Abstract
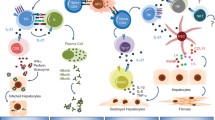
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a worldwide health problem, with approximately one third of populations have been infected, among which 3–5 % of adults and more than 90 % of children developed to chronic HBV infection. Host immune factors play essential roles in the outcome of HBV infection. Thus, ineffective immune response against HBV may result in persistent virus replications and liver necroinflammations, then lead to chronic HBV infection, liver cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma. Cytokine balance was shown to be an important immune characteristic in the development and progression of hepatitis B, as well as in an effective antiviral immunity. Large numbers of cytokines are not only involved in the initiation and regulation of immune responses but also contributing directly or indirectly to the inhibition of virus replication. Besides, cytokines initiate downstream signaling pathway activities by binding to specific receptors expressed on the target cells and play important roles in the responses against viral infections and, therefore, might affect susceptibility to HBV and/or the natural course of the infection. Since cytokines are the primary causes of inflammation and mediates liver injury after HBV infection, we have discussed recent advances on the roles of various cytokines [including T helper type 1 cells (Th1), Th2, Th17, regulatory T cells (Treg)-related cytokines] in different phases of HBV infection and cytokine-related mechanisms for impaired viral control and liver damage during HBV infection. We then focus on experimental therapeutic applications of cytokines to gain a better understanding of this newly emerging aspect of disease pathogenesis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Villa E, Fattovich G, Mauro A, Pasino M (2011) Natural history of chronic HBV infection: special emphasis on the prognostic implications of the inactive carrier state versus chronic hepatitis. Dig Liver Dis 43(Suppl 1):S8–S14
Ganem D, Prince AM (2004) Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med 350:1118–1129
Dienstag JL (2008) Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med 359:1486–1500
Zhang Z, Zhang JY, Wang LF, Wang FS (2012) Immunopathogenesis and prognostic immune markers of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:223–230
Chisari FV, Isogawa M, Wieland SF (2010) Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Pathol Biol (Paris) 58:258–266
Bauer T, Sprinzl M, Protzer U (2011) Immune control of hepatitis B virus. Dig Dis 29:423–433
Guidotti LG, Chisari FV (2001) Noncytolytic control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immune response. Annu Rev Immunol 19:65–91
Fisicaro P, Valdatta C, Boni C et al (2009) Early kinetics of innate and adaptive immune responses during hepatitis B virus infection. Gut 58:974–982
Uprichard SL, Wieland SF, Althage A, Chisari FV (2003) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of hepatitis B virus gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:1310–1315
Wieland SF, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV (2000) Intrahepatic induction of alpha/beta interferon eliminates viral RNA-containing capsids in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Virol 74:4165–4173
He YL, Zhao YR, Zhang SL, Lin SM (2006) Host susceptibility to persistent hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 12:4788–4793
Zhang W, Yue B, Wang GQ, Lu SL (2002) Serum and ascites levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor, TNF-alpha and IL-6 in patients with chronic virus hepatitis B and hepatitis cirrhosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 1:577–580
Odeh M, Sabo E, Srugo I, Oliven A (2004) Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha correlate with severity of hepatic encephalopathy due to chronic liver failure. Liver Int 24:110–116
Xiao P, Chen QF, Yang YL, Guo ZH, Chen H (2006) Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and its relation with anti-HBc. World J Gastroenterol 12:482–484
Liu M, Miao T, Zhu H et al (2012) IL-2-engineered nano-APC effectively activates viral antigen-mediated T cell responses from chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients. J Immunol 188:1534–1543
Rossol S, Marinos G, Carucci P, Singer MV, Williams R, Naoumov NV (1997) Interleukin-12 induction of Th1 cytokines is important for viral clearance in chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Invest 99:3025–3033
le Song H, Binh VQ, Duy DN et al (2003) Serum cytokine profiles associated with clinical presentation in Vietnamese infected with hepatitis B virus. J Clin Virol 28:93–103
Schurich A, Pallett LJ, Lubowiecki M et al (2013) The third signal cytokine IL-12 rescues the anti-viral function of exhausted HBV-specific CD8 T cells. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003208
Dadmanesh M, Ghorban K, Hassanshahi G, Momeni M, Arababadi MK (2014) Current information concerning association of IL-12 and hepatitis B infection. Clin Lab 60:185–191
He D, Yan G, Wang Y (2012) Serum levels of interleukin-12 in various clinical states with hepatitis B virus infection. Cell Immunol 272:162–165
Jegaskanda S, Ahn SH, Skinner N et al (2014) Down-regulation of IL-18 mediated cell signalling and IFN-gamma expression by the hepatitis B virus e antigen. J Virol 88:10412–10420
Li W, Kubo S, Okuda A et al (2010) Effect of IL-18 on expansion of gammadelta T cells stimulated by zoledronate and IL-2. J Immunother 33:287–296
Hegde S, Chen X, Keaton JM, Reddington F, Besra GS, Gumperz JE (2007) NKT cells direct monocytes into a DC differentiation pathway. J Leukoc Biol 81:1224–1235
Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ, Paul WE (1999) The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol 17:701–738
Jiang Y, Ma Z, Xin G et al (2010) Th1 and Th2 immune response in chronic hepatitis B patients during a long-term treatment with adefovir dipivoxil. Mediat Inflamm 2010:143026
Yao Y, Li J, Lu Z et al (2011) Proteomic analysis of the interleukin-4 (IL-4) response in hepatitis B virus-positive human hepatocelluar carcinoma cell line HepG2.2.15. Electrophoresis 32:2004–2012
Barathan M, Mariappan V, Shankar EM, Abdullah BJ, Goh KL, Vadivelu J (2013) Hypericin-photodynamic therapy leads to interleukin-6 secretion by HepG2 cells and their apoptosis via recruitment of BH3 interacting-domain death agonist and caspases. Cell Death Dis 4:e697
Missale G, Ferrari C, Fiaccadori F (1995) Cytokine mediators in acute inflammation and chronic course of viral hepatitis. Ann Ital Med Int 10:14–18
Buke AC, Buke M, Altuglu IE et al (2004) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6 productions in response to platelet-activating factor in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Med Princ Pract 13:273–276
Park Y, Han KH, Kim HS (2011) Serum cytokine levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B according to lamivudine therapy. J Clin Lab Anal 25:414–421
Karimi-Googheri M, Daneshvar H, Nosratabadi R et al (2014) Important roles played by TGF-beta in hepatitis B infection. J Med Virol 86:102–108
Hong MH, Chou YC, Wu YC et al (2012) Transforming growth factor-beta1 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication by the reduction of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha expression. PLoS One 7:e30360
Park SO, Kumar M, Gupta S (2012) TGF-beta and iron differently alter HBV replication in human hepatocytes through TGF-beta/BMP signaling and cellular microRNA expression. PLoS One 7:e39276
Sun C, Fu B, Gao Y et al (2012) TGF-beta1 down-regulation of NKG2D/DAP10 and 2B4/SAP expression on human NK cells contributes to HBV persistence. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002594
Wu JF, Wu TC, Chen CH et al (2010) Serum levels of interleukin-10 and interleukin-12 predict early, spontaneous hepatitis B virus e antigen seroconversion. Gastroenterology 138(165–172):e161–e163
Sabat R, Grutz G, Warszawska K et al (2010) Biology of interleukin-10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 21:331–344
Das A, Ellis G, Pallant C et al (2012) IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol 189:3925–3935
Fenoglio D, Bernuzzi F, Battaglia F et al (2012) Th17 and regulatory T lymphocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis and systemic sclerosis as models of autoimmune fibrotic diseases. Autoimmun Rev 12:300–304
Wu W, Li J, Chen F, Zhu H, Peng G, Chen Z (2010) Circulating Th17 cells frequency is associated with the disease progression in HBV infected patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:750–757
Kolls JK, Linden A (2004) Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity 21:467–476
Zhao L, Tang Y, You Z et al (2011) Interleukin-17 contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis through inducing hepatic interleukin-6 expression. PLoS One 6:e18909
Du WJ, Zhen JH, Zeng ZQ et al (2013) Expression of interleukin-17 associated with disease progression and liver fibrosis with hepatitis B virus infection: IL-17 in HBV infection. Diagn Pathol 8:40
Huang Z, van Velkinburgh JC, Ni B, Wu Y (2012) Pivotal roles of the interleukin-23/T helper 17 cell axis in hepatitis B. Liver Int 32:894–901
Langrish CL, McKenzie BS, Wilson NJ, de Waal MR, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2004) IL-12 and IL-23: master regulators of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 202:96–105
Wang Q, Zhou J, Zhang B et al (2013) Hepatitis B virus induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes liver damage via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003410
Liang SC, Tan XY, Luxenberg DP et al (2006) Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med 203:2271–2279
Eyerich S, Eyerich K, Pennino D et al (2009) Th22 cells represent a distinct human T cell subset involved in epidermal immunity and remodeling. J Clin Invest 119:3573–3585
Hughes T, Becknell B, McClory S et al (2009) Stage 3 immature human natural killer cells found in secondary lymphoid tissue constitutively and selectively express the TH 17 cytokine interleukin-22. Blood 113:4008–4010
Radaeva S, Sun R, Pan HN, Hong F, Gao B (2004) Interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a protective role in T cell-mediated murine hepatitis: IL-22 is a survival factor for hepatocytes via STAT3 activation. Hepatology 39:1332–1342
Park O, Wang H, Weng H et al (2011) In vivo consequences of liver-specific interleukin-22 expression in mice: implications for human liver disease progression. Hepatology 54:252–261
Zhang Y, Cobleigh MA, Lian JQ et al (2011) A proinflammatory role for interleukin-22 in the immune response to hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology 141:1897–1906
Monteleone G, Pallone F, Macdonald TT (2009) Interleukin-21 (IL-21)-mediated pathways in T cell-mediated disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:185–191
Spolski R, Leonard WJ (2008) The Yin and Yang of interleukin-21 in allergy, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 20:295–301
Spolski R, Leonard WJ (2010) IL-21 and T follicular helper cells. Int Immunol 22:7–12
Publicover J, Goodsell A, Nishimura S et al (2011) IL-21 is pivotal in determining age-dependent effectiveness of immune responses in a mouse model of human hepatitis B. J Clin Invest 121:1154–1162
Franks I (2011) Viral hepatitis: interleukin 21 has a key role in age-dependent response to HBV. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:243
Tuncbilek S (2014) Relationship between cytokine gene polymorphisms and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 20:6226–6235
Sodsai P, Surakiatchanukul T, Kupatawintu P, Tangkitvanich P, Hirankarn N (2013) Association of cytokine and cytokine receptor gene polymorphisms with the risk of chronic hepatitis B. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 31:277–285
Lian JQ, Yang XF, Zhao RR et al (2014) Expression profiles of circulating cytokines, chemokines and immune cells in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Hepat Mon 14:e18892
Abbas Z, Siddiqui AR (2011) Management of hepatitis B in developing countries. World J Hepatol 3:292–299
Liver EAFTSOT (2012) EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 57:167–185
Arababadi MK, Pourfathollah AA, Jafarzadeh A, Hassanshahi G (2010) Serum levels of IL-10 and IL-17A in occult HBV-infected South-East Iranian patients. Hepat Mon 10:31–35
Zhang JY, Zhang Z, Lin F et al (2010) Interleukin-17-producing CD4(+) T cells increase with severity of liver damage in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 51:81–91
He D, Li M, Guo S et al (2013) Expression pattern of serum cytokines in hepatitis B virus infected patients with persistently normal alanine aminotransferase levels. J Clin Immunol 33:1240–1249
Bertolino P, McCaughan GW, Bowen DG (2002) Role of primary intrahepatic T-cell activation in the ‘liver tolerance effect’. Immunol Cell Biol 80:84–92
Dumortier J, Schonig K, Oberwinkler H et al (2005) Liver-specific expression of interferon gamma following adenoviral gene transfer controls hepatitis B virus replication in mice. Gene Ther 12:668–677
Isogawa M, Robek MD, Furuichi Y, Chisari FV (2005) Toll-like receptor signaling inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J Virol 79:7269–7272
Chokshi S, Cooksley H, Riva A et al (2014) Identification of serum cytokine profiles associated with HBeAg seroconversion following antiviral treatment interruption. Viral Immunol 27:235–244
Zhang G, Li Z, Han Q et al (2011) Altered TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma levels associated with PD1 but not TNFA polymorphisms in patients with chronic HBV infection. Infect Genet Evol 11:1624–1630
Wang B, Wang J, Zheng Y et al (2010) A study of TNF-alpha-238 and −308 polymorphisms with different outcomes of persistent hepatitis B virus infection in China. Pathology 42:674–680
Basturk B, Karasu Z, Kilic M, Ulukaya S, Boyacioglu S, Oral B (2008) Association of TNF-alpha −308 polymorphism with the outcome of hepatitis B virus infection in Turkey. Infect Genet Evol 8:20–25
Fletcher GJ, Samuel P, Christdas J et al (2011) Association of HLA and TNF polymorphisms with the outcome of HBV infection in the South Indian population. Genes Immun 12:552–558
Toe JG, Pellegrini M, Mak TW (2013) Promoting immunity during chronic infection—the therapeutic potential of common gamma-chain cytokines. Mol Immunol 56:38–47
Zeuzem S, Carreno V (2001) Interleukin-12 in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and C. Antivir Res 52:181–188
Tung NH, Quang TH, Son JH et al (2011) Inhibitory effect of ginsenosides from steamed ginseng-leaves and flowers on the LPS-stimulated IL-12 production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Arch Pharm Res 34:681–685
Gao QJ, Liu DW, Zhang SY et al (2009) Polymorphisms of some cytokines and chronic hepatitis B and C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 15:5610–5619
Dong Y, Xi H, Yu Y, Wang Q, Jiang K, Li L (2002) Effects of oxymatrine on the serum levels of T helper cell 1 and 2 cytokines and the expression of the S gene in hepatitis B virus S gene transgenic mice: a study on the anti-hepatitis B virus mechanism of oxymatrine. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:1299–1306
Gur A, Dikici B, Nas K, Bosnak M, Haspolat K, Sarac AJ (2005) Bone mineral density and cytokine levels during interferon therapy in children with chronic hepatitis B: does interferon therapy prevent from osteoporosis? BMC Gastroenterol 5:30
Kao JT, Lai HC, Tsai SM et al (2012) Rather than interleukin-27, interleukin-6 expresses positive correlation with liver severity in naive hepatitis B infection patients. Liver Int 32:928–936
Pillai MR, Collison LW, Wang X et al (2011) The plasticity of regulatory T cell function. J Immunol 187:4987–4997
Aalaei-Andabili SH, Alavian SM (2012) Regulatory T cells are the most important determinant factor of hepatitis B infection prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine 30:5595–5602
Xu D, Fu J, Jin L et al (2006) Circulating and liver resident CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells actively influence the antiviral immune response and disease progression in patients with hepatitis B. J Immunol 177:739–747
Liu F, Tong F, He Y, Liu H (2011) Detectable expression of IL-35 in CD4+ T cells from peripheral blood of chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin Immunol 139:1–5
Zhang KQ, Polga D, Salzman SA, Burmester JK (2002) Amino acids 67 and 68 of transforming growth factor-beta regulate binding to a glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol-linked membrane protein on vascular endothelial cells. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther 7:25–30
Besnard AG, Sabat R, Dumoutier L et al (2011) Dual Role of IL-22 in allergic airway inflammation and its cross-talk with IL-17A. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:1153–1163
Chen Y, Xie X, Gu L, Huang XH, Peng XM (2013) Furin mRNA expression in peripheral blood correlates with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatol Res 43:208–216
Fiorentino DF, Bond MW, Mosmann TR (1989) Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med 170:2081–2095
Ejrnaes M, Filippi CM, Martinic MM et al (2006) Resolution of a chronic viral infection after interleukin-10 receptor blockade. J Exp Med 203:2461–2472
Wang B, Zhao XP, Fan YC, Zhang JJ, Zhao J, Wang K (2013) IL-17A but not IL-22 suppresses the replication of hepatitis B virus mediated by over-expression of MxA and OAS mRNA in the HepG2.2.15 cell line. Antiviral Res 97:285–292
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B et al (2000) Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13:715–725
Xie MH, Aggarwal S, Ho WH et al (2000) Interleukin (IL)-22, a novel human cytokine that signals through the interferon receptor-related proteins CRF2-4 and IL-22R. J Biol Chem 275:31335–31339
Kotenko SV, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko OV et al (2001) Identification of the functional interleukin-22 (IL-22) receptor complex: the IL-10R2 chain (IL-10Rbeta ) is a common chain of both the IL-10 and IL-22 (IL-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor, IL-TIF) receptor complexes. J Biol Chem 276:2725–2732
Brand S, Dambacher J, Beigel F et al (2007) IL-22-mediated liver cell regeneration is abrogated by SOCS-1/3 overexpression in vitro. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G1019–G1028
Zenewicz LA, Yancopoulos GD, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Karow M, Flavell RA (2007) Interleukin-22 but not interleukin-17 provides protection to hepatocytes during acute liver inflammation. Immunity 27:647–659
Kakimi K, Lane TE, Wieland S et al (2001) Blocking chemokine responsive to gamma-2/interferon (IFN)-gamma inducible protein and monokine induced by IFN-gamma activity in vivo reduces the pathogenetic but not the antiviral potential of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 194:1755–1766
Xiang X, Gui H, King NJ et al (2012) IL-22 and non-ELR-CXC chemokine expression in chronic hepatitis B virus-infected liver. Immunol Cell Biol 90:611–619
Zeng R, Spolski R, Casas E, Zhu W, Levy DE, Leonard WJ (2007) The molecular basis of IL-21-mediated proliferation. Blood 109:4135–4142
Spolski R, Leonard WJ (2008) Interleukin-21: basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 26:57–79
Ettinger R, Kuchen S, Lipsky PE (2008) The role of IL-21 in regulating B-cell function in health and disease. Immunol Rev 223:60–86
Iannello A, Tremblay C, Routy JP, Boulassel MR, Toma E, Ahmad A (2008) Decreased levels of circulating IL-21 in HIV-infected AIDS patients: correlation with CD4+ T-cell counts. Viral Immunol 21:385–388
Hu X, Ma S, Huang X et al (2011) Interleukin-21 is upregulated in hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure and associated with severity of liver disease. J Viral Hepat 18:458–467
Kwon H, Lok AS (2011) Hepatitis B therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:275–284
Tseng TC, Kao JH, Chen DS (2014) Peginterferon alpha in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Expert Opin Biol Ther 14:995–1006
Liu YZ, Hou FQ, Ding P, Ren YY, Li SH, Wang GQ (2012) Pegylated interferon alpha enhances recovery of memory T cells in e antigen positive chronic hepatitis B patients. Virol J 9:274
Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F et al (2012) IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest 122:529–537
Xu C, Guo H, Pan XB et al (2010) Interferons accelerate decay of replication-competent nucleocapsids of hepatitis B virus. J Virol 84:9332–9340
Brunetto MR, Oliveri F, Colombatto P, Coco B, Ciccorossi P, Bonino F (2003) Treatment of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B with interferon or pegylated interferon. J Hepatol 39(Suppl 1):S164–S167
Rigopoulou EI, Suri D, Chokshi S et al (2005) Lamivudine plus interleukin-12 combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B: antiviral and immunological activity. Hepatology 42:1028–1036
Szkaradkiewicz A, Jopek A, Wysocki J (2005) Effects of IL-12 and IL-18 on HBcAg-specific cytokine production by CD4 T lymphocytes of children with chronic hepatitis B infection. Antiviral Res 66:23–27
Grimm D, Heeg M, Thimme R (2013) Hepatitis B virus: from immunobiology to immunotherapy. Clin Sci (Lond) 124:77–85
Ghany MG, Doo EC (2009) Antiviral resistance and hepatitis B therapy. Hepatology 49:S174–S184
Nebbia G, Peppa D, Maini MK (2012) Hepatitis B infection: current concepts and future challenges. QJM 105:109–113
Ahlenstiel G, Edlich B, Hogdal LJ et al (2011) Early changes in natural killer cell function indicate virologic response to interferon therapy for hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 141:1231–1239, 1239 e1231-1232
Craxi A, Di Bona D, Camma C (2003) Interferon-alpha for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 39(Suppl 1):S99–S105
Shi B, Ren G, Hu Y, Wang S, Zhang Z, Yuan Z (2012) HBsAg inhibits IFN-alpha production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TNF-alpha and IL-10 induction in monocytes. PLoS One 7:e44900
Walsh R, Locarnini S (2012) Hepatitis B precore protein: pathogenic potential and therapeutic promise. Yonsei Med J 53:875–885
Reijnders JG, Perquin MJ, Zhang N, Hansen BE, Janssen HL (2010) Nucleos(t)ide analogues only induce temporary hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in most patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 139:491–498
Buster EH, Hansen BE, Lau GK et al (2009) Factors that predict response of patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B to peginterferon-alfa. Gastroenterology 137:2002–2009
Janssen HL, van Zonneveld M, Senturk H et al (2005) Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised trial. Lancet 365:123–129
Lau GK, Piratvisuth T, Luo KX et al (2005) Peginterferon Alfa-2a, lamivudine, and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 352:2682–2695
Piccolo P, Lenci I, Demelia L et al (2009) A randomized controlled trial of pegylated interferon-alpha2a plus adefovir dipivoxil for hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Antivir Ther 14:1165–1174
Takkenberg B, Terpstra V, Zaaijer H et al (2011) Intrahepatic response markers in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon alpha-2a and adefovir. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:1527–1535
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376:1094–1108
Rutgeerts P, Vermeire S, Van Assche G (2009) Biological therapies for inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 136:1182–1197
Ostuni P, Botsios C, Punzi L, Sfriso P, Todesco S (2003) Hepatitis B reactivation in a chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and low dose methotrexate. Ann Rheum Dis 62:686–687
Chevaux JB, Nani A, Oussalah A et al (2010) Prevalence of hepatitis B and C and risk factors for nonvaccination in inflammatory bowel disease patients in Northeast France. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16:916–924
Robinson H, Walker-Bone K (2009) Anti-TNF-alpha therapy for rheumatoid arthritis among patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:448–450
Ryu HH, Lee EY, Shin K et al (2012) Hepatitis B virus reactivation in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with anti-TNFalpha agents: a retrospective analysis of 49 cases. Clin Rheumatol 31:931–936
Lee YH, Bae SC, Song GG (2013) Hepatitis B virus reactivation in HBsAg-positive patients with rheumatic diseases undergoing anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy or DMARDs. Int J Rheum Dis 16:527–531
Vassilopoulos D (2011) Should we routinely treat patients with autoimmune/rheumatic diseases and chronic hepatitis B virus infection starting biologic therapies with antiviral agents? Yes. Eur J Intern Med 22:572–575
Nosotti L, Francesconi F, Izzi S, Berardesca E, Morrone A, Bonifati C (2010) Safety of antitumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy in psoriatic patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Br J Dermatol 162:1408–1410
Arababadi MK, Pourfathollah AA, Jafarzadeh A et al (2011) Non-association of IL-12 +1188 and IFN-gamma +874 polymorphisms with cytokines serum level in occult HBV infected patients. Saudi J Gastroenterol 17:30–35
Pramoolsinsup C (2002) Management of viral hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(Suppl):S125–S145
Carreno V, Zeuzem S, Hopf U et al (2000) A phase I/II study of recombinant human interleukin-12 in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 32:317–324
Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, Fisher PB (2004) Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 22:929–979
Goddard S, Youster J, Morgan E, Adams DH (2004) Interleukin-10 secretion differentiates dendritic cells from human liver and skin. Am J Pathol 164:511–519
Tjwa ET, van Oord GW, Hegmans JP, Janssen HL, Woltman AM (2011) Viral load reduction improves activation and function of natural killer cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 54:209–218
Chou YC, Chen ML, Hu CP et al (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta1 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication primarily through transcriptional inhibition of pregenomic RNA. Hepatology 46:672–681
Tarr PE, Lin R, Mueller EA, Kovarik JM, Guillaume M, Jones TC (1996) Evaluation of tolerability and antibody response after recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rhGM-CSF) and a single dose of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccine 14:1199–1204
Martin J, Bosch O, Moraleda G, Bartolome J, Quiroga JA, Carreno V (1993) Pilot study of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 18:775–780
Wang J, Zhu Q, Zhang T, Yu H (2002) A pilot study on the combined therapy of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and hepatitis B vaccine on chronic hepatitis B virus carrier children. Chin Med J (Engl) 115:1824–1828
Qing Y, Chen M, Zhao J et al (2010) Construction of an HBV DNA vaccine by fusion of the GM-CSF gene to the HBV-S gene and examination of its immune effects in normal and HBV-transgenic mice. Vaccine 28:4301–4307
Overton ET, Sungkanuparph S, Klebert M et al (2011) GM-CSF fails to improve immune responses to booster hepatitis B vaccination in HIV-infected individuals. Open Virol J 5:109–113
Yuan Q, Li PD, Li BH et al (2009) Differential IL-4/Stat6 activities correlate with differential expression of regulatory genes SOCS-1, SHP-1, and PP2A in colon cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135:131–140
Corry DB, Kheradmand F (2002) Biology and therapeutic potential of the interleukin-4/interleukin-13 signaling pathway in asthma. Am J Respir Med 1:185–193
Fan Z, Spencer JA, Lu Y et al (2010) In vivo tracking of ‘color-coded’ effector, natural and induced regulatory T cells in the allograft response. Nat Med 16:718–722
Meyers JA, Liu AY, McTiernan A et al (2008) Serum leptin concentrations and markers of immune function in overweight or obese postmenopausal women. J Endocrinol 199:51–60
Gorski KS, Waller EL, Bjornton-Severson J et al (2006) Distinct indirect pathways govern human NK-cell activation by TLR-7 and TLR-8 agonists. Int Immunol 18:1115–1126
Wilson MT, Johansson C, Olivares-Villagomez D et al (2003) The response of natural killer T cells to glycolipid antigens is characterized by surface receptor down-modulation and expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10913–10918
Comella K, Nakamura M, Melnik K et al (2001) Effects of antibody concentration on the separation of human natural killer cells in a commercial immunomagnetic separation system. Cytometry 45:285–293
Matsuda JL, Naidenko OV, Gapin L et al (2000) Tracking the response of natural killer T cells to a glycolipid antigen using CD1d tetramers. J Exp Med 192:741–754
Wynn TA (2004) Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol 4:583–594
Meier R, Golovko D, Tavri S et al (2011) Depicting adoptive immunotherapy for prostate cancer in an animal model with magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 65:756–763
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported in part by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81171565), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY14H030001), and the Major national S&T Projects for infectious diseases (2012ZX10002002). We acknowledge Prof. M. Eric Gershwin and the reviewers for the helpful and thoughtful comments for the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
Xuefen Li, Xia Liu, Li Tian, and Yu Chen declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Liu, X., Tian, L. et al. Cytokine-Mediated Immunopathogenesis of Hepatitis B Virus Infections. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 50, 41–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-014-8465-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-014-8465-4