Abstract
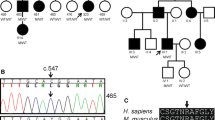
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSAN1) is a rare, autosomal dominantly inherited, slowly progressive and length-dependent axonal peripheral neuropathy. HSAN1 is associated with several mutations in serine-palmitoyltransferase (SPT), the first enzyme in the de novo sphingolipid biosynthetic pathway. HSAN1 mutations alter the substrate specificity of SPT, which leads to the formation of 1-deoxysphingolipids, an atypical and neurotoxic subclass of sphingolipids. This study describes the clinical and neurophysiological phenotype of a German family with a novel SPTCL2 mutation (c.529A > G; N177D) associated with HSAN1 and the biochemical characterization of this mutation.) The mutaion was identified in five family members that segregated with the diesease. Patients were characterized genetically and clinically for neurophysiological function. Their plasma sphingolipid profiles were analyzed by LC–MS. The biochemical properties of the mutation were characterized in a cell-based activity assay. Affected family members showed elevated 1-deoxysphingolipid plasma levels. HEK293 cells expressing the N177D SPTLC2 mutant showed increased de novo 1-deoxysphingolipid formation, but also displayed elevated canonical SPT activity and increased C20 sphingoid base production. This study identifies the SPTLC2 N177D variant as a novel disease-causing mutation with increased 1-deoxySL formation and its association with a typical HSAN1 phenotype.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer-Grumbach, M. (2013). Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 115, 893–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-52902-2.00050-3.
Auer-Grumbach, M., Bode, H., Pieber, T. R., Schabhuttl, M., Fischer, D., Seidl, R., et al. (2013). Mutations at Ser331 in the HSN type I gene SPTLC1 are associated with a distinct syndromic phenotype. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 56(5), 266–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2013.02.002.
Auranen, M., Toppila, J., Suriyanarayanan, S., Lone, M. A., Paetau, A., Tyynismaa, H., et al. (2017). Clinical and metabolic consequences of l-serine supplementation in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1C. Cold Spring Harbor Molecular Case Studies. https://doi.org/10.1101/mcs.a002212.
Bode, H., Bourquin, F., Suriyanarayanan, S., Wei, Y., Alecu, I., Othman, A., et al. (2016). HSAN1 mutations in serine palmitoyltransferase reveal a close structure-function-phenotype relationship. Human Molecular Genetics, 25(5), 853–865. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv611.
Breslow, D. K., Collins, S. R., Bodenmiller, B., Aebersold, R., Simons, K., Shevchenko, A., et al. (2010). Orm family proteins mediate sphingolipid homeostasis. Nature, 463, 1048–1053. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08787.
Davis, D. L., Gable, K., Suemitsu, J., Dunn, T. M., & Wattenberg, B. W. (2019). The ORMDL/Orm-serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) complex is directly regulated by ceramide: Reconstitution of SPT regulation in isolated membranes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra118.007291.
Dawkins, J. L., Hulme, D. J., Brahmbhatt, S. B., Auer-Grumbach, M., & Nicholson, G. A. (2001). Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Nature Genetics, 27(3), 309–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/85879.
Dohrn, M. F., Glockle, N., Mulahasanovic, L., Heller, C., Mohr, J., Bauer, C., et al. (2017). Frequent genes in rare diseases: panel-based next generation sequencing to disclose causal mutations in hereditary neuropathies. Journal of Neurochemistry, 143(5), 507–522. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14217.
Dyck, P. J. (1993). Neuronal atrophy and degeneration predominantly affecting peripheral sensory and autonomic neurons. In P. J. Dyck, K. P. Thomas, J. W. Griffin, P. A. Low, & J. F. Poduslo (Eds.), Peripheral Neuropathy (3rd ed., pp. 1065–1093). Philladelphia: Saunders.
Edvardson, S., Cinnamon, Y., Jalas, C., Shaag, A., Maayan, C., Axelrod, F. B., et al. (2012). Hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy caused by a mutation in dystonin. Annals of Neurology, 71(4), 569–572. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23524.
Eichler, F. S., Hornemann, T., McCampbell, A., Kuljis, D., Penno, A., Vardeh, D., et al. (2009). Overexpression of the wild-type SPT1 subunit lowers desoxysphingolipid levels and rescues the phenotype of HSAN1. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(46), 14646–14651. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2536-09.2009.
Ernst, D., Murphy, S. M., Sathiyanadan, K., Wei, Y., Othman, A., Laura, M., et al. (2015). Novel HSAN1 mutation in serine palmitoyltransferase resides at a putative phosphorylation site that is involved in regulating substrate specificity. NeuroMolecular Medicine, 17(1), 47–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8339-1.
Fridman, V., Suriyanarayanan, S., Novak, P., David, W., Macklin, E. A., McKenna-Yasek, D., et al. (2019). Randomized trial of l-serine in patients with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1. Neurology, 92(4), e359–e370. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000006811.
Garofalo, K., Penno, A., Schmidt, B. P., Lee, H. J., Frosch, M. P., von Eckardstein, A., et al. (2011). Oral l-serine supplementation reduces production of neurotoxic deoxysphingolipids in mice and humans with hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type 1. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121(12), 4735–4745. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci57549.
Geraldes, R., de Carvalho, M., Santos-Bento, M., & Nicholson, G. (2004). Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 in a Portuguese family-electrodiagnostic and autonomic nervous system studies. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 227, 35–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2004.08.002.
Guntert, T., Hanggi, P., Othman, A., Suriyanarayanan, S., Sonda, S., Zuellig, R. A., et al. (2016). 1-Deoxysphingolipid-induced neurotoxicity involves N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor signaling. Neuropharmacology, 110(Pt A), 211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.033.
Gupta, S. D., Gable, K., Alexaki, A., Chandris, P., Proia, R. L., Dunn, T. M., et al. (2015). Expression of the ORMDLS, modulators of serine palmitoyltransferase, is regulated by sphingolipids in mammalian cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290(1), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.588236.
Hornemann, T., Penno, A., Rütti, M. F., Ernst, D., Kivrak-Pfiffner, F., Rohrer, L., et al. (2009). The SPTLC3 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase generates short chain sphingoid bases. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 26322–26330. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.023192.
Hornemann, T., Richard, S., Rütti, M. F., Wei, Y., von Eckardstein, A., Serine-palmitoyltransferase, M., et al. (2006). Cloning and initial characterization of a new subunit for mammalian serine-palmitoyltransferase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 37275–37281. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M608066200.
Houlden, H., Blake, J., & Reily, M. M. (2004). Hereditary sensory neuropathies. Current Opinion in Neurology, 17(5), 569–577.
Houlden, H., King, R., Blake, J., Groves, M., Love, S., Woodward, C., et al. (2006). Clinical, pathological and genetic characterization of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSAN I). Brain, 129, 411–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh712.
Klein, C. J., Wu, Y., Kruckeberg, K. E., Hebbring, S. J., Anderson, S. A., Cunningham, J. M., et al. (2005). SPTLC1 and RAB7 mutation analysis in dominantly inherited and idiopathic sensory neuropathies. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 76(7), 1022–1024. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2004.050062.
Laura, M., Murphy, S. M., Hornemann, T., Bode, H., Polke, J., Blake, J., et al. (2012). P42 Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1: correlation of severity and plasma atypical deoxy-sphyngoid bases. Neuromuscular Disorders, 22, S18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8966(12)70050-0.
Leipold, E., Liebmann, L., Korenke, G. C., Heinrich, T., Gieszelmann, S., Baets, J., et al. (2013). A de novo gain-of-function mutation in SCN11A causes loss of pain perception. Nature Genetics, 45(11), 1399–1404. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2767.
Murphy, S. M., Ernst, D., Wei, Y., Laurà, M., Liu, Y.-T., Polke, J., et al. (2013). Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSANI) caused by a novel mutation in SPTLC2. Neurology, 80, 2106–2111. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318295d789.
Penno, A., Reilly, M. M., Houlden, H., Laurá, M., Rentsch, K., Niederkofler, V., et al. (2010). Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 is caused by the accumulation of two neurotoxic sphingolipids. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 11178–11187. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.092973.
Rotthier, A., Auer-Grumbach, M., Janssens, K., Baets, J., Penno, A., Almeida-Souza, L., et al. (2010). Mutations in the SPTLC2 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase cause hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type I. American Journal of Human Genetics, 87(4), 513–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.09.010.
Rotthier, A., Penno, A., Rautenstrauss, B., Auer-Grumbach, M., Stettner, G. M., Asselbergh, B., et al. (2011). Characterization of two mutations in the SPTLC1 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase associated with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type I. Human Mutation, 32(6), E2211–E2225. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.21481.
Suh, B. C., Hong, Y. B., Nakhro, K., Nam, S. H., Chung, K. W., & Choi, B.-O. (2014). Early-onset severe hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 with S331F SPTLC1 mutation. Molecular medicine Reports, 9, 481–486. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1808.
Suriyanarayanan, S., Toppila, J., Auranen, M., Paetau, A., Shcherbii, M., Palin, E., et al. (2016). The variant p.(Arg183Trp) in SPTLC2 causes late-onset hereditary sensory neuropathy. NeuroMolecular Medicine, 18(1), 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8379-1.
Yard, B. A., Carter, L. G., Johnson, K. A., Overton, I. M., Dorward, M., Liu, H., et al. (2007). The structure of serine palmitoyltransferase; gateway to sphingolipid biosynthesis. Journal of Molecular Biology, 370(5), 870–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.086.
Acknowledgements
The family is thanked for participating in this study. The study was supported by 7th Framework Program of the European Commission (“RESOLVE,” Project number 305707); the Swiss National Foundation-SNF (Project 31003A_153390/1); and the Rare Disease Initiative Zurich (“radiz,”), University of Zurich).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval
The manuscript is a retrospective case report that does not require ethics committee approval at our institution.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suriyanarayanan, S., Othman, A., Dräger, B. et al. A Novel Variant (Asn177Asp) in SPTLC2 Causing Hereditary Sensory Autonomic Neuropathy Type 1C. Neuromol Med 21, 182–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08534-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08534-w