Abstract
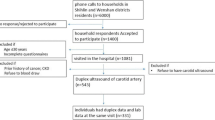
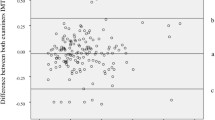
We investigated carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) and quantitative carotid stiffness (QCS) index in relation to plasma glycosylated hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) and duration of diabetes mellitus in 337 Chinese diabetic patients. In categorical analyses, carotid IMT was 710 μm in subjects with a duration of diabetes mellitus ≤2 years, 760 μm in subjects with a duration of diabetes mellitus more than two years and with plasma HbA1C < 6.5% (P < 0.05), and 790 μm in subjects with a duration of diabetes mellitus more than two years but with plasma HbA1C ≥ 6.5% (P < 0.01). The corresponding values for QCS values were 4.5, 4.6 and 5.1 (P < 0.05), respectively. In multiple stepwise regression analyses carotid IMT was significantly associated with the duration of diabetes mellitus, systolic blood pressure and serum concentration of total cholesterol, whereas QCS was significantly associated with age, HbA1C, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (P < 0.05). In conclusion, carotid IMT as a structural measure of arterial wall is increased in patients with a longer history of diabetes mellitus, whereas QCS as functional index is mainly influenced by the quality of blood glucose control.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Bonora, S. Kiechl, F. Oberhollenzer, G. Egger, R.C. Bonadonna, M. Muggeo, J. Willeit, Diabetologia 43, 156–164 (2000)
M. Wohlin, J. Sundström, J. Ärnlöv, B. Andrén, B. Zethelius, L. Lind, Atherosclerosis 170, 181–185 (2003)
M. de Michele, S. Panico, E. Clelentano, G. Covetti, M. Intrieri, F. Zarrilli, L. Sacchetti, R. Tang, M.G. Bond, P. Rubba, Metabolism 51, 52–56 (2002)
N.M. van Popele, D.E. Grobbee, M.L. Bots, R. Asmar, J. Topouchian, R.S. Reneman, A.P. Hoeks, D.A. van der Kuip, A. Hofman, J.C. Wittenman, Stroke 32, 454–460 (2001)
T. Araki, M. Emoto, M. Teramura, H. Yokoyama, K. Movi, S. Hatsuda, T. Maeno, K. Shinohara, H. Koyama, T. Shoji, M. Inaba, Y. Nishizawa, Metabolism. 55, 996–1001 (2006)
A.I. Tropeano, P. Boutouyrie, S. Katsahian, B. Laloux, S. Laurent, J Hypertens 22, 2153–60 (2004)
Y.F. Zhang, J. Hong, W.W. Zhan, X.Y. Li, W.Q. Gu, Y.S. Yang, M. Xu, G. Ning, Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 64, 153–7 (2006)
M.A. Espeland, T.E. Craven, W.A. Riley, J. Corson, A. Romont, C.D. Furberg, Stroke 27, 480–485 (1996)
E. Lonn, S. Yusuf, V. Dzavik, C. Doris, Q. Yi, S. Smith, A. Moore-Cox, J. Bosch, W. Riley, K. Teo, Circulation 103, 919–925 (2001)
N. Hosomi, K. Mizushige, H. Ohyama, T. Takahashi, M. Kitadai, Y. Hatanaka, H. Matsuo, M. Kohno, J.A. Koziol, Stroke 32, 1539–1545 (2001)
C. Snehalatha, V. Vijay, R. Suresh Mohan, K. Satyavani, S. Sivasankari, T. Megha, S. Radhika, A. Ramachandran, Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17, 444–447 (2001)
W.T. Friedewald, R.I. Levy, D.S. Fredrickson, Clin Chem 18, 499–502 (1972)
Acknowledgments
The present study would not have been possible without the participation of the patients. We are sincerely indebted to Dr Wang Jiguang for revision of the manuscript and to Shanghai Clinical Center for Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases for providing clinical and laboratory results of the study participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YP., Zhan, WW., Zhang, YF. et al. Carotid intima-media thickness and stiffness in relation to type 2 diabetes in Chinese. Endocr 31, 289–293 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-007-0035-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-007-0035-6