Abstract
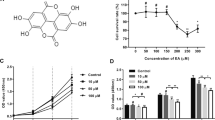
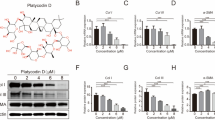
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of resveratrol (Res) treatment on pathological scar fibroblasts and the changes in TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway. For this purpose, cultured pathological scar fibroblasts were treated with various concentrations of Res (10, 50, and, 100 µmol/l), and the morphological changes in target cells were studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The cellular proliferation was assessed by MTT assay; the mRNA and protein expressions of TGF-β1 and Smad-2,3,4,7 were determined by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunofluorescence assay, respectively. We found that Res-treated fibroblasts exhibited the typical apoptotic morphological changes. As shown by MTT assay, the OD values of Res-treated fibroblasts, as a measure of cell growth, were significantly lower than those of controls (P < 0.05). In addition, as compared to controls, TGF-β1 and Smad-2,3,4 mRNA/protein expression decreased but those of Smad7 increased in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.05). It was, therefore, concluded that Res treatment inhibited the pathological scar fibroblast proliferation and induced cell apoptosis through the mechanism involving downregulation of TGF-β1, Smad-2,3,4, and upregulation of Smad7.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Z. F., Zhu, F., Xiao, L., Wang, M., Tian, R., Shi, C. J., et al. (2011). Side population cells in the human gallbladder cancer cell line GBC-SD are regulated by TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2011(31), 749–755.
Zhao, K. S. (2012). Biological features and effects of resveratrol. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology, 2012(28), 1709–1711.
Ma, S. T., Yang, D. C., Tang, B., Li, D., Li, G., & Yang, Y. J. (2012). Resveratrol resists alcoholic myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting the matrix metalloproteinases. Chinese Journal of Arteriosclerosis, 2012(20), 21–24.
Vieira de Almeida, L. M., Pineiro, C. C., Brolese, G., Leal, R. B., Gottfried, C., & Goncalves, C. A. (2008). Protective effects of resveratrol on hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity in primary cortical astrocyte culture. Neurochemical Research, 2008(33), 8–15.
Ding, J. C., Zhai, X. X., Chen, X. H., Li, J. G., & Zhang, (2008). Effects of Wubeizi ointment solution on the proliferation of keloid-derived fibroblasts. Journal Hebei Medical University, 2008(29), 829–833.
Wang, K., & Liu, G. (2012). Advances in the treatment of keloids. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2012(11), 202–204.
Jiao, H. Q., Wang, R., Sun, H. M., Liu, Y., Guo, M., Su, H. X., et al. (2009). Effect of resveratrol on the growth of human skin cancer cell line A431 and its underlying mechanism. Journal of Capital Medical University, 2009(30), 212–217.
Suzuki, H., Yagi, K., Kondo, M., Miyazono, K., & Miyazawa, K. (2008). C-Ski inhibits the TGF-beta signaling pathway through stabilization of the inactive Smad complexes on Smad binding elements. Oncogene, 2008(23), 5068–5076.
Grady, W. M. (2008). Transforming growth factor-beta, Smads, and cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 2008(11), 3191–3197.
Sun, H. J., Meng, X. Y., & Hu, C. T. (2012). MicroRNA-200c inhibits cell proliferation and collagen synthesis in human keloid fibroblasts via TGF-β1/smad pathway. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 2012(21), 1539–1542.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grant from the Scientific Research Projects of Xuzhou City, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Xx., Ding, Jc. & Tang, Zm. Resveratrol Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Pathological Scar Fibroblasts Through the Mechanism Involving TGF-β1/Smads Signaling Pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys 71, 1267–1272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0317-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0317-6