Abstract
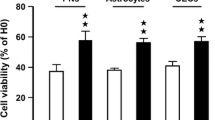
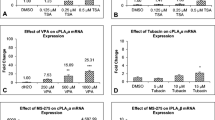
Clinacanthus nutans Lindau (C. nutans), commonly known as Sabah Snake Grass in southeast Asia, is widely used in folk medicine due to its analgesic, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties. Our recent study provided evidence for the regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) mRNA expression by epigenetic factors (Tan et al. in Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9314-z, 2015). This enzyme catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid from glycerophospholipids, and formation of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids or toxic lipid peroxidation products such as 4-hydroxynonenal. In this study, we examined the effects of C. nutans ethanol leaf extracts on epigenetic regulation of cPLA2 mRNA expression in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and mouse primary cortical neurons. C. nutans modulated induction of cPLA2 expression in SH-SY5Y cells by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, MS-275, MC-1568, and TSA. C. nutans extracts also inhibited histone acetylase (HAT) activity. Levels of cPLA2 mRNA expression were increased in primary cortical neurons subjected to 0.5-h oxygen–glucose deprivation injury (OGD). This increase was significantly inhibited by C. nutans treatment. Treatment of primary neurons with the HDAC inhibitor MS-275 augmented OGD-induced cPLA2 mRNA expression, and this increase was modulated by C. nutans extracts. OGD-stimulated increase in cPLA2 mRNA expression was also reduced by a Tip60 HAT inhibitor, NU9056. In view of a key role of cPLA2 in the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids and free radical damage, and the fact that epigenetic effects on genes are often long-lasting, results suggest a role for C. nutans and phytochemicals to inhibit the production of arachidonic acid-derived pro-inflammatory eicosanoids and chronic inflammation, through epigenetic regulation of cPLA2 expression.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanyam, K., Altaf, M., Varier, R. A., Swaminathan, V., Ravindran, A., Sadhale, P. P., et al. (2004a). Polyisoprenylated benzophenone, garcinol, a natural histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, represses chromatin transcription and alters global gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(32), 33716–33726. doi:10.1074/jbc.M402839200.
Balasubramanyam, K., Varier, R. A., Altaf, M., Swaminathan, V., Siddappa, N. B., Ranga, U., et al. (2004b). Curcumin, a novel p300/CREB-binding protein-specific inhibitor of acetyltransferase, represses the acetylation of histone/nonhistone proteins and histone acetyltransferase-dependent chromatin transcription. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(49), 51163–51171. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409024200.
Borghi, S. M., Carvalho, T. T., Staurengo-Ferrari, L., Hohmann, M. S., Pinge-Filho, P., Casagrande, R., et al. (2013). Vitexin inhibits inflammatory pain in mice by targeting TRPV1, oxidative stress, and cytokines. Journal of Natural Products, 76(6), 1141–1149. doi:10.1021/np400222v.
Burgess, A., Vigneron, S., Brioudes, E., Labbé, J.-C., Lorca, T., & Castro, A. (2010). Loss of human Greatwall results in G2 arrest and multiple mitotic defects due to deregulation of the cyclin B-Cdc2/PP2A balance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 12564–12569.
Chi, P. L., Luo, S. F., Hsieh, H. L., Lee, I. T., Hsiao, L. D., Chen, Y. L., et al. (2011). Cytosolic phospholipase A2 induction and prostaglandin E2 release by interleukin-1beta via the myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent pathway and cooperation of p300, Akt, and NF-kappaB activity in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 63(10), 2905–2917. doi:10.1002/art.30504.
Choi, S. W., & Friso, S. (2010). Epigenetics: A new bridge between nutrition and health. Advances in Nutrition, 1(1), 8–16. doi:10.3945/an.110.1004.
Chuang, D. M., Leng, Y., Marinova, Z., Kim, H. J., & Chiu, C. T. (2009). Multiple roles of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative conditions. Trends in Neurosciences, 32(11), 591–601. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2009.06.002.
Cowan, M. J., Yao, X. L., Pawliczak, R., Huang, X., Logun, C., Madara, P., et al. (2004). The role of TFIID, the initiator element and a novel 5′ TFIID binding site in the transcriptional control of the TATA-less human cytosolic phospholipase A2-alpha promoter. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1680(3), 145–157. doi:10.1016/j.bbaexp.2004.09.006.
Daduang, S., Sattayasai, N., Sattayasai, J., Tophrom, P., Thammathaworn, A., Chaveerach, A., et al. (2005). Screening of plants containing Naja naja siamensis cobra venom inhibitory activity using modified ELISA technique. Analytical Biochemistry, 341(2), 316–325. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.037.
Ekici, M., Hohl, M., Schuit, F., Martinez-Serrano, A., & Thiel, G. (2008). Transcription of genes encoding synaptic vesicle proteins in human neural stem cells: Chromatin accessibility, histone methylation pattern, and the essential role of rest. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(14), 9257–9268. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709388200.
Farooqui, A. A., Yang, H.-C., Rosenberger, T. A., & Horrocks, L. A. (1997). Phospholipase A2 and its role in brain tissue. Journal of Neurochemistry, 69, 889–901.
Franci, G., Casalino, L., Petraglia, F., Miceli, M., Menafra, R., Radic, B., et al. (2013). The class I-specific HDAC inhibitor MS-275 modulates the differentiation potential of mouse embryonic stem cells. Biol Open, 2(10), 1070–1077. doi:10.1242/bio.20135587.
Furumai, R., Komatsu, Y., Nishino, N., Khochbin, S., Yoshida, M., & Horinouchi, S. (2001). Potent histone deacetylase inhibitors built from trichostatin A and cyclic tetrapeptide antibiotics including trapoxin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(1), 87–92. doi:10.1073/pnas.011405598.
Gavet, O., & Pines, J. (2012). Progressive activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 coordinates entry to mitosis. Developmental Cell, 18(4), 533–543.
Goldberg, M. P., & Choi, D. W. (1993). Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. Journal of Neuroscience, 13(8), 3510–3524.
Guo, C., Li, J., Myatt, L., Zhu, X., & Sun, K. (2010). Induction of Galphas contributes to the paradoxical stimulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha expression by cortisol in human amnion fibroblasts. Molecular Endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.), 24(5), 1052–1061. doi:10.1210/me.2009-0488.
Herranz, M., & Esteller, M. (2007). DNA methylation and histone modifications in patients with cancer: Potential prognostic and therapeutic targets. Methods in Molecular Biology, 361, 25–62. doi:10.1385/1-59745-208-4:25.
Huang, C. Y., Chen, J. J., Wu, J. S., Tsai, H. D., Lin, H., Yan, Y. T., et al. (2015a). Novel link of anti-apoptotic ATF3 with pro-apoptotic CTMP in the ischemic brain. Molecular Neurobiology, 51(2), 543–557. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8710-0.
Huang, D., Guo, W., Gao, J., Chen, J., & Olatunji, J. O. (2015b). Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau ethanol extract inhibits hepatoma in mice through upregulation of the immune response. Molecules, 20(9), 17405–17428. doi:10.3390/molecules200917405.
Jamsa, A., Hasslund, K., Cowburn, R. F., Backstrom, A., & Vasange, M. (2004). The retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor differentiated SH-SY5Y cell line as a model for Alzheimer’s disease-like tau phosphorylation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 319(3), 993–1000. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.075.
Kazantsev, A. G., & Thompson, L. M. (2008). Therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors for central nervous system disorders. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 7(10), 854–868. doi:10.1038/nrd2681.
Kunsorn, P., Ruangrungsi, N., Lipipun, V., Khanboon, A., Rungsihirunrat, K., & Chaijaroenkul, W. (2013). The identities and anti-herpes simplex virus activity of Clinacanthus nutans and Clinacanthus siamensis. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 3(4), 284–290. doi:10.1016/s2221-1691(13)60064-7.
Lau, K. W., Lee, S. K., & Chin, J. H. (2014). Effect of the methanol leaves extract of Clinacanthus nutans on the activity of acetylcholinesterase in male mice. Journal of Acute Disease, 3(1), 22–25. doi:10.1016/S2221-6189(14)60005-6.
Lin, T. N., Wang, C. K., Cheung, W. M., & Hsu, C. Y. (2000). Induction of angiopoietin and Tie receptor mRNA expression after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 20(2), 387–395. doi:10.1097/00004647-200002000-00021.
Liu, N. K., Deng, L. X., Zhang, Y. P., Lu, Q. B., Wang, X. F., Hu, J. G., et al. (2014). Cytosolic phospholipase A2 protein as a novel therapeutic target for spinal cord injury. Annals of Neurology, 75(5), 644–658. doi:10.1002/ana.24134.
Loizou, S., Lekakis, I., Chrousos, G. P., & Moutsatsou, P. (2010). Beta-sitosterol exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in human aortic endothelial cells. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 54(4), 551–558. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200900012.
Lopez-Atalaya, J. P., Ito, S., Valor, L. M., Benito, E., & Barco, A. (2013). Genomic targets, and histone acetylation and gene expression profiling of neural HDAC inhibition. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(17), 8072–8084. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt590.
Mandal, A., Ojha, D., Lalee, A., Kaity, S., Das, M., Chattopadhyay, D., et al. (2014). Bioassay directed isolation of a novel anti-inflammatory cerebroside from the leaves of Aerva sanguinolenta. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 1–12. doi:10.1007/s00044-014-1261-0.
Muhlethaler-Mottet, A., Meier, R., Flahaut, M., Bourloud, K. B., Nardou, K., Joseph, J. M., et al. (2008). Complex molecular mechanisms cooperate to mediate histone deacetylase inhibitors anti-tumour activity in neuroblastoma cells. Molecular Cancer, 7, 55. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-7-55.
Nebbioso, A., Dell’Aversana, C., Bugge, A., Sarno, R., Valente, S., Rotili, D., et al. (2010). HDACs class II-selective inhibition alters nuclear receptor-dependent differentiation. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 45(4), 219–228.
Pongphasuk, N., & Khunkitti, W. (1996). Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of the Extract from Garcinia mangostana Linn. Traditional Medicine and Nutraceuticals, 6, 125–130.
Portela, A., & Esteller, M. (2010). Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nature Biotechnology, 28(10), 1057–1068. doi:10.1038/nbt.1685.
Russo, V. E., Martienssen, R. A., & Riggs, A. D. (1996). Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation (Vol. 69, Genetics Research, Vol. 02). Cold Spring: Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sakdarat, S., Shuyprom, A., Ayudhya, T., Waterman, P. G., & Karagianis, G. (2006). Chemical composition investigation of the Clinacanthus nutans Lindau leaves. Thai Journal of Phytopharmacy, 13(2), 14–24.
Saleem, M. (2009). Lupeol, a novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer dietary triterpene. Cancer Letters, 285(2), 109–115. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.033.
Sandur, S. K., Ichikawa, H., Sethi, G., Ahn, K. S., & Aggarwal, B. B. (2006). Plumbagin (5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) suppresses NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-regulated gene products through modulation of p65 and IkappaBalpha kinase activation, leading to potentiation of apoptosis induced by cytokine and chemotherapeutic agents. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(25), 17023–17033. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601595200.
Smitinand, T. (1980). Thai plant names (Botanical Names—Vernacular Names). Royal Forest Department, Phahonyothin, Bangkhen, Bangkok, Thailand.
Sun, G. Y., He, Y., Chuang, D. Y., Lee, J. C., Gu, Z., Simonyi, A., et al. (2012). Integrating cytosolic phospholipase A(2) with oxidative/nitrosative signaling pathways in neurons: A novel therapeutic strategy for AD. Molecular Neurobiology, 46(1), 85–95. doi:10.1007/s12035-012-8261-1.
Sung, B., Pandey, M. K., Ahn, K. S., Yi, T., Chaturvedi, M. M., Liu, M., et al. (2008). Anacardic acid (6-nonadecyl salicylic acid), an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase, suppresses expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products involved in cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and inflammation through inhibition of the inhibitory subunit of nuclear factor-kappaB alpha kinase, leading to potentiation of apoptosis. Blood, 111(10), 4880–4891. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-10-117994.
Tan, C. S., Ng, Y. K., & Ong, W. Y. (2015). Epigenetic regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Molecular Neurobiology. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9314-z.
Trimble, L. A., Street, I. P., Perrier, H., Tremblay, N. M., Weech, P. K., & Bernstein, M. A. (1993). NMR structural studies of the tight complex between a trifluoromethyl ketone inhibitor and the 85-kDa human phospholipase A2. Biochemistry, 32, 12560–12565.
Tsou, J. H., Chang, K. Y., Wang, W. C., Tseng, J. T., Su, W. C., Hung, L. Y., et al. (2007). Nucleolin regulates c-Jun/Sp1-dependent transcriptional activation of cPLA2 in phorbol ester-treated non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Nucleic Acids Research, 36(1), 217–227. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm1027.
Tu, S. F., Liu, R. H., Cheng, Y. B., Hsu, Y. M., Du, Y. C., El-Shazly, M., et al. (2014). Chemical constituents and bioactivities of Clinacanthus nutans aerial parts. Molecules, 19(12), 20382–20390. doi:10.3390/molecules191220382.
Tuntiwachwuttikul, P., Pootaeng-on, Y., Phansa, P., & Taylor, W. C. (2004a). Cerebrosides and a Monoacylmonogalactosylglycerol from Clinacanthus nutans. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 52(1), 27–32. doi:10.1248/cpb.52.27.
Tuntiwachwuttikul, P., Pootaeng-On, Y., Phansa, P., & Taylor, W. C. (2004b). Cerebrosides and a monoacylmonogalactosylglycerol from Clinacanthus nutans. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (Tokyo), 52(1), 27–32.
Uawonggul, N., Chaveerach, A., Thammasirirak, S., Arkaravichien, T., Chuachan, C., & Daduang, S. (2006). Screening of plants acting against Heterometrus laoticus scorpion venom activity on fibroblast cell lysis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 103(2), 201–207. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.08.003.
Wanikiat, P., Panthong, A., Sujayanon, P., Yoosook, C., Rossi, A. G., & Reutrakul, V. (2008). The anti-inflammatory effects and the inhibition of neutrophil responsiveness by Barleria lupulina and Clinacanthus nutans extracts. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 116(2), 234–244. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.11.035.
Wirotesangthong, M., & Rattanakiat, S. (2006). Anti-herpes simplex virus type 2 activities of some Thai medicinal plants. Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 30, 19–27.
Wu, J. S., Tsai, H. D., Huang, C. Y., Chen, J. J., & Lin, T. N. (2014). 15-Deoxy-12,14-PGJ 2, by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, suppresses p22phox transcription to protect brain endothelial cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Molecular Neurobiology, 50(1), 221–238. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8600-x.
Yong, Y. K., Tan, J. J., Teh, S. S., Mah, S. H., Ee, G. C., Chiong, H. S., et al. (2013). Clinacanthus nutans extracts are antioxidant with antiproliferative effect on cultured human cancer cell lines. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2013, 462751. doi:10.1155/2013/462751.
Yoshida, M., Kijima, M., Akita, M., & Beppu, T. (1990). Potent and specific inhibition of mammalian histone deacetylase both in vivo and in vitro by trichostatin A. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 265(28), 17174–17179.
Yuliya, E. B., Theodora, P., Pim, J. K., Mary, E. M., Hendrikus, H., Johan, G., et al. (2014). Neuroprotective and cognitive enhancing effects of a multi-targeted food intervention in an animal model of neurodegeneration and depression. Neuropharmacology, 79, 738–749.
Zhou, X., Gan, P., Hao, L., Tao, L., Jia, J., Gao, B., et al. (2014). Antiinflammatory effects of orientin-2″-O-galactopyranoside on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 37(8), 1282–1294.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Annie Hsu from the Department of Pharmacology, NUS, for guidance on preparation of extracts from C. nutans and Ms. Andrea Foo, Jia-Yun Yip, and Victoria E. Buckland from the National Junior College who participated in this work as part of their school research attachment programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, C.SH., Ho, C.FY., Heng, SS. et al. Clinacanthus nutans Extracts Modulate Epigenetic Link to Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells and Primary Cortical Neurons. Neuromol Med 18, 441–452 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8404-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8404-z