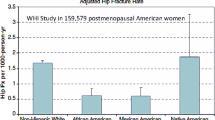
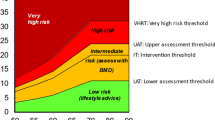
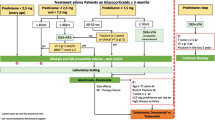
Abstract
Older adults have a higher prevalence of hypertension, and specifically systolic hypertension, than any other age group in the general population as the likelihood of developing hypertension during an average lifespan is high. Osteoporosis like hypertension is a chronic medical condition that can predispose the elderly to increased fracture risk. The relationship between hypertension, antihypertensive medications and osteoporosis-related fractures is complex as hypertension and the medications used to treat hypertension such as thiazide diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers and beta-adrenergic blockers may have differential effects on bone. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of the relationship between hypertension and bone and to examine the association between different antihypertensive medications on fracture risk in the elderly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein M. Hypertension as a risk factor for progression of chronic renal disease. Blood Press Suppl. 1994;1:23–8.
Kannel WB. Hypertension as a risk factor for cardiac events–epidemiologic results of long-term studies. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;21(Suppl 2):S27–37.
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–23.
Hernandez-Hernandez R, Armas-Padilla MC, Armas-Hernandez MJ, Velasco M. The prevalence of hypertension and the state of cardiovascular health in Venezuela and surrounding nations. Ethn Dis. 1998;8:398–405.
Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, Vander Hoorn S, Murray CJ. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet. 2002;360:1347–60.
Center JR, Nguyen TV, Schneider D, Sambrook PN, Eisman JA. Mortality after all major types of osteoporotic fracture in men and women: an observational study. Lancet. 1999;353:878–82.
Nguyen ND, Ahlborg HG, Center JR, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV. Residual lifetime risk of fractures in women and men. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:781–8.
Cummings SR, Nevitt MC, Browner WS, Stone K, Fox KM, Ensrud KE, Cauley J, Black D, Vogt TM. Risk factors for hip fracture in white women. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:767–73.
Mangiafico RA, Russo E, Riccobene S, Pennisi P, Mangiafico M, D’Amico F, Fiore CE. Increased prevalence of peripheral arterial disease in osteoporotic postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2006;24:125–31.
van der Klift M, Pols HA, Hak AE, Witteman JC, Hofman A, de Laet CE. Bone mineral density and the risk of peripheral arterial disease: the Rotterdam Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002;70:443–9.
Wiens M, Etminan M, Gill SS, Takkouche B. Effects of antihypertensive drug treatments on fracture outcomes: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Intern Med. 2006;260:350–62.
Toulis KA, Hemming K, Stergianos S, Nirantharakumar K, Bilezikian JP. Beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists and fracture risk: a meta-analysis of selectivity, gender, and site-specific effects. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:121–9.
Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L. Hypertension is a risk factor for fractures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009;84:103–11.
Perez-Castrillon JL, Martin-Escudero JC, Alvarez Manzanares P, Cortes Sancho R, Iglesias Zamora S, Garcia Alonso M. Hypertension as a risk factor for hip fracture. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:146–7.
Wada H, Hirano F, Kuroda T, Shiraki M. Breast arterial calcification and hypertension associated with vertebral fracture. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2012;12:330–5.
Yang S, Nguyen ND, Center JR, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV. Association between hypertension and fragility fracture: a longitudinal study. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:97–103.
Sennerby U, Melhus H, Gedeborg R, Byberg L, Garmo H, Ahlbom A, Pedersen NL, Michaelsson K. Cardiovascular diseases and risk of hip fracture. JAMA. 2009;302:1666–73.
Cappuccio FP, Meilahn E, Zmuda JM, Cauley JA. High blood pressure and bone-mineral loss in elderly white women: a prospective study. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Lancet. 1999;354:971–5.
Strazzullo P, Galletti F, Cirillo M, Siani A, Nunziata V, Giannattasio R, Mancini M. Altered extracellular calcium homoeostasis in essential hypertension: a consequence of abnormal cell calcium handling. Clin Sci. 1986;71:239–44.
Cappuccio FP, Kalaitzidis R, Duneclift S, Eastwood JB. Unravelling the links between calcium excretion, salt intake, hypertension, kidney stones and bone metabolism. J Nephrol. 2000;13:169–77.
El-Bikai R, Tahir MR, Tremblay J, Joffres M, Seda C, Sedova L, Awadalla P, Laberge C, Knoppers BM, Dumas P, Gaudet D, Ste-Marie LG, Hamet P. Association of age-dependent height and bone mineral density decline with increased arterial stiffness and rate of fractures in hypertensive individuals. J Hypertens. 2015;33:727–35.
Masunari N, Fujiwara S. Impact of antihypertensive drug use on bone mineral density and osteoporotic fracture—from an epidemiological perspective. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2010;4:15–33.
Harrington F, Murray A, Ford GA. Relationship of baroreflex sensitivity and blood pressure in an older population. J Hypertens. 2000;18:1629–33.
Takaoka S, Yamaguchi T, Tanaka K, Morita M, Yamamoto M, Yamauchi M, Yano S, Sugimoto T. Fracture risk is increased by the complication of hypertension and treatment with calcium channel blockers in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013;31:102–7.
Tinetti ME, McAvay GJ, Fried TR, Allore HG, Salmon JC, Foody JM, Bianco L, Ginter S, Fraenkel L. Health outcome priorities among competing cardiovascular, fall injury, and medication-related symptom outcomes. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:1409–16.
Schoofs M, van der Klift M, Hofman A, de Laet CE, Herings RM, Stijnen T, Pols HA, Stricker BH. Thiazide diuretics and the risk for hip fracture. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:476–82.
Butt DA, Mamdani M, Austin PC, Tu K, Gomes T, Glazier RH. The risk of falls on initiation of antihypertensive drugs in the elderly. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:2649–57.
Gribbin J, Hubbard R, Gladman J, Smith C, Lewis S. Risk of falls associated with antihypertensive medication: self-controlled case series. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:879–84.
Gribbin J, Hubbard R, Gladman JR, Smith C, Lewis S. Risk of falls associated with antihypertensive medication: population-based case–control study. Age Ageing. 2010;39:592–7.
Berry SD, Zhu Y, Choi H, Kiel DP, Zhang Y. Diuretic initiation and the acute risk of hip fracture. Osteoporosis Int. 2013;24:689–95.
Butt DA, Mamdani M, Austin PC, Tu K, Gomes T, Glazier RH. The risk of hip fracture after initiating antihypertensive drugs in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:1739–44.
Shuto H, Imakyure O, Matsumoto J, Egawa T, Jiang Y, Hirakawa M, Kataoka Y, Yanagawa T. Medication use as a risk factor for inpatient falls in an acute care hospital: a case-crossover study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;69:535–42.
Barry EL, Gesek FA, Kaplan MR, Hebert SC, Friedman PA. Expression of the sodium-chloride cotransporter in osteoblast-like cells: effect of thiazide diuretics. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:C109–16.
Peters R, Beckett N, Burch L, de Vernejoul MC, Liu L, Duggan J, Swift C, Gil-Extremera B, Fletcher A, Bulpitt C. The effect of treatment based on a diuretic (indapamide) ± ACE inhibitor (perindopril) on fractures in the hypertension in the very elderly trial (HYVET). Age Ageing. 2010;39:609–16.
Solomon DH, Mogun H, Garneau K, Fischer MA. Risk of fractures in older adults using antihypertensive medications. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:1561–7.
Song HJ, Lee J, Kim YJ, Jung SY, Kim HJ, Choi NK, Park BJ. Beta 1 selectivity of beta-blockers and reduced risk of fractures in elderly hypertension patients. Bone. 2012;51:1008–15.
Shimizu H, Nakagami H, Osako MK, Hanayama R, Kunugiza Y, Kizawa T, Tomita T, Yoshikawa H, Ogihara T, Morishita R. Angiotensin II accelerates osteoporosis by activating osteoclasts. FASEB J. 2008;22:2465–75.
Asaba Y, Ito M, Fumoto T, Watanabe K, Fukuhara R, Takeshita S, Nimura Y, Ishida J, Fukamizu A, Ikeda K. Activation of renin-angiotensin system induces osteoporosis independently of hypertension. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24:241–50.
Kwok T, Leung J, Zhang YF, Bauer D, Ensrud KE, Barrett-Connor E, Leung PC. Does the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers affect bone loss in older men? Osteoporosis Int. 2012;23:2159–67.
Perez-Castrillon JL, Silva J, Justo I, Sanz A, Martin-Luquero M, Igea R, Escudero P, Pueyo C, Diaz C, Hernandez G, Duenas A. Effect of quinapril, quinapril-hydrochlorothiazide, and enalapril on the bone mass of hypertensive subjects: relationship with angiotensin converting enzyme polymorphisms. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:453–9.
Choi HJ, Park C, Lee YK, Ha YC, Jang S, Shin CS. Risk of fractures in subjects with antihypertensive medications: a nationwide claim study. Int J Cardiol. 2015;184:62–7.
Butt DA, Mamdani M, Gomes T, Lix L, Lu H, Tu K, Hypertension Outcome Surveillance Team. Risk of osteoporotic fractures with angiotensin II receptor blockers versus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertensive community-dwelling elderly. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29:2483–8.
Rejnmark L, Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L. Treatment with beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium-channel blockers is associated with a reduced fracture risk: a nationwide case–control study. J Hypertens. 2006;24:581–9.
Thorell K, Ranstad K, Midlov P, Borgquist L, Halling A. Is use of fall risk-increasing drugs in an elderly population associated with an increased risk of hip fracture, after adjustment for multimorbidity level: a cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2014;14:131.
Guggino SE, Lajeunesse D, Wagner JA, Snyder SH. Bone remodeling signaled by a dihydropyridine- and phenylalkylamine-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:2957–60.
Zaidi M, MacIntyre I, Datta H. Intracellular calcium in the control of osteoclast function. II. Paradoxical elevation of cytosolic free calcium by verapamil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;167:807–12.
Gradosova I, Zivna H, Palicka V, Hubena S, Svejkovska K, Zivny P. Protective effect of amlodipine on rat bone tissue after orchidectomy. Pharmacology. 2012;89:37–43.
Takeda S, Elefteriou F, Levasseur R, Liu X, Zhao L, Parker KL, Armstrong D, Ducy P, Karsenty G. Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell. 2002;111:305–17.
Bonnet N, Gadois C, McCloskey E, Lemineur G, Lespessailles E, Courteix D, Benhamou CL. Protective effect of beta blockers in postmenopausal women: influence on fractures, bone density, micro and macroarchitecture. Bone. 2007;40:1209–16.
Funding
Dr. Debra Butt is supported by an Investigator Award from the Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Toronto.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Debra A. Butt, Raghad Alharty, Richard Leu and Angela M. Cheung declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal/Human Studies
The article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butt, D.A., Alharty, R., Leu, R. et al. Hypertension, Antihypertensive Drugs and the Risk of Fractures. Clinic Rev Bone Miner Metab 13, 160–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12018-015-9191-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12018-015-9191-z