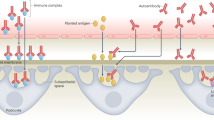
Abstract
The term “autoimmunity” refers to a pathological condition in which the immunological tolerance of self-antigens is broken through, cross-reactive T cells are activated, and autoantibodies are produced by B cells. The intricate interplay among those aberrantly activated immune cells as well as inflammatory cytokines secreted by them contributes to the development of proinflammatory cascade which eventually leads to the occurrence of autoimmune diseases (AIDs) and organ damage. Autoimmune diseases occupy a broad spectrum of human diseases with more than 70 different disorders and afflict approximately 5–8 % of the world’s population. AIDs can be categorized into organ-specific and systemic. Although the exact mechanism of AIDs remains elusive, it is generally believed that both genetic polymorphism and environmental exposure are involved in the development of AIDs. Aberrant epigenetic marks are also identified in patients with AIDs. In addition, dysregulation of innate immune system and molecular mimicry are indicated to play important roles in the initiation and maintenance of autoreactive inflammation. Based on the progress made in elucidating molecular mechanisms underlying AIDs, novel biomarkers for prediction, early diagnosis, prognosis and treatment response, and therapeutic strategies are proposed, which represents a promising future in the battle against AIDs. However, challenges remain regarding the clinical application of these potential new tools.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardenas-Roldan J, Rojas-Villarraga A, Anaya JM (2013) How do autoimmune diseases cluster in families? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 11:73
Mackay IR (2010) Travels and travails of autoimmunity: a historical journey from discovery to rediscovery. Autoimmun Rev 9:A251–A258
Tiffin N, Adeyemo A, Okpechi I (2013) A diverse array of genetic factors contribute to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8:2
Bogdanos DP, Smyk DS, Rigopoulou EI et al (2012) Twin studies in autoimmune disease: genetics, gender and environment. J Autoimmun 38:J156–J169
Lindh E, Brannstrom J, Jones P et al (2013) Autoimmunity and cystatin SA1 deficiency behind chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1. J Autoimmun 42:1–6
Miller FW, Cooper RG, Vencovsky J et al (2013) Genome-wide association study of dermatomyositis reveals genetic overlap with other autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Rheum 65:3239–3247
Orozco, G., Viatte, S., Bowes, J., et al. (2013), Novel RA susceptibility locus at 22q12 identified in an extended UK genome wide association study. Arthritis Rheum
Selmi C, Lu Q, Humble MC (2012) Heritability versus the role of the environment in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 39:249–252
Singh AK, Mahlios J, Mignot E (2013) Genetic association, seasonal infections and autoimmune basis of narcolepsy. J Autoimmun 43:26–31
Slae M, Heshin-Bekenstein M, Simckes A, Heimer G, Engelhard D, Eisenstein EM (2014) Female polysomy-X and systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43:508–512
Jabbari A, Petukhova L, Cabral RM, Clynes R, Christiano AM (2013) Genetic basis of alopecia areata: a roadmap for translational research. Dermatol Clin 31:109–117
Castiblanco J, Arcos-Burgos M, Anaya JM (2013) What is next after the genes for autoimmunity? BMC Med 11:197
Umiċeviċ Mirkov M, Cui J, Vermeulen SH et al (2013) Genome-wide association analysis of anti-TNF drug response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1375–1381
Hedrich CM, Tsokos GC (2011) Epigenetic mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Trends Mol Med 17:714–724
Hou S, Qi J, Liao D et al (2013) Copy number variations of complement component C4 are associated with Behcet’s disease but not with ankylosing spondylitis associated with acute anterior uveitis. Arthritis Rheum 65:2963–2970
Lu Q (2013) The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 41:1–5
De Santis M, Selmi C (2012) The therapeutic potential of epigenetics in autoimmune diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 42:92–101
Aringer M, Gunther C, Lee-Kirsch MA (2013) Innate immune processes in lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol 147:216–222
Pollard KM, Kono DH (2013) Requirements for innate immune pathways in environmentally induced autoimmunity. BMC Med 11:100
Kirchner M, Sonnenschein A, Schoofs S, Schmidtke P, Umlauf VN, Mannhardt-Laakmann W (2013) Surface expression and genotypes of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J 11:9
Ospelt C, Brentano F, Rengel Y et al (2008) Overexpression of toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: toll-like receptor expression in early and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3684–3692
Goh FG, Midwood KS (2012) Intrinsic danger: activation of Toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:7–23
Wahren-Herlenius M, Dorner T (2013) Immunopathogenic mechanisms of systemic autoimmune disease. Lancet 382:819–831
Ghazarian L, Simoni Y, Pingris K, Beaudoin L, Lehuen A (2013) Regulatory role of NKT cells in the prevention of type 1 diabetes. Med Sci (Paris) 29:722–728
Germolec D, Kono DH, Pfau JC, Pollard KM (2012) Animal models used to examine the role of the environment in the development of autoimmune disease: findings from an NIEHS Expert Panel Workshop. J Autoimmun 39:285–293
Miller FW, Alfredsson L, Costenbader KH et al (2012) Epidemiology of environmental exposures and human autoimmune diseases: findings from a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Expert Panel Workshop. J Autoimmun 39:259–271
Selmi C, Leung PS, Sherr DH et al (2012) Mechanisms of environmental influence on human autoimmunity: a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences expert panel workshop. J Autoimmun 39:272–284
Rigopoulou EI, Smyk DS, Matthews CE et al (2012) Epstein-barr virus as a trigger of autoimmune liver diseases. Adv Virol 2012:987471
Tugnet N, Rylance P, Roden D, Trela M, Nelson P (2013) Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) and autoimmune rheumatic disease: is there a link? Open Rheumatol J 7:13–21
Hasni SA (2012) Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24:429–434
Getts DR, Chastain EM, Terry RL, Miller SD (2013) Virus infection, antiviral immunity, and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 255:197–209
Maecker HT, Lindstrom TM, Robinson WH et al (2012) New tools for classification and monitoring of autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:317–328
Konforte D, Diamandis EP, van Venrooij WJ, Lories R, Ward MM (2012) Autoimmune diseases: early diagnosis and new treatment strategies. Clin Chem 58:1510–1514
Robledo G, Davila-Fajardo CL, Marquez A et al (2012) Association between -174 interleukin-6 gene polymorphism and biological response to rituximab in several systemic autoimmune diseases. DNA Cell Biol 31:1486–1491
Zhang Y, Zhao M, Sawalha AH, Richardson B, Lu Q (2013) Impaired DNA methylation and its mechanisms in CD4 (+) T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 41:92–99
Zhou Y, Qiu X, Luo Y et al (2011) Histone modifications and methyl-CpG-binding domain protein levels at the TNFSF7 (CD70) promoter in SLE CD4+ T cells. Lupus 20:1365–1371
Carlsen AL, Schetter AJ, Nielsen CT et al (2013) Circulating microRNA expression profiles associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 65:1324–1334
Shi J, van de Stadt LA, Levarht EW et al (2013) Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies are present in arthralgia patients and predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 65:911–915
Auger I, Charpin C, Balandraud N, Martin M, Roudier J (2012) Autoantibodies to PAD4 and BRAF in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 11:801–803
Quintana FJ, Yeste A, Weiner HL, Covacu R (2012) Lipids and lipid-reactive antibodies as biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 248:53–57
Sciascia S, Ceberio L, Garcia-Fernandez C, Roccatello D, Karim Y, Cuadrado MJ (2012) Systemic lupus erythematosus and infections: clinical importance of conventional and upcoming biomarkers. Autoimmun Rev 12:157–163
Ortea I, Roschitzki B, Ovalles JG et al (2012) Discovery of serum proteomic biomarkers for prediction of response to infliximab (a monoclonal anti-TNF antibody) treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: an exploratory analysis. J Proteomics 77:372–382
Szodoray P, Nakken B, Barath S et al (2013) Altered Th17 cells and Th17/regulatory T-cell ratios indicate the subsequent conversion from undifferentiated connective tissue disease to definitive systemic autoimmune disorders. Hum Immunol 74:1510–1518
Kleczynska W, Jakiela B, Plutecka H, Milewski M, Sanak M, Musial J (2011) Imbalance between Th17 and regulatory T-cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 49:646–653
Jamshidian A, Shaygannejad V, Pourazar A, Zarkesh-Esfahani SH, Gharagozloo M (2013) Biased Treg/Th17 balance away from regulatory toward inflammatory phenotype in relapsed multiple sclerosis and its correlation with severity of symptoms. J Neuroimmunol 262:106–112
Hajas A, Barath S, Szodoray P et al (2013) Derailed B cell homeostasis in patients with mixed connective tissue disease. Hum Immunol 74:833–841
Selmi C (2013) Autoimmunity in 2012. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 45:290–301
Graber JJ, Dhib-Jalbut S (2011) Biomarkers of disease activity in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 305:1–10
Lateef A, Petri M (2012) Unmet medical needs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 14(Suppl 4):S4
Ben-Ami Shor D, Harel M, Eliakim R, Shoenfeld Y (2013) The hygiene theory harnessing helminths and their ova to treat autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 45:211–216
Leung PS, Dhirapong A, Wu PY, Tao MH (2010) Gene therapy in autoimmune diseases: challenges and opportunities. Autoimmun Rev 9:170–174
Reilly CM, Thomas M, Gogal R Jr et al (2008) The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A upregulates regulatory T cells and modulates autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J Autoimmun 31:123–130
Tanaka H, Shimizu N, Tougasaki E et al (2013) Successful treatment by azacitidine therapy of intestinal Behcet’s disease associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Hematol 97:520–524
Brooks WH, Le Dantec C, Pers JO, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y (2010) Epigenetics and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 34:J207–J219
Lichtman EI, Helfgott SM, Kriegel MA (2012) Emerging therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus—focus on targeting interferon-alpha. Clin Immunol 143:210–221
Guiducci C, Gong M, Xu Z et al (2010) TLR recognition of self nucleic acids hampers glucocorticoid activity in lupus. Nature 465:937–941
Kim DH, Lee JC, Kim S et al (2011) Inhibition of autoimmune diabetes by TLR2 tolerance. J Immunol 187:5211–5220
Radovits BJ, Kievit W, Laan RF (2009) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha antagonists in the management of rheumatoid arthritis in the elderly: a review of their efficacy and safety. Drugs Aging 26:647–664
Yao X, Huang J, Zhong H et al (2014) Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol Ther 141:125–139
Long SA, Buckner JH, Greenbaum CJ (2013) IL-2 therapy in type 1 diabetes: “trials” and tribulations. Clin Immunol 149:324–331
Harvey PR, Gordon C (2013) B-cell targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus: successes and challenges. BioDrugs 27:85–95
Marek-Trzonkowska N, Mysliwiec M, Dobyszuk A et al (2012) Administration of CD4 + CD25highCD127- regulatory T cells preserves beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes in children. Diabetes Care 35:1817–1820
Scalapino KJ, Daikh DI (2009) Suppression of glomerulonephritis in NZB/NZW lupus prone mice by adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells. PLoS One 4:e6031
Liang J, Zhang H, Hua B et al (2010) Allogenic mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot clinical study. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1423–1429
Sun L, Wang D, Liang J et al (2010) Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 62:2467–2475
Wang D, Akiyama K, Zhang H et al (2012) Double allogenic mesenchymal stem cells transplantations could not enhance therapeutic effect compared with single transplantation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:273291
Zhao Y, Jiang Z, Zhao T et al (2012) Reversal of type 1 diabetes via islet beta cell regeneration following immune modulation by cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells. BMC Med 10:3
Van Brussel I, Lee WP, Rombouts M et al (2014) Tolerogenic dendritic cell vaccines to treat autoimmune diseases: can the unattainable dream turn into reality? Autoimmun Rev 13:138–150
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81220108017, No. 81373205, and No. 81270024), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (Grant No. 20120162130003), and the Programs of Science-Technology Commission of Hunan Province (2013FJ4202, 2011TP4019-7) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the National Key Clinical Specialty Construction Project of National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Q. Unmet Needs in Autoimmunity and Potential New Tools. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 47, 111–118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-014-8414-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-014-8414-2