Abstract
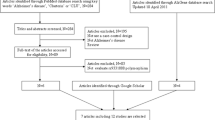
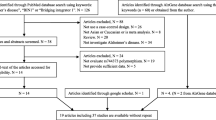
Large-scale genomewide association studies have reported that the CLU rs11136000 polymorphism is significantly associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in people of Caucasian ancestry. Recently, this association was investigated in Asian populations (Chinese, Japanese, and Korean). However, these studies reported either a weak association or no association between the rs11136000 polymorphism and AD. We believe that this discrepancy may be caused by the relatively small sample size of the previous studies and the genetic heterogeneity of the rs11136000 polymorphism in AD among different populations. For this study, we searched the PubMed and AlzGene databases. We selected 18 independent studies (6 studies of Asian populations and 12 of populations of Caucasian ancestry) that evaluated the association between the rs11136000 polymorphism and AD using a case–control experimental design. We evaluated the genetic heterogeneity of the rs11136000 polymorphism in Caucasian and Asian populations. We then investigated the rs11136000 polymorphism by a meta-analysis in Asian populations using allele, dominant, and recessive models. We identified a significant association between rs11136000 and AD with the allele model (P = 2.00 × 10−4) and the dominant model (P = 5.00 × 10−3). Meanwhile, a similar genetic risk of the rs11136000 polymorphism in AD was observed in Asian and Caucasian populations. Further meta-analysis in pooled Asian and Caucasian populations indicated a more significant association with the allele (P = 8.30 × 10−24), dominant (P = 4.46 × 10−17), and recessive (P = 3.92 × 10−12) models. Collectively, our findings from this meta-analysis indicate that the effect of the CLU rs11136000 polymorphism on AD risk in Asian cohorts (Chinese, Japanese, and Korean) is consistent with the protective effect observed in Caucasian AD cohorts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M., Zou, F., Chai, H. S., Younkin, C. S., Crook, J., Pankratz, V. S., et al. (2012). Novel late-onset Alzheimer disease loci variants associate with brain gene expression. Neurology, 79(3), 221–228.
Bertram, L., McQueen, M. B., Mullin, K., Blacker, D., & Tanzi, R. E. (2007). Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nature Genetics, 39(1), 17–23.
Braskie, M. N., Jahanshad, N., Stein, J. L., Barysheva, M., McMahon, K. L., de Zubicaray, G. I., et al. (2011). Common Alzheimer’s disease risk variant within the CLU gene affects white matter microstructure in young adults. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(18), 6764–6770.
Carrasquillo, M. M., Belbin, O., Hunter, T. A., Ma, L., Bisceglio, G. D., Zou, F., et al. (2010). Replication of CLU, CR1, and PICALM associations with Alzheimer’s disease. Archives of Neurology, 67(8), 961–964.
Chen, L. H., Kao, P. Y., Fan, Y. H., Ho, D. T., Chan, C. S., Yik, P. Y., et al. (2012). Polymorphisms of CR1, CLU and PICALM confer susceptibility of Alzheimer’s disease in a southern Chinese population. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(1), e211–e217.
Chung, S. J., Lee, J. H., Kim, S. Y., You, S., Kim, M. J., Lee, J. Y., et al. (2012). Association of GWAS top hits with late-onset Alzheimer disease in Korean population. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders. doi:10.1097/WAD.0b013e31826d7281.
Dye, R. V., Miller, K. J., Singer, E. J., & Levine, A. J. (2012). Hormone replacement therapy and risk for neurodegenerative diseases. International Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2012, 258454.
Erk, S., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., Opitz von Boberfeld, C., Esslinger, C., Schnell, K., Kirsch, P., et al. (2011). Hippocampal function in healthy carriers of the CLU Alzheimer’s disease risk variant. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(49), 18180–18184.
Giedraitis, V., Kilander, L., Degerman-Gunnarsson, M., Sundelof, J., Axelsson, T., Syvanen, A. C., et al. (2009). Genetic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease in the Uppsala Longitudinal Study of Adult Men. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 27(1), 59–68.
Golenkina, S. A., Gol’tsov, A., Kuznetsova, I. L., Grigorenko, A. P., Andreeva, T. V., Reshetov, D. A., et al. (2010). Analysis of clustering gene (CLU/APOJ) polymorphism in Alzheimer’s disease patients and in normal cohorts from Russian populations. Molekuliarnaia Biologiia, 44(4), 620–626.
Harold, D., Abraham, R., Hollingworth, P., Sims, R., Gerrish, A., Hamshere, M. L., et al. (2009). Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Genetics, 41(10), 1088–1093.
Hollingworth, P., Harold, D., Sims, R., Gerrish, A., Lambert, J. C., Carrasquillo, M. M., et al. (2011). Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Genetics, 43(5), 429–435.
Jiang, Y., Zhang, R., Zheng, J., Liu, P., Tang, G., Lv, H., et al. (2012). Meta-analysis of 125 rheumatoid arthritis-related single nucleotide polymorphisms studied in the past two decades. PLoS One, 7(12), e51571.
Kamboh, M. I., Minster, R. L., Demirci, F. Y., Ganguli, M., Dekosky, S. T., Lopez, O. L., et al. (2012). Association of CLU and PICALM variants with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(3), 518–521.
Lambert, J. C., Heath, S., Even, G., Campion, D., Sleegers, K., Hiltunen, M., et al. (2009). Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Genetics, 41(10), 1094–1099.
Lewis, C. M., & Knight, J. (2012). Introduction to genetic association studies. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2012(3), 297–306.
Lin, Y. L., Chen, S. Y., Lai, L. C., Chen, J. H., Yang, S. Y., Huang, Y. L., et al. (2012). Genetic polymorphisms of clusterin gene are associated with a decreased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Epidemiology, 27(1), 73–75.
Liu, G., Zhang, S., Cai, Z., Ma, G., Zhang, L., Jiang, Y., et al. (2013). PICALM gene rs3851179 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer’s disease in an Asian population. Neuromolecular Medicine, 15(2), 384–388.
Ma, J. F., Liu, L. H., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Deng, Y. L., Huang, Y., et al. (2011). Association study of clusterin polymorphism rs11136000 with late onset Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese Han population. American Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias, 26(8), 627–630.
Miyashita, A., Koike, A., Jun, G., Wang, L. S., Takahashi, S., Matsubara, E., et al. (2013). SORL1 is genetically associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in Japanese, Koreans and Caucasians. PLoS One, 8(4), e58618.
Naj, A. C., Jun, G., Beecham, G. W., Wang, L. S., Vardarajan, B. N., Buros, J., et al. (2011). Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Genetics, 43(5), 436–441.
Ohara, T., Ninomiya, T., Hirakawa, Y., Ashikawa, K., Monji, A., Kiyohara, Y., et al. (2012). Association study of susceptibility genes for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the Japanese population. Psychiatric Genetics, 22(6), 290–293.
Pedersen, N. L. (2010). Reaching the limits of genome-wide significance in Alzheimer disease: back to the environment. Journal of American Medical Association, 303(18), 1864–1865.
Seshadri, S., Fitzpatrick, A. L., Ikram, M. A., DeStefano, A. L., Gudnason, V., Boada, M., et al. (2010). Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. Journal of American Medical Association, 303(18), 1832–1840.
Thambisetty, M., Beason-Held, L. L., An, Y., Kraut, M., Nalls, M., Hernandez, D. G., et al. (2013). Alzheimer risk variant CLU and brain function during aging. Biological Psychiatry, 73(5), 399–405.
Trikalinos, T. A., Salanti, G., Khoury, M. J., & Ioannidis, J. P. (2006). Impact of violations and deviations in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium on postulated gene–disease associations. American Journal of Epidemiology, 163(4), 300–309.
Yu, J. T., Li, L., Zhu, Q. X., Zhang, Q., Zhang, W., Wu, Z. C., et al. (2010). Implication of CLU gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Clinica Chimica Acta, 411(19–20), 1516–1519.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 31171219, 81271213, and 31200934) and US–China Biomedical Collaborative Research Program (NSFC Grant Number 812111108) to Keshen Li.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guiyou Liu, Haiyang Wang, and Jiafeng Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Wang, H., Liu, J. et al. The CLU Gene rs11136000 Variant is Significantly Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease in Caucasian and Asian Populations. Neuromol Med 16, 52–60 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8250-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8250-1