Abstract
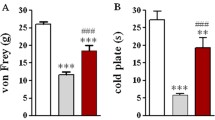
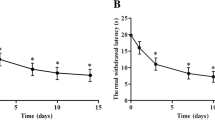
The aim of this work is to provide a comprehensive and unbiased understanding at the molecular correlates of peripheral nerve injury. In this study, we screened the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the DRG from rats using RNA-seq technique. Moreover, the bioinformatics methods were used to figure out the signaling pathways and expression regulation pattern of the DEGs enriched in. In addition, quantitative real-time RT-PCR was carried out to further confirm the expression of DEGs. 414 genes were upregulated, while 184 genes were downregulated in the DRG of rats 7 days after partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL) surgery. Moreover, GO and KEGG enrichment analysis suggested that most of the altered genes were involved in inflammatory responses and signaling transduction. In addition, our results state that they shared similar characters in the DRG among four types of neuropathic pain models. Eighteen genes have been altered (17 of them were upregulated) in the DRG of all four types of neuropathic pain models, in which Vgf, Atf3, Cd74, Gal, Jun, Npy, Serpina3n, and Hspb1 have been reported to be involved in neuropathic pain. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR results further confirmed the mRNA expression levels of Vgf, Atf3, Cd74, Gal, Jun, Npy, Serpina3n, and Hspb1 in the DRG of rats with pSNL surgery. The present study suggested that these eight genes may play important roles in neuropathic pain, revealing that these genes might serve as therapeutic targets for neuropathic pain. Moreover, anti-inflammatory therapy might be an effective approach for neuropathic pain treatment and prevention.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audic, S., & Claverie, J. M. (1997). The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Research,7(10), 986–995.
Burke, D., Fullen, B. M., Stokes, D., & Lennon, O. (2017). Neuropathic pain prevalence following spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Pain,21(1), 29–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.905.
Chen, Y. C., Pristerá, A., Ayub, M., Swanwick, R. S., Karu, K., Hamada, Y., et al. (2013). Identification of a receptor for neuropeptide VGF and its role in neuropathic pain. Journal of Biological Chemistry,288(48), 34638.
Cobos, E. J., Nickerson, C. A., Gao, F., Chandran, V., Bravo-Caparrós, I., González-Cano, R., et al. (2018). Mechanistic differences in neuropathic pain modalities revealed by correlating behavior with global expression profiling. Cell Reports,22(5), 1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.006.
Costigan, M., Belfer, I., Griffin, R. S., Dai, F., Barrett, L. B., Coppola, G., et al. (2010). Multiple chronic pain states are associated with a common amino acid-changing allele in KCNS1. Brain,133(9), 2519–2527. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq195.
Costigan, M., Mannion, R. J., Kendall, G., Lewis, S. E., Campagna, J. A., Coggeshall, R. E., et al. (1998). Heat shock protein 27: Developmental regulation and expression after peripheral nerve injury. Journal of Neuroscience,18(15), 5891–5900. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq195.
Dawes, J. M., Antunes-Martins, A., Perkins, J. R., Paterson, K. J., Sisignano, M., Schmid, R., et al. (2014). Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of skin and dorsal root ganglia after ultraviolet-B-induced inflammation. PLoS ONE,9(4), e93338.
Descalzi, G., & Mitsi, V. (2017). Neuropathic pain promotes adaptive changes in gene expression in brain networks involved in stress and depression. Science Signal. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaj1549.
Dewey, C. N., & Li, B. (2011). RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics,12(1), 323.
Dworkin, R. H., O’Connor, A. B., Audette, J., Baron, R., Gourlay, G. K., Haanpaa, M. L., et al. (2010). Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain: An overview and literature update. Mayo Clinic Proceedings,85(3 Suppl), S3–S14. https://doi.org/10.4065/mcp.2009.0649.
Fairbanks, C. A., Peterson, C. D., Speltz, R. H., Riedl, M. S., Kitto, K. F., Dykstra, J. A., et al. (2014). The VGF-derived peptide TLQP-21 contributes to inflammatory and nerve injury-induced hypersensitivity. Pain,155(7), 1229–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.03.012.
Feinberg, A. P. (2018). The key role of epigenetics in human disease prevention and mitigation. New England Journal of Medicine,378(14), 1323–1334. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1402513.
Finnerup, N. B., Haroutounian, S., Kamerman, P., Baron, R., Bennett, D. L., Bouhassira, D., et al. (2016). Neuropathic pain: An updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain,157(8), 1599–1606. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000492.
Flatters, S. J., Fox, A. J., & Dickenson, A. H. (2002). Nerve injury induces plasticity that results in spinal inhibitory effects of galanin. Pain,98(3), 249–258.
Gewandter, J. S., Dworkin, R. H., Turk, D. C., Farrar, J. T., Fillingim, R. B., Gilron, I., et al. (2015). Research design considerations for chronic pain prevention clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain,156(7), 1184–1197. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000191.
Hao, Y., Luo, X., Ba, X., Wang, J., Zhou, S., Yang, S., et al. (2019). Huachansu suppresses TRPV1 up-regulation and spinal astrocyte activation to prevent oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain in rats. Gene,680, 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.035.
Intondi, A. B., Dahlgren, M. N., Eilers, M. A., & Taylor, B. K. (2008). Intrathecal neuropeptide Y reduces behavioral and molecular markers of inflammatory or neuropathic pain. Pain,137(2), 352–365.
Ji, R. R., Chamessian, A., & Zhang, Y. Q. (2016). Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science,354(6312), 572–577. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8924.
Kim, D. S., Lee, S. J., Park, S. Y., Yoo, H. J., Kim, S. H., Kim, K. J., et al. (2001). Differentially expressed genes in rat dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury. NeuroReport,12(15), 3401–3405.
Kuner, R. (2010). Central mechanisms of pathological pain. Nature Medicine,16(11), 1258–1266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2231.
Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M., & Salzberg, S. L. (2009). Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biology,10(3), R25.
Lee, E., Jung, D. Y., Kim, J. H., Patel, P. R., Hu, X., Lee, Y., et al. (2015). Transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 channel regulates diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance, and leptin resistance. The FASEB Journal,29(8), 3182–3192. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-268300.
Lee, C. S., Ramsey, A. A., Britogariepy, H. D., Michot, B., Podborits, E., Melnyk, J., et al. (2017). Molecular, cellular, and behavioral changes associated with pathological pain signaling occur after dental pulp injury. Molecular Pain,13, 1744806917715173.
Liang, L., Lutz, B. M., Bekker, A., & Tao, Y. X. (2015). Epigenetic regulation of chronic pain. Epigenomics,7(2), 235–245. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi.14.75.
Lin, Y., Chen, J., & Shen, B. (2017). Interactions between genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors for healthcare. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology,1005, 167–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5717-5_8.
Matsuura, Y., Ohtori, S., Iwakura, N., Suzuki, T., Kuniyoshi, K., & Takahashi, K. (2013). Expression of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) in uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons in a lower trunk avulsion pain model in rats. European Spine Journal,22(8), 1794–1799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2733-5.
Moss, A., Ingram, R., Koch, S., Theodorou, A., Low, L., Baccei, M., et al. (2008). Origins, actions and dynamic expression patterns of the neuropeptide VGF in rat peripheral and central sensory neurones following peripheral nerve injury. Molecular Pain,4, 62. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-62.
Nascimento, D. S. M., Potes, C. S., Soares, M. L., Ferreira, A. C., Malcangio, M., Castro-Lopes, J. M., et al. (2017). Drug-induced HSP90 inhibition alleviates pain in monoarthritic rats and alters the expression of new putative pain players at the DRG. Molecular Neurobiology,55(5), 3959–3975.
Poh, K. W., Yeo, J. F., Stohler, C. S., & Ong, W. Y. (2012). Comprehensive gene expression profiling in the prefrontal cortex links immune activation and neutrophil infiltration to antinociception. Journal of Neuroscience,32(1), 35–45. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2389-11.2012.
Robinson, M. D., & Oshlack, A. (2010). A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biology,11(3), R25. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r25.
Robinson, M. D., & Smyth, G. K. (2007). Moderated statistical tests for assessing differences in tag abundance. Bioinformatics,23(21), 2881–2887. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm453.
Robinson, M. D., & Smyth, G. K. (2008). Small-sample estimation of negative binomial dispersion, with applications to SAGE data. Biostatistics,9(2), 321–332. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxm030.
Sanna, M. D., & Galeotti, N. (2018). The HDAC1/c-JUN complex is essential in the promotion of nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain through JNK signaling. European Journal of Pharmacology,825, 99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.02.034.
Son, S. J., Lee, K. M., Jeon, S. M., Park, E. S., Park, K. M., & Cho, H. J. (2007). Activation of transcription factor c-jun in dorsal root ganglia induces VIP and NPY upregulation and contributes to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Experimental Neurology,204(1), 467–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.09.020.
Sun, W., Uchida, K., Suzuki, Y., Zhou, Y., Kim, M., Takayama, Y., et al. (2016). Lack of TRPV2 impairs thermogenesis in mouse brown adipose tissue. EMBO Reports,17(3), 383–399. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201540819.
Sun, W., Zhou, Q., Ba, X., Feng, X., Hu, X., Cheng, X., et al. (2018). Oxytocin relieves neuropathic pain through GABA release and presynaptic TRPV1 inhibition in spinal cord. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00248.
Tarazona, S., Garcíaalcalde, F., Dopazo, J., Ferrer, A., & Conesa, A. (2011). Differential expression in RNA-seq: A matter of depth. Genome Research,21(12), 2213–2223.
Vicuna, L., Strochlic, D. E., Latremoliere, A., Bali, K. K., Simonetti, M., Husainie, D., et al. (2015). The serine protease inhibitor SerpinA3 N attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting T cell-derived leukocyte elastase. Nature Medicine,21(5), 518–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3852.
Wang, F., Xu, S., Shen, X., Guo, X., Peng, Y., & Yang, J. (2011). Spinal macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a major contributor to rodent neuropathic pain-like hypersensitivity. Anesthesiology,114(3), 643–659. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31820a4bf3.
Wu, J., Mao, X., Cai, T., Luo, J., & Wei, L. (2006). KOBAS server: A web-based platform for automated annotation and pathway identification. Nucleic Acids Research,34, W720.
Xiao, H. S., Huang, Q. H., Zhang, F. X., Bao, L., Lu, Y. J., Guo, C., et al. (2002). Identification of gene expression profile of dorsal root ganglion in the rat peripheral axotomy model of neuropathic pain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA,99(12), 8360–8365. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.122231899.
Xie, C., Mao, X., Huang, J., Ding, Y., Wu, J., Dong, S., et al. (2011). KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Research,39, 316–322.
Xu, X., Yang, X., Zhang, P., Chen, X., Liu, H., & Li, Z. (2012). Effects of exogenous galanin on neuropathic pain state and change of galanin and its receptors in DRG and SDH after sciatic nerve-pinch injury in rat. PLoS ONE,7(5), e37621. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037621.
Yang, J. A., He, J. M., Lu, J. M., & Jie, L. J. (2018a). Jun, Gal, Cd74, and C1qb as potential indicator for neuropathic pain. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry,119(6), 4792–4798. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26673.
Yang, S., Yu, Z., Sun, W., Jiang, C., Ba, X., Zhou, Q., et al. (2018b). The antiviral alkaloid berberine ameliorates neuropathic pain in rats with peripheral nerve injury. Acta Neurologica Belgica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-1006-9.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Health and Family Planning Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (No. SZXJ2017044), Shenzhen Municipal Science, Technology and Innovation Commission (No. JCYJ20180302144710880).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y Hao, H Xie, and Q Deng were responsible for the concept and design of the study; W Sun, D Kou, Z Yu, M Zhai, S Yang, C Jiang, X Ba, X Liao, D Xiong, and L Xiao were involved with experimental and analytical aspects of the manuscript; Y Hao, H Xie, Q Deng, and W Sun performed data interpretation, presentation, and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Kou, D., Yu, Z. et al. A Transcriptomic Analysis of Neuropathic Pain in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Following Peripheral Nerve Injury. Neuromol Med 22, 250–263 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08581-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08581-3