Abstract
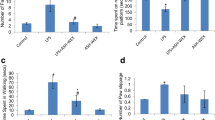
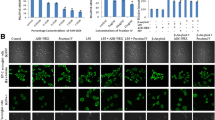
Reactive gliosis, microgliosis, and subsequent secretion of various inflammatory mediators like cytokines, proteases, reactive oxygen, and nitrogen species are the suggested key players associated with systemic inflammation-driven neuroinflammation and cognitive impairments in various neurological disorders. Conventionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to suppress inflammation but due to their adverse effects, their usage is not well accepted. Natural products are emerging better therapeutic agents due to their affordability and inherent pleiotropic biological activities. In Ayurveda, Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is well known for its immunomodulatory properties. The current study is an extension of our previous report on in vitro model system and was aimed to investigate anti-neuroinflammatory potential of water extract from the Ashwagandha leaves (ASH-WEX) against systemic LPS-induced neuroinflammation and associated behavioral impairments using in vivo rat model system. Oral feeding of ASH-WEX for 8 weeks significantly ameliorated the anxiety-like behavior as evident from Elevated plus maze test. Suppression of reactive gliosis, inflammatory cytokines production like TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and expression of nitro-oxidative stress enzymes like iNOS, COX2, NOX2 etc were observed in ASH-WEX-treated animals. NFκB, P38, and JNK MAPKs pathways analysis showed their involvement in inflammation suppression which was further confirmed by inhibitor studies. The current study provides first ever preclinical evidence and scientific validation that ASH-WEX exhibits the anti-neuroinflammatory potential against systemic LPS-induced neuroinflammation and ameliorates associated behavioral abnormalities. Aqueous extract from Ashwagandha leaves and its active phytochemicals may prove to be promising candidates to prevent neuroinflammation associated with various neuropathologies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aid, S., Langenbach, R., & Bosetti, F. (2008). Neuroinflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide is exacerbated in mice genetically deficient in cyclooxygenase-2. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 5(1), 17.
Allan, S. M., & Rothwell, N. J. (2003). Inflammation in central nervous system injury. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 358(1438), 1669–1677.
Archana, R., & Namasivayam, A. (1998). Antistressor effect of Withania somnifera. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 64(1), 91–93.
Bachstetter, A. D., Xing, B., de Almeida, L., Dimayuga, E. R., Watterson, D. M., & Van Eldik, L. J. (2011). Microglial p38α MAPK is a key regulator of proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation induced by toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands or beta-amyloid (Aβ). Journal of Neuroinflammation, 8(1), 79.
Badger, A. M., Cook, M. N., Lark, M. W., Newman-Tarr, T. M., Swift, B. A., Nelson, A. H., et al. (1998). SB 203580 inhibits p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, nitric oxide production, and inducible nitric oxide synthase in bovine cartilage-derived chondrocytes. The Journal of Immunology, 161(1), 467–473.
Baitharu, I., Jain, V., Deep, S. N., Hota, K. B., Hota, S. K., Prasad, D., & Ilavazhagan, G. (2013). Withania somnifera root extract ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia induced memory impairment in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 145(2), 431–441.
Bargagna-Mohan, P., Paranthan, R. R., Hamza, A., Dimova, N., Trucchi, B., Srinivasan, C., et al. (2010). Withaferin A targets intermediate filaments glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin in a model of retinal gliosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(10), 7657–7669.
Barrientos, R. M., Watkins, L. R., Rudy, J. W., & Maier, S. F. (2009). Characterization of the sickness response in young and aging rats following E. coli infection. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 23(4), 450–454.
Bassi, G. S., Kanashiro, A., Santin, F. M., de Souza, G. E., Nobre, M. J., & Coimbra, N. C. (2012). Lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behaviour evaluated in different models of anxiety and innate fear in rats. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 110(4), 359–369.
Bhatnagar, M., Sisodia, S. S., & Bhatnagar, R. (2005). Antiulcer and antioxidant activity of Asparagus racemosus Willd and Withania somnifera Dunal in rats. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1056(1), 261–278.
Bhattacharya, S. K., Bhattacharya, A., Sairam, K., & Ghosal, S. (2000). Anxiolytic-antidepressant activity of Withania somnifera glycowithanolides: An experimental study. Phytomedicine, 7(6), 463–469.
Biesmans, S., Meert, T. F., Bouwknecht, J. A., Acton, P. D., Davoodi, N., De Haes, P., et al. (2013). Systemic immune activation leads to neuroinflammation and sickness behavior in mice. Mediators of Inflammation, 2013, 271359.
Block, M. L., Zecca, L., & Hong, J. S. (2007). Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(1), 57.
Bossù, P., Cutuli, D., Palladino, I., Caporali, P., Angelucci, F., Laricchiuta, D., et al. (2012). A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-α and IL-18. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 9(1), 101.
Cargnello, M., & Roux, P. P. (2011). Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 75(1), 50–83.
Carvey, P. M., Chang, Q., Lipton, J. W., & Ling, Z. (2003). Prenatal exposure to the bacteriotoxin lipopolysaccharide leads to long-term losses of dopamine neurons in offspring: A potential, new model of Parkinson’s disease. Frontiers in Biosciences, 8, s826–s837.
Cho, N. H., Seong, S. Y., Choi, M. S., & Kim, I. S. (2001). Expression of chemokine genes in human dermal microvascular endothelial cell lines infected with Orientia tsutsugamushi. Infection and Immunity, 69(3), 1265–1272.
Conductier, G., Blondeau, N., Guyon, A., Nahon, J. L., & Rovère, C. (2010). The role of monocyte chemoattractant protein MCP1/CCL2 in neuroinflammatory diseases. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 224(1), 93–100.
Cuadrado, A., & Nebreda, A. R. (2010). Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochemical Journal, 429(3), 403–417.
Cunningham, C., Campion, S., Lunnon, K., Murray, C. L., Woods, J. F., Deacon, R. M., et al. (2009). Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Biological Psychiatry, 65(4), 304–312.
Da Silva, J., Pierrat, B., Mary, J. L., & Lesslauer, W. (1997). Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibits inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in mouse astrocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272(45), 28373–28380.
Dantzer, R. (2004). Cytokine-induced sickness behaviour: A neuroimmune response to activation of innate immunity. European Journal of Pharmacology, 500(1–3), 399–411.
Dantzer, R. (2006). Cytokine, sickness behavior, and depression. Neurologic Clinics, 24(3), 441–460.
Dantzer, R., & Kelley, K. W. (2007). Twenty years of research on cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 21(2), 153–160.
Dantzer, R., O’Connor, J. C., Freund, G. G., Johnson, R. W., & Kelley, K. W. (2008). From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(1), 46.
Endale, M., Kim, T. H., Kwak, Y. S., Kim, N. M., Kim, S. H., Cho, J. Y., et al. (2017). Torilin inhibits inflammation by limiting TAK1-mediated MAP kinase and NF-κB activation. Mediators of Inflammation, 2017, 13.
Fan, K., Wu, X., Fan, B., Li, N., Lin, Y., Yao, Y., & Ma, J. (2012). Up-regulation of microglial cathepsin C expression and activity in lipopolysaccharide -induced neuroinflammation. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 9, 96.
Gaestel, M. (2006). MAPKAP kinases—MKs—two’s company, three’s a crowd. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 7(2), 120.
Gao, H. M., Jiang, J., Wilson, B., Zhang, W., Hong, J. S., & Liu, B. (2002). Microglial activation-mediated delayed and progressive degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: Relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 81(6), 1285–1297.
González, H., Elgueta, D., Montoya, A., & Pacheco, R. (2014). Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 274(1), 1–13.
Grover, A., Shandilya, A., Punetha, A., Bisaria, V. S., & Sundar, D. (2010). Inhibition of the NEMO/IKKβ association complex formation, a novel mechanism associated with the NF-κB activation suppression by Withania somnifera’s key metabolite withaferin A. BMC Genomics, 11(4), S25.
Gupta, A., & Singh, S. (2014). Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effect of Withania somnifera root on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Pharmaceutical Biology, 52(3), 308–320.
Gupta, M., & Kaur, G. (2016). Aqueous extract from the Withania somnifera leaves as a potential anti-neuroinflammatory agent: A mechanistic study. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 13(1), 193.
Han, Z., Boyle, D. L., Chang, L., Bennett, B., Karin, M., Yang, L., et al. (2001). c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 108(1), 73–81.
Hart, B. L. (1988). Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 12(2), 123–137.
Herrera, J. A., Espinosa-Oliva, A. M., Oliva-Martin, M. J., Carrillo-Jimenez, A., Venero, J. & de Pablos, M. R. (2015). Collateral damage: Contribution of peripheral inflammation to neurodegenerative diseases. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 15(21), 2193–2210.
Heyninck, K., Lahtela-Kakkonen, M., Van der Veken, P., Haegeman, G., & Berghe, W. V. (2014). Withaferin A inhibits NF-kappaB activation by targeting cysteine 179 in IKKβ. Biochemical Pharmacology, 91(4), 501–509.
Johnson, G. L., & Nakamura, K. (2007). The c-jun kinase/stress-activated pathway: Regulation, function and role in human disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 1773(8), 1341–1348.
Kaileh, M., Berghe, W. V., Heyerick, A., Horion, J., Piette, J., Libert, C., et al. (2007). Withaferin A strongly elicits IκB kinase β hyperphosphorylation concomitant with potent inhibition of its kinase activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(7), 4253–4264.
Kataria, H., Kumar, S., Chaudhary, H., & Kaur, G. (2016). Withania somnifera suppresses tumor growth of intracranial allograft of glioma cells. Molecular Neurobiology, 53(6), 4143–4158.
Kaur, T., & Kaur, G. (2017). Withania somnifera as a potential candidate to ameliorate high fat diet-induced anxiety and neuroinflammation. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 14(1), 201.
Kaur, T., Singh, H., Mishra, R., Manchanda, S., Gupta, M., Saini, V., et al. (2017). Withania somnifera as a potential anxiolytic and immunomodulatory agent in acute sleep deprived female Wistar rats. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 427(1–2), 91–101.
Kent, S., Bluthé, R. M., Kelley, K. W., & Dantzer, R. (1992). Sickness behavior as a new target for drug development. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 13, 24–28.
Khedgikar, V., Kushwaha, P., Gautam, J., Verma, A., Changkija, B., Kumar, A., et al. (2013). Withaferin A: A proteasomal inhibitor promotes healing after injury and exerts anabolic effect on osteoporotic bone. Cell Death & Disease, 4(8), e778.
Konsman, J. P., Parnet, P., & Dantzer, R. (2002). Cytokine-induced sickness behaviour: Mechanisms and implications. Trends in Neurosciences, 25(3), 154–159.
Kumar, S., Harris, R. J., Seal, C. J., & Okello, E. J. (2012). An aqueous extract of Withania somnifera root inhibits amyloid β fibril formation in vitro. Phytotherapy Research, 26(1), 113–117.
Lacosta, S., Merali, Z., & Anisman, H. (1999). Behavioral and neurochemical consequences of lipopolysaccharide in mice: Anxiogenic-like effects. Brain Research, 818(2), 291–303.
Li, Q., Yu, H., Zinna, R., Martin, K., Herbert, B., Liu, A., et al. (2011). Silencing mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase-2 arrests inflammatory bone loss. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 336(3), 633–642.
Liang, D., Li, F., Fu, Y., Cao, Y., Song, X., Wang, T., et al. (2014). Thymol inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response via down-regulation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Inflammation, 37(1), 214–222.
Liddelow, S. A., Guttenplan, K. A., Clarke, L. E., Bennett, F. C., Bohlen, C. J., Schirmer, L., et al. (2017). Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature, 541(7638), 481.
Ling, Z., Gayle, D. A., Ma, S. Y., Lipton, J. W., Tong, C. W., Hong, J. S., & Carvey, P. M. (2002). In utero bacterial endotoxin exposure causes loss of tyrosine hydroxylase neurons in the postnatal rat midbrain. Movement Disorders, 17(1), 116–124.
Ling, Z., Zhu, Y., wai Tong, C., Snyder, J. A., Lipton, J. W., & Carvey, P. M. (2006). Progressive dopamine neuron loss following supra-nigral lipopolysaccharide (LPS) infusion into rats exposed to LPS prenatally. Experimental Neurology, 199(2), 499–512.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆CT method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408.
Lowenstein, C. J., Alley, E. W., Raval, P., Snowman, A. M., Snyder, S. H., Russell, S. W., & Murphy, W. J. (1993). Macrophage nitric oxide synthase gene: Two upstream regions mediate induction by interferon gamma and lipopolysaccharide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 90(20), 9730–9734.
Lull, M. E., & Block, M. L. (2010). Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics, 7(4), 354–365.
Lynch, M. A. (2009). The multifaceted profile of activated microglia. Molecular Neurobiology, 40(2), 139–156.
Maitra, R., Porter, M. A., Huang, S., & Gilmour, B. P. (2009). Inhibition of NFκB by the natural product Withaferin A in cellular models of Cystic Fibrosis inflammation. Journal of Inflammation, 6(1), 15.
Manchanda, S., & Kaur, G. (2017). Withania somnifera leaf alleviates cognitive dysfunction by enhancing hippocampal plasticity in high fat diet induced obesity model. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 17(1), 136.
Manchanda, S., Mishra, R., Singh, R., Kaur, T., & Kaur, G. (2017). Aqueous leaf extract of Withania somnifera as a potential neuroprotective agent in sleep-deprived rats: A mechanistic study. Molecular Neurobiology, 54(4), 3050–3061.
Maroon, J. C., Bost, J. W., & Maroon, A. (2010). Natural anti-inflammatory agents for pain relief. Surgical Neurology International, 1, 80
Mirjalili, M. H., Moyano, E., Bonfill, M., Cusido, R. M., & Palazón, J. (2009). Steroidal lactones from Withania somnifera, an ancient plant for novel medicine. Molecules, 14(7), 2373–2393.
Moon, Y. J., Lee, J. Y., Oh, M. S., Pak, Y. K., Park, K. S., Oh, T. H., & Yune, T. Y. (2012). Inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress by Angelica dahuricae radix extract decreases apoptotic cell death and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 90(1), 243–256.
Nagareddy, P. R., & Lakshmana, M. (2006). Withania somnifera improves bone calcification in calcium-deficient ovariectomized rats. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 58(4), 513–519.
Narinderpal, K., Junaid, N., & Raman, B. (2013). A Review on pharmacological profile of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha). Research and Reviews: Journal of Botanical Sciences, 2, 6–14.
Oh, J. H., Lee, T. J., Park, J. W., & Kwon, T. K. (2008). Withaferin A inhibits iNOS expression and nitric oxide production by Akt inactivation and down-regulating LPS-induced activity of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 cells. European Journal of Pharmacology, 599(1–3), 11–17.
Ohsawa, K., Imai, Y., Kanazawa, H., Sasaki, Y., & Kohsaka, S. (2000). Involvement of Iba1 in membrane ruffling and phagocytosis of macrophages/microglia. Journal of Cell Science, 113(17), 3073–3084.
Owens, T., Babcock, A. A., Millward, J. M., & Toft-Hansen, H. (2005). Cytokine and chemokine inter-regulation in the inflamed or injured CNS. Brain Research Reviews, 48(2), 178–184.
Park, K. J., Gaynor, R. B., & Kwak, Y. T. (2003). Heat shock protein 27 association with the IκB kinase complex regulates tumor necrosis factor α-induced NF-κB activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(37), 35272–35278.
Park, S. Y., Jin, M. L., Kim, Y. H., Kim, Y., & Lee, S. J. (2012). Anti-inflammatory effects of aromatic-turmerone through blocking of NF-κB, JNK, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in amyloid β-stimulated microglia. International Immunopharmacology, 14(1), 13–20.
Pietersma, A., Tilly, B. C., Gaestel, M., de Jong, N., Lee, J. C., Koster, J. F., & Sluiter, W. (1997). p38 mitogen activated protein kinase regulates endothelial VCAM-1 expression at the post-transcriptional level. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 230(1), 44–48.
Pratte, M. A., Nanavati, K. B., Young, V., & Morley, C. P. (2014). An alternative treatment for anxiety: A systematic review of human trial results reported for the Ayurvedic herb ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 20(12), 901–908.
Purushotham, P. M., Kim, J. M., Jo, E. K., & Senthil, K. (2017). Withanolides against TLR4-activated innate inflammatory signalling pathways: A comparative computational and experimental study. Phytotherapy Research, 31(1), 152–163.
Qin, L., Wu, X., Block, M. L., Liu, Y., Breese, G. R., Hong, J. S., et al. (2007). Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia, 55(5), 453–462.
Salim, S., Chugh, G., & Asghar, M. (2012). Inflammation in anxiety. Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 88, 1–25.
Singh, N., Bhalla, M., de Jager, P., & Gilca, M. (2011). An overview on ashwagandha: A Rasayana (Rejuvenator) of Ayurveda. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 8(5S), 208–213.
Sinsimer, K. S., Gratacós, F. M., Knapinska, A. M., Lu, J., Krause, C. D., Wierzbowski, A. V., et al. (2008). Chaperone Hsp27, a novel subunit of AUF1 protein complexes, functions in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA decay. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28(17), 5223–5237.
Sivamani, S., Joseph, B., & Kar, B. (2014). Anti-inflammatory activity of Withania somnifera leaf extract in stainless steel implant induced inflammation in adult zebrafish. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 12(1), 1–6.
Solanki, I., Parihar, P., & Parihar, M. S. (2016). Neurodegenerative diseases: From available treatments to prospective herbal therapy. Neurochemistry International, 95, 100–108.
Spencer, S. J., Mouihate, A., & Pittman, Q. J. (2007). Peripheral inflammation exacerbates damage after global ischemia independently of temperature and acute brain inflammation. Stroke, 38(5), 1570–1577.
Sun, G. Y., Li, R., Cui, J., Hannink, M., Gu, Z., Fritsche, K. L., et al. (2016). Withania somnifera and its withanolides attenuate oxidative and inflammatory responses and up-regulate antioxidant responses in BV-2 microglial cells. Neuromolecular Medicine, 18(3), 241–252.
Swiergiel, A. H., & Dunn, A. J. (2007). Effects of interleukin-1β and lipopolysaccharide on behavior of mice in the elevated plus-maze and open field tests. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 86(4), 651–659.
Udayakumar, R., Kasthurirengan, S., Mariashibu, T. S., Rajesh, M., Anbazhagan, V. R., Kim, S. C., et al. (2009). Hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic effects of Withania somnifera root and leaf extracts on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 10(5), 2367–2382.
Ven Murthy, M. R., Ranjekar, K., Ramassamy, C., & Deshpande, M. (2010). Scientific basis for the use of Indian ayurvedic medicinal plants in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: 1. Ashwagandha. Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 10(3), 238–246.
Wang, A., Al-Kuhlani, M., Johnston, S. C., Ojcius, D. M., Chou, J., & Dean, D. (2013). Transcription factor complex AP-1 mediates inflammation initiated by Chlamydia pneumoniae infection. Cellular Microbiology, 15(5), 779–794.
Yamamoto, K., Arakawa, T., Ueda, N., & Yamamoto, S. (1995). Transcriptional roles of nuclear factor B and nuclear factor-interleukin-6 in the tumor necrosis factor-dependent induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in MC3T3-E1 cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270(52), 31315–31320.
Yuan, L., Wu, Y., Ren, X., Liu, Q., Wang, J., & Liu, X. (2014). Isoorientin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of ROS-related MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in BV-2 microglia. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 386(1–2), 153–165.
Zeng, K. W., Wang, S., Dong, X., Jiang, Y., & Tu, P. F. (2014). Sesquiterpene dimer (DSF-52) from Artemisia argyi inhibits microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of NF-κB, JNK/p38 MAPKs and Jak2/Stat3 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine, 21(3), 298–306.
Zeng, K. W., Zhang, T., Fu, H., Liu, G. X., & Wang, X. M. (2012). Modified Wu-Zi-Yan-Zong prescription, a traditional Chinese polyherbal formula, suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammatory processes in rat astrocytes via NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine, 19(2), 122–129.
Zhu, L. H., Bi, W., Qi, R. B., Wang, H. D., & Lu, D. X. (2011). Luteolin inhibits microglial inflammation and improves neuron survival against inflammation. International Journal of Neuroscience, 121(6), 329–336.
Zubair Alam, M., Alam, Q., Amjad Kamal, M., Jiman-Fatani, A., Azhar, A. I., Azhar Khan, E., M., & Haque, A. (2017). Infectious Agents and neurodegenerative diseases: Exploring the links. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 17(12), 1390–1399.
Acknowledgements
The current research work was funded by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India (GOI) to Prof. Gurcharan Kaur (Grant No: BT/PR12200/MED/30/1439/2014). Muskan Gupta is thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for the fellowship. Infrastructure provided by University Grants Commission (UGC), India under UPE and CPEPA schemes and Department of Biotechnology (DBT), India under DISC facility is highly acknowledged. Shaffi Manchanda, Taranjeet Kaur, Anuradha Sharma, Harpal Singh, and Manpreet Kaur are deeply acknowledged for their help and support during experimental study. The funding source had no role in study design; collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in writing of report; and in decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures of animal handling and experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines laid down by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC) of Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar, Punjab, India (Registration number: 226/CPCSEA) and that the studies have been approved by Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC) of Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar, Punjab, India (226/CPCSEA/2015/18). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, M., Kaur, G. Withania somnifera as a Potential Anxiolytic and Anti-inflammatory Candidate Against Systemic Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation. Neuromol Med 20, 343–362 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8497-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8497-7