–2.4), and 1.8 (1.4–2.4) among men, and 5.5 (2.6–11.5), 3.1 (1.5–6.7), and 1.9 (0.9–4.3) among women, respectively. In a multivariable adjusted model, however, the significance of inverse associations with total and indirect bilirubin became attenuated. The relation was consistent particularly with direct bilirubin in subgroups of metabolic syndrome components such as central obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, and low HDL-cholesterol in both men and women. Of the three subtypes of serum bilirubin, the inverse association of metabolic syndrome was significantly apparent and consistent with direct bilirubin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Stocker, Y. Yamamoto, A.F. McDonagh, A.N. Glazer, B.N. Ames, Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 235, 1043–1046 (1987)
T.W. Wu, J. Wu, R.K. Li, D. Mickle, D. Carey, Albumin-bound bilirubins protect hyman ventricular myocytes against oxyradical damage. Biochem. Cell Biol. 69, 683–688 (1991)
H.A. Schwertner, L. Vitek, Gilbert syndrome, UGT1A1*28 allel, and cardiovascular disease risk: Possible protective effects and therapeutic applications of bilirubin. Atherosclerosis 198, 1–11 (2008)
S.C. Hunt, F. Kronenberg, J.H. Eckfeldt, P.N. Hopkins, R.H. Myers, G. Heiss, Association of plasma bilirubin with coronary heart disease and segregation of bilirubin as a major gene trait: the NHLBI family heart study. Atherosclerosis 154, 747–754 (2001)
B. Krijgsman, J.A. Papadkis, E.S. Ganotakis, D.P. Mikhailidis, G. Hamilton, The effect of peripheral vascular disease on the serum levels of natural anti-oxidants: bilirubin and albumin. Int. Angiol. 21, 44–52 (2002)
D. Erdogan, H. Gullu, E. Yildirim, D. Tok, O. Ciftci, S.T. Baycan, H. Muderrisoglu, Low serum bilirubin levels are independently and inversely related to impaired flow-mediated vasodilation and increased carotid intima-media thickness in both men and women. Atherosclerosis 184, 431–437 (2006)
H.J. Kimm, J.E. Yun, J. Jo, S.H. Jee, Low serum bilirubin level as an independent predictor of stroke incidence: a prospective study in Korean men and women. Stroke 40, 3422–3427 (2009)
E.S. Ford, A.H. Mokdad, W.H. Giles, D.W. Brown, The metabolic syndrome and antioxidant concentrations: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes 52, 2346–2352 (2003)
P.M. Gorter, J.K. Olijhoek, Y. van der Graaf, A. Algra, T.J. Rabelink, F.L. Visseren, Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease or abdominal aortic aneurysm. Atherosclerosis 173, 363–369 (2004)
M.K. Rutter, J.B. Meigs, L.M. Sullivan, R.B. D’Agostino, P.W. Wilson, C-reactive protein, the metabolic syndrome and prediction of cardiovascular events in the Framingham Offspring Study. Circulation 110, 380–385 (2004)
J.S. Torgerson, A.K. Lindroos, C.D. Sjostrom, R. Olsson, L. Lissner, L. Sjostrom, Are elevated aminotransferases and decreased bilirubin additional characteristics of the metabolic syndrome? Obes. Res. 5, 105–114 (1997)
L.Y. Lin, H.K. Kuo, J.J. Hwang, L.P. Lai, F.T. Chiang, C.D. Tseng, J.L. Lin, Serum bilirubin is inversely associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents. Atherosclerosis 203, 563–568 (2009)
L.H. Bremier, K.A. Spyropolous, A.F. Winder, D.P. Mikhailidis, G. Hamilton, Is bilirubin protective against coronary artery disease? Clin. Chem. 40, 1987–1988 (1994)
L.H. Bremier, G. Wannamethee, S. Ebrahim, A.G. Shaper, Serum bilirubin and risk of ischemic heart disease in middle-aged British men. Clin. Chem. 41, 1504–1508 (1995)
H.A. Schwertner, W.G. Jackson, G. Tolan, Association of Low serum concentration of bilirubin with increased risk of coronary artery disease. Clin. Chem. 40, 18–23 (1994)
S. Pineda, O.Y. Bang, J.L. Saver, S. Starkman, S.W. Yun, D.S. Liebeskind, L.K. Ali, S.H. Shah, B. Ovbiagele, Association of serum bilirubin with ischemic stroke outcomes. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 17, 147–152 (2008)
H.J. Hwang, S.H. Kim, Inverse relationship between fasting direct bilirubin and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Clin. Chim. Acta 411, 1496–1501 (2010)
T. Nakagami, K. Toyomura, T. Kinoshita, S. Morisawa, A beneficial role of bile pigments as an endogenous tissue protector: anticomplement effects of biliverdin and conjugated bilirubin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1158, 189–193 (1993)
M. Mamtani, A. Patel, R. Renge, H. Kulkarni, Prognostic value of direct bilirubin in neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Indian J. Pediatr. 74, 819–822 (2007)
S. Shiomi, D. Habu, T. Kuroki, S. Ishida, N. Tatsumi, Clinical usefulness of conjugated bilirubin levels in patients with acute liver diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 34, 88–93 (1993)
B. Li, Z. Wang, J.J. Fang, C.Y. Xu, W.X. Chen, Evaluation of prognostic markers in severe drug-induced liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 13, 628–632 (2007)
O. Yavuz, S. Aras, Interaction between serum bilirubin level and lipid profile. T Klin. Tip Bilim. 22, 276–280 (2002)
R.J. Simon Maxwell, Y.H. Gregory, Free radicals and antioxidants in cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 44, 307–317 (1997)
T.W. Wu, K.P. Fung, C.C. Yang, Unconjugated bilirubin inhibits the oxidation of human low density lipoprotein better than Trolox. Life Sci. 54, 477–481 (1994)
J. Neuzil, R. Stocker, Free and albumin-bound bilirubin are efficient co-antioxidants for alpha-tocopherol, inhibiting plasma and low density lipoprotein lipid peroxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 16712–16719 (1994)
T. Yamaguchi, F. Horio, T. Hashizume, M. Ttanaka, S. Ikeda, A. Kakinuma, H. Nakajima, Bilirubin is oxidized in rats treated with endotoxin and acts as a physiological antioxidant synergistically with ascorbic acid in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 4, 11–19 (1995)
T. Aizawa, N. Ishizaka, J. Taguchi, S. Kimura, K. Kurokawa, M. Ohno, Baloon injury does not induce heme oxygenase-1 expression, but administration of hemin inhibits neointimal formation in balloon-injury rat carotid artery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261, 302–307 (1999)
B. Frei, R. Stocker, B.N. Ames, Antioxidant defenses and lipid peroxidation in human blood plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 9748–9752 (1988)
C. Hammerman, R. Goldstein, M. Kaplan, M. Eran, D. Goldschmidt, A.I. Eidelman, L.M. Gartner, Bilirubin in the premature: toxic waste or natural defense? Clin. Chem. 44, 2551–2553 (1998)
F. Armutcu, M. Ataymen, H. Atmaca, A. Gurel, Oxidative stress markers, C-reactive protein and heat shock protein 70 levels in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 46, 785–790 (2008)
B. Burchell, R. Hume, Molecular genetic basis of Gilbert’s syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 960–966 (1999)
S.J. Yoon, H.S. Lee, S.W. Lee, J.E. Yun, S.Y. Kim, E.R. Cho, S.J. Lee, E.J. Jee, H.Y. Lee, J. Park, H.S. Kim, S.H. Jee, The association between adiponectin and diabetes in the Korean population. Metabolism 57, 853–857 (2008)
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 285, 2486–2497 (2001)
S. Inoue, P. Zimmet, I. Caterson, C. Chunming, Y. Ikeda, A.K. Khalid, Y.S. Kim, J. Bassett, The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. International Obesity Task Force. Western Pacific Region of the World Health Organization (2000)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (10526) from the Seoul City R&BD program and by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family affairs, Republic of Korea (0920330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, J., Yun, J.E., Lee, H. et al. Total, direct, and indirect serum bilirubin concentrations and metabolic syndrome among the Korean population. Endocr 39, 182–189 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9417-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9417-2