Abstract
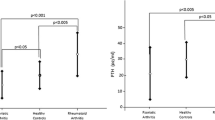
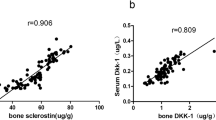
Our aim was to compare bone gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and primary osteoporosis (OP) patients. Secondary aims were to determine the association of gene expression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway with inflammatory cytokines in the bone microenvironment and to assess the serum levels of Wnt/β-catenin proteins in both groups. RA patients referred for hip replacement surgery were recruited. Primary OP patients were used as controls. Gene expression of Wnt pathway mediators, matrix proteins, and pro-inflammatory cytokines were analyzed in bone samples. Bone turnover markers, inflammatory cytokines, and Wnt mediators were measured in serum. Twenty-two patients were included: 10 with RA and 12 with primary OP. The expressions of Wnt10b (p = 0.034), its co-receptor LRP6 (p = 0.041), and its negative regulator DKK1 (p = 0.008) were upregulated in RA bone. IL17 gene expression in bone was upregulated in RA patients (p = 0.031) and correlated positively with Wnt10b (r = 0.810, p = 0.015), DKK2 (r = 0.800, p = 0.010), and RANKL/OPG ratio (r = 0.762, p = 0.028). DKK2 (p = 0.04) was significantly decreased in RA serum compared with primary OP. In conclusion, bone fragility in RA patients is induced by an unbalanced bone microenvironment and is associated with a specific gene expression pattern, namely, the upregulation of IL17 and DKK1, suggesting that the modulation of these two pathways might prevent RA systemic bone loss.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamanos Y, Drosos AA (2005) Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 4:130–136
Orstavik RE, Haugeberg G, Mowinckel P, Hoiseth A, Uhlig T, Falch JA et al (2004) Vertebral deformities in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with population-based controls. Arch Intern Med 164:420–425
Husby G, Williams RC Jr (1988) Synovial localization of tumor necrosis factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun 1:363–371
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Chantry D, Haworth C, Turner M, Abney E et al (1990) Cytokine production in the rheumatoid joint: implications for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 49(Suppl 1):480–486
Nouri AM, Panayi GS, Goodman SM (1984) Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol 55:295–302
Symons JA, McDowell TL, di Giovine FS, Wood NC, Capper SJ, Duff GW (1989) Interleukin 1 in rheumatoid arthritis: potentiation of immune responses within the joint. Lymphokine Res 8:365–372
Houssiau FA, Devogelaer JP, Van Damme J, de Deuxchaisnes CN, Van Snick J (1988) Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum 31:784–788
Hirano T, Matsuda T, Turner M, Miyasaka N, Buchan G, Tang B et al (1988) Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 18:1797–1801
Hirota K, Hashimoto M, Yoshitomi H, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Yamaguchi T et al (2007) T cell self-reactivity forms a cytokine milieu for spontaneous development of IL-17+ Th cells that cause autoimmune arthritis. J Exp Med 204:41–47
Sato K, Suematsu A, Okamoto K, Yamaguchi A, Morishita Y, Kadono Y et al (2006) Th17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. J Exp Med 203:2673–2682
Lubberts E, van den Bersselaar L, Oppers-Walgreen B, Schwarzenberger P, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Kolls JK et al (2003) IL-17 promotes bone erosion in murine collagen-induced arthritis through loss of the receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin balance. J Immunol 170:2655–2662
Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K, Zwerina J, Ominsky MS, Dwyer D et al (2007) Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling. Nat Med 13:156–163
Koay MA, Brown MA (2005) Genetic disorders of the LRP5-Wnt signalling pathway affecting the skeleton. Trends Mol Med 11:129–137
Cui Y, Niziolek PJ, MacDonald BT, Zylstra CR, Alenina N, Robinson DR et al (2011) Lrp5 functions in bone to regulate bone mass. Nat Med 17:684–691
Krishnan V, Bryant HU, Macdougald OA (2006) Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Invest 116:1202–1209
Cadigan KM, Liu YI (2006) Wnt signaling: complexity at the surface. J Cell Sci 119:395–402
Westendorf JJ, Kahler RA, Schroeder TM (2004) Wnt signaling in osteoblasts and bone diseases. Gene 341:19–39
Zhang C, Cho K, Huang Y, Lyons JP, Zhou X, Sinha K et al (2008) Inhibition of Wnt signaling by the osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osterix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6936–6941
Zhang C (2010) Transcriptional regulation of bone formation by the osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osx. J Orthop Surg Res 5:37
Krause C, Korchynskyi O, de Rooij K, Weidauer SE, de Gorter DJ, van Bezooijen RL et al (2010) Distinct modes of inhibition by sclerostin on bone morphogenetic protein and Wnt signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 285:41614–41626
Li X, Ominsky MS, Niu QT, Sun N, Daugherty B, D’Agostin D et al (2008) Targeted deletion of the sclerostin gene in mice results in increased bone formation and bone strength. J Bone Miner Res 23:860–869
Winkler DG, Sutherland MK, Geoghegan JC, Yu C, Hayes T, Skonier JE et al (2003) Osteocyte control of bone formation via sclerostin, a novel BMP antagonist. EMBO J 22:6267–6276
Abdulghani S, Caetano-Lopes J, Canhao H, Fonseca JE (2009) Biomechanical effects of inflammatory diseases on bone-rheumatoid arthritis as a paradigm. Autoimmun Rev 8:668–671
Caetano-Lopes J, Nery AM, Henriques R, Canhão H, Duarte J, Amaral PM et al (2009) Chronic arthritis induces quantitative and qualitative bone disturbances leading to compromised biomechanical properties. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27:475–482
Caetano-Lopes J, Nery AM, Canhao H, Duarte J, Cascao R, Rodrigues A et al (2010) Chronic arthritis leads to disturbances in the bone collagen network. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R9
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Marques A, Mota A, Canhão H, Romeu JC, Machado P, Ruano A et al. (2013) A FRAX model for the estimation of osteoporotic fracture probability in Portugal. Acta Reumatol Port (in press)
Aleixo I, Vale AC, Lúcio M, Amaral PM, Rosa LG, Caetano-Lopes J et al (2013) A method for the evaluation of femoral head trabecular bone compressive properties. Advanced Materials Forum VI. Mater Sci Forum 730–732:3–8
Egyhazi S, Bjohle J, Skoog L, Huang F, Borg AL, Frostvik Stolt M et al (2004) Proteinase K added to the extraction procedure markedly increases RNA yield from primary breast tumors for use in microarray studies. Clin Chem 50:975–976
Caetano-Lopes J, Lopes A, Rodrigues A, Fernandes D, Perpetuo IP, Monjardino T et al (2011) Upregulation of inflammatory genes and downregulation of sclerostin gene expression are key elements in the early phase of fragility fracture healing. PLoS One 6:e16947
Wong ML, Medrano JF (2005) Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. Biotechniques 39:75–85
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM (1996) Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res 6:986–994
Li Y, Lu W, King TD, Liu CC, Bijur GN, Bu G (2010) Dkk1 stabilizes Wnt co-receptor LRP6: implication for Wnt ligand-induced LRP6 down-regulation. PLoS One 5:e11014
Li X, Liu P, Liu W, Maye P, Zhang J, Zhang Y et al (2005) Dkk2 has a role in terminal osteoblast differentiation and mineralized matrix formation. Nat Genet 37:945–952
Lee YS, Lee KA, Yoon HB, Yoo SA, Park YW, Chung Y et al (2012) The Wnt inhibitor secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 (sFRP1) promotes human Th17 differentiation. Eur J Immunol 42:2564–2573
Noh M (2012) Interleukin-17A increases leptin production in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol 83:661–670
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S et al (1999) IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 103:1345–1352
Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, Suva LJ, Lane TF, Hankenson KD et al (2005) Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:3324–3329
Baek WY, de Crombrugghe B, Kim JE (2010) Postnatally induced inactivation of Osterix in osteoblasts results in the reduction of bone formation and maintenance. Bone 46:920–928
Selmi C, Lu Q, Humble MC (2012) Heritability versus the role of the environment in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 39:249–252
Ngalamika O, Zhang Y, Yin H, Zhao M, Gershwin ME, Lu Q (2012) Epigenetics, autoimmunity and hematologic malignancies: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 39:451–465
Miller FW, Alfredsson L, Costenbader KH, Kamen DL, Nelson LM, Norris JM et al (2012) Epidemiology of environmental exposures and human autoimmune diseases: findings from a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Expert Panel Workshop. J Autoimmun 39:259–271
Miller FW, Pollard KM, Parks CG, Germolec DR, Leung PS, Selmi C et al (2012) Criteria for environmentally associated autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 39:253–258
Selmi C, Leung PS, Sherr DH, Diaz M, Nyland JF, Monestier M et al (2012) Mechanisms of environmental influence on human autoimmunity: a national institute of environmental health sciences expert panel workshop. J Autoimmun 39:272–284
Germolec D, Kono DH, Pfau JC, Pollard KM (2012) Animal models used to examine the role of the environment in the development of autoimmune disease: findings from an NIEHS Expert Panel Workshop. J Autoimmun 39:285–293
Disclosure
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Joana Caetano-Lopes, Ana Rodrigues, Helena Canhão, and João E Fonseca contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caetano-Lopes, J., Rodrigues, A., Lopes, A. et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Bone Fragility Is Associated With Upregulation of IL17 and DKK1 Gene Expression. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 47, 38–45 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8366-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8366-y