Abstract
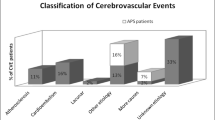
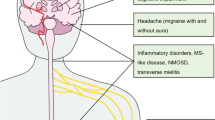
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is the most frequent cause of venous and arterial thrombotic events in young patients. The brain arterial tree is primarily affected, but coronary ischemic manifestations are also relatively frequent. Coronary involvement was suggested to be closely related to the accelerated atherosclerosis linked to the underlying disease in APS associated to systemic autoimmune diseases, in particular, systemic lupus erythematosus. However, arterial ischemic events can occur in primary APS—with no other systemic disorders—even in the absence of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and overt atherosclerosis. From a biological point of view, this finding speaks in favor for a pro-coagulant activity of anti-phospholipid antibodies rather than for their role in atherosclerotic plaque formation. On the other hand, the clinical challenge is to avoid the risk to misdiagnose young patients with potentially life-threatening symptoms, such as myocardial infarction (MI). In fact, the occurrence of nonspecific symptoms related to coronary ischemic events is frequently misdiagnosed because of its rarity in young patients. This issue is well illuminated by two cases of MI in young patients reported in the manuscript together with a systematic review of the associations and implications of coronary ischemic events in APS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T et al (2006) International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost 4:295–306
Hughes GR (2008) Hughes syndrome (the antiphospholipid syndrome): ten clinical lessons. Autoimmun Rev 7:262–266
Cervera R, Piette JC, Font J et al (2002) Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1000 patients. Arthritis Rheum 46:1019–1027
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Shoenfeld Y et al (2009) Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 5-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1428–1432
Font J, Cervera R (2006) Cardiac manifestations in antiphospholipid syndrome. In: Khamashta MA (ed) Hughes syndrome, 2nd edn. Springer, London, pp 41–53
Adler Y, Kinkelstein Y, Zanderman-Goddard G et al (1995) The presence of antiphospholipid antibodies in acute myocardial infarction. Lupus 4:309–313
Boekholdt SM, Kramer MHH (2007) Arterial thrombosis and the role of thrombophilia. Semin Thromb Hemost 33:588–596
Vaarala O, Manttari M, Manninen V et al (1995) Anti-cardiolipin antibodies and risk of myocardial infarction in a prospective cohort of middle-aged men. Circulation 91:23–27
Brey RL, Abbott RD, Curb JD et al (2001) ß2-Glycoprotein 1-dependent anticardiolipin antibodies and risk of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction. Honol Heart Program Stroke 32:1701–1706
Soltész P, Szekanecz Z, Kiss E, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Cardiac manifestations in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun Rev 6:379–386
Vaarala O (1998) Antiphospholipid antibodies and myocardial infarction. Lupus 7:132–134
Hamsten A, Norberg R, Bjorkholm M et al (1986) Antibodies to cardiolipin in young survivors of myocardial infarction: an association with recurrent cardiovascular events. Lancet 1:113–116
Jalowiec DA, Hill JA (1989) Myocardial infarction in the young and in women. Cardiovasc Clin 20:197–206
Zimmerman FH, Cameron A, Fisher LD, Ng G (1995) Myocardial infarction in young adults: angiographic characterization, risk factors and prognosis (Coronary Artery Surgery Study Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol 26:654–661
Chen L, Chester M, Kaski JC (1995) Clinical factors and angiographic features associated with premature coronary artery disease. Chest 108:364–369
Kanitz MG, Giovannucci SJ, Jones JS, Mott M (1996) Myocardial infarction in young adults: risk factors and clinical features. J Emerg Med 14:139–145
Stamler J, Stamler R, Neaton JD et al (1999) Low risk factor profile and long-term cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular mortality and life expectancy: findings for 5 large cohorts of young adult and middle-aged men and women. JAMA 282:2012–2018
Choudhury L, Marsh JD (1999) Myocardial infarction in young patients. Am J Med 107:254–261
Osula S, Bell GM, Hornung RS (2002) Acute myocardial infarction in young adults: causes and management. Postgrad Med J 78:27–30
Meroni PL, Peyvandi F, Foco L, on behalf of the Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology Italian Study Group et al (2007) Anti-beta 2 glycoprotein I antibodies and the risk of myocardial infarction in young premenopausal women. J Thromb Haemost 5:2421–2428
Urbanus RT, Siegerink B, Roest M, Rosendaal FR, de Groot PG, Algra A (2009) Antiphospholipid antibodies and risk of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke in young women in the RATIO study: a case–control study. Lancet Neurol 8:998–1005
Veres K, Lakos G, Kerényi A et al (2004) Antiphospholipid antibodies in acute coronary syndrome. Lupus 13:423–427
Sweiss NJ, Bo R, Kapadia R et al (2010) IgA Anti-b2-glycoprotein I autoantibodies are associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 5:e12280
Espinosa G, Cervera R (2009) Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Opin Pulm Med 15:413–417
Sangle SR, D’Cruz DP (2008) Syndrome X (angina pectoris with normal coronary arteries) and myocardial infarction in patients with antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Lupus 17:83–85
Saponjski J, Stojanovich L, Djokovic A, Petkovic M, Mrda D (2011) Systemic vascular diseases in the antiphospholipid syndrome. What is the best diagnostic choice? Autoimmun Rev 10(4):235–237
Giannakopoulos B, Passam F, Rahgozar S, Krilis SA (2007) Current concepts on the pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 109:422–430
Pierangeli SS, Chen PP, Raschi E et al (2008) Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome: pathogenic mechanisms. Semin Thromb Hemost 34:236–250
Shoenfeld Y, Blank M, Cervera R, Font J, Raschi E, Meroni PL (2006) Infectious origin of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 65:2–6
Asherson RA, Cervera R (2003) Unusual manifestations of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 25:61–78
Amigo MC (2007) The heart and APS. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 32:178–183
Zinger H, Sherer Y, Shoenfeld Y (2009) Atherosclerosis in autoimmune rheumatic diseases—mechanisms and clinical findings. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 37:20–28
Bilora F, Boccioletti V, Girolami B et al (2002) Are antiphospholipid antibodies an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis? Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 8:103–113
Medina G, Casaos D, Jara LJ et al (2003) Increased carotid artery intima-media thickness may be associated with stroke in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 62:607–610
Mukherjee D, Hsu A, Moliterno DJ, Lincoff AM, Goormastic M, Topol EJ (2003) Risk factors for premature coronary artery disease and determinants of adverse outcomes after revascularization in patients < or = 40 years old. Am J Cardiol 92:1465–1467
Ames PR, Margarita A, Sokoll KB, Weston M, Brancaccio V (2005) Premature atherosclerosis in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: preliminary data. Ann Rheum Dis 64:315–317
Jiménez S, García-Criado MA, Tàssies D et al (2005) Preclinical vascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus and primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology 44:756–761
Belizna CC, Richard V, Thuillez C, Levesque H, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Insights into atherosclerosis therapy in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun Rev 7:46–51
Margarita A, Batuca J, Scenna G et al (2007) Subclinical atherosclerosis in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann NY Acad Sci 108:475–480
Der H, Kerekes G, Veres K et al (2007) Impaired endothelial function and increased carotid intima-media thickness in association with elevated von Willebrand antigen level in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 16:497–503
Bassi N, Ghirardello A, Iaccarino L et al (2007) OxLDL/beta2GPI-anti-oxLDL/beta2GPI complex and atherosclerosis in SLE patients. Autoimmun Rev 7:52–58
Belizna CC, Richard V, Primard E et al (2008) Early atheroma in primary and secondary antiphospholipid syndrome: an intrinsic finding. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37:373–380
Ames PR, Margarita A, Alves JD (2009) Antiphospholipid antibodies and atherosclerosis: insights from systemic lupus erythematosus and primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 37:29–35
Cugno M, Borghi MO, Lonati LM et al (2010) Patients with antiphospholipid syndrome display endothelial perturbation. J Autoimmun 34:105–110
Asanuma Y, Oeser A, Shintani AK et al (2003) Premature coronary-artery atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Eng J Med 349:2407–2415
Roman MJ, Shanker BA, Davis A et al (2003) Prevalence and correlates of accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349:2399–2406
Ohlenschlaeger T, Garred P, Madsen HO, Jacobsen S (2004) Mannose binding lectin variant alleles and the risk of arterial thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 351:260–267
Petri M (2004) The lupus anticoagulant is a risk factor for myocardial infarction (but not atherosclerosis): Hopkins Lupus Cohort. Thromb Res 114:593–595
Farzaneh-Far A, Roman MJ, Lockshin MD et al (2006) Relationship of antiphospholipid antibodies to cardiovascular manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:3918–3925
Hollan I, Mikkelsen K, Førre OT et al (2011) Antiphospholipid antibodies in rheumatic and non-rheumatic patients with coronary artery disease. First International Congress on Controversies in Rheumatology and Autoimmunity, Florence 10–12 March 2011, Abstract
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Hunt BJ, Khamashta MA (2007) A systematic review of secondary thromboprophylaxis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 57:1487–1495
Ho YL, Chen MF, Wu CC et al (1996) Successful treatment of acute myocardial infarction by thrombolytic therapy in a patient with primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Cardiology 87:354–357
Takeuchi S, Obayashi T, Toyama J (1998) Primary antiphospholipid syndrome with acute myocardial infarction recanalised by PTCA. Heart 79:96–98
Morgan-Hughes G (2002) Acute myocardial infarction in young adults. Postgrad Med J 78:381
Davies JOJ, Hunt BJ (2007) Myocardial infarction in young patients without coronary atherosclerosis: assume primary antiphospholipid syndrome until proved otherwise. Int J Clin Pract 61:379–384
Tuthill JI, Khamashta MA (2009) Management of antiphospholipid syndrome. J Autoimmun 33:92–98
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA (2007) The treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome: a harmonic contrast. Best Pract Res Clin Rheum 21:1079–1092
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gualtierotti, R., Biggioggero, M. & Meroni, P.L. Cutting-Edge Issues in Coronary Disease and the Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 44, 51–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-011-8268-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-011-8268-9