Abstract
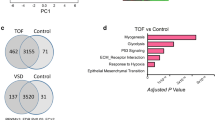
Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) is a cyanotic congenital heart disease with prominent right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) associated with impaired myocardial oxygen and nutrient supply. Consequently, the right ventricle may manifest in altered molecular phenotype with a number of adaptive and inherited gene profiles which are largely unknown. The aim of the present study was to investigate the myocardial differential gene expression profile and to assess myocardial vascularisation in patients with ToF. DNA microarray analysis on right ventricular biopsies from ToF-patients operated for primary corrective surgery (referred as ToF-1; n = 12, mean age 0.5 year) and age matched controls (n = 6) was validated by Northern hybridisation and RT-PCR. Employing immunohistochemistry and video image analysis expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), vascular density (by α-SMA and CD31 staining) and myocyte cross sectional area (Gomori’s reticuline staining) were assessed in ToF-1 and adult patients (referred as ToF-2, n = 12, mean age 30 years) who underwent surgery for pulmonary regurgitation and compared the data with respective age matched controls (n = 6/12). DNA microarray analysis revealed altered expression pattern for 236 genes including enhanced (1.5–2.2-fold) expression of angiogenic factors and their receptors including; VEGF, flt-1, flk-1 angiopoietin-2, FGF-2, FGF-R1, PDGF-A, whereas, flt-4, Tie, TGF-β, TGF-β3R showed decreased (1.6–3.4-fold) expression in ToF-patients. Northern blot analysis verified the expression patterns of VEGF and flk-1 in both ToF-1 and ToF-2 patients. VEGF staining in cardiomyocytes was increased in ToF-1 (1.5-fold, p < 0.05) as compared to ToF-2. Video image analysis revealed enhanced vascular density (p < 0.01) with enlarged myocyte cross sectional area (p < 0.01), but vascular wall thickness remained unchanged in ToF-1 patients as compared to age matched controls. Our data suggest that RVH is associated with profound changes in gene profile for a number of genes, where VEGF/VEGF-R system contributes to enhance, but stunted myocardial angiogenesis in patients with ToF.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peters, T. H. F., Klompe, L., Bogers, A. J. J. C., & Sharma, H. S. (2002). Molecular phenotype of the developing heart with a congenital anomaly. In B. Ostadal, M. Nagano, & N. S. Dhalla (Eds.), Cardiac development (pp. 197–212). Norwell, MA: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Monaco, M., & Williams, I. (2012). Tetralogy of Fallot: Fetal diagnosis to surgical correction. Minerva Pediatrica, 64(5), 461–470.
Peters, T. H. F., Sharma, H. S., Yilmaz, E., & Bogers, A. J. J. C. (1999). Quantitative analysis of collagens and fibronectin expression in human right ventricular hypertrophy. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 874, 278–285.
Zhang, H. S., Wu, Q. Y., Xu, M., Zhou, Y. X., & Shui, C. X. (2012). Mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathways play an important role in right ventricular hypertrophy of tetralogy of Fallot. Chinese Medical Journal (English), 25(13), 2243–2249.
Putman, L. M., van Gameren, M., Meijboom, F. J., de Jong, P. L., Roos-Hesselink, J. W., Witsenburg, M., et al. (2009). Seventeen years of adult congenital heart surgery: a single centre experience. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, 36(1), 96–104.
van de Woestijne, P. C., Mokhles, M. M., de Jong, P. L., Witsenburg, M., Takkenberg, J. J., & Bogers, A. J. (2011). Right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction with an allograft conduit in patients after tetralogy of Fallot correction: Long-term follow-up. Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 92(1), 161–166.
van de Woestijne, P. C., Klompe, L., de Jong, P. L., Peters, T. H. F., Kappetein, A. P., Sharma, H. S., et al. (2004). Right ventricular fibrosis in different forms of pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect. Experimental & Clinical Cardiology, 9(3), 187–192.
Meijboom, F. J., Roos-Hesselink, J. W., McGhie, J. S., Spitaels, S. E., van Domburg, R. T., Utens, L. M., et al. (2008). Consequences of a selective approach toward pulmonary valve replacement in adult patients with tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary regurgitation. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 135(1), 50–55.
Boluyt, M. O., O’Neill, L., Meredith, A. L., Bing, O. H., Brooks, W. W., Conrad, C. H., et al. (1994). Alterations in cardiac gene expression during the transition from stable hypertrophy to heart failure. Marked upregulation of genes encoding extracellular matrix components. Circulation Research, 75, 23–32.
Distefano, G., & Sciacca, P. (2012). Molecular pathogenesis of myocardial remodeling and new potential therapeutic targets in chronic heart failure. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 38, 41.
Carmeliet, P. (2005). Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature, 438(7070), 932–936.
Folkman, J. (1998). Angiogenic therapy of the human heart. Circulation, 97(7), 628–629.
Waltenberger, J., Mayr, U., Pentz, S., & Hombach, V. (1996). Functional upregulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor KDR by hypoxia. Circulation, 94, 1647–1654.
Deindl, E., & Schaper, W. (2005). The art of arteriogenesis. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 43(1), 1–15.
Riley, P. R., & Smart, N. (2011). Vascularizing the heart. Cardiovascular Research, 91, 260–268.
Shweiki, D., Itin, A., Soffer, D., & Keshet, E. (1992). Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature, 359, 843–845.
Pugh, C. W., & Ratcliffe, P. J. (2003). Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nature Medicine, 9(6), 677–684.
Yancopoulos, G. D., Davis, S., Gale, N. W., Rudge, J. S., Wiegand, S. J., & Holash, J. (2000). Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature, 407, 242–248.
Tomanek, R. J., Christensen, L. P., Simons, M., Murakami, M., Zheng, W., & Schatteman, G. C. (2010). Embryonic coronary vasculogenesis and angiogenesis are regulated by interactions between multiple FGFs and VEGF and are influenced by mesenchymal stem cells. Developmental Dynamics, 239(12), 3182–3191.
Tomanek, R. J., Sandra, A., Zheng, W., Brock, T., Bjercke, R. J., & Holifield, J. S. (2001). Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor differentially modulate early postnatal coronary angiogenesis. Circulation Research, 88(11), 1135–1141.
Jason, A., Clayton, J. A., Chalothorn, D., & Faber, J. E. (2008). Vascular endothelial growth factor-A specifies formation of native collaterals and regulates collateral growth in ischemia. Circulation Research, 103, 1027–1036.
Alagappan, V. K. T., McKay, S., Willems-Widyastuti, A., Garrelds, I. M., Bogers, A. J. J. C., Hoogsteden, H. C., et al. (2005). Pro-inflammatory cytokines up-regulate mRNA expression and secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor in cultured human airway smooth muscle cells. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 43(1), 119–129.
Sharma, H. S., Tang, Z. H., Gho, B. C. H., & Verdouw, P. D. (1995). Nucleotide sequence and expression of the porcine vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1260, 235–238.
Tan, F. L., Moravec, C. S., Li, J., Apperson-Hansen, C., McCarthy, P. M., Young, J. B., et al. (2002). The gene expression fingerprint of human heart failure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99, 11387–11392.
Kaynak, B., von Heydebreck, A., Mebus, S., Seelow, D., Hennig, S., Vogel, J., et al. (2003). Genome-wide array analysis of normal and malformed human hearts. Circulation, 107(19), 2467–2474.
Pike-Overzet, K., de Ridder, D., Schonewille, T., & Staal, F. J. (2009). DNA microarray studies of hematopoietic subpopulations. Methods in Molecular Biology, 506, 403–421.
Sharma, H. S., Peters, T. H. F., Moorhouse, M. J., van der Spek, P. J., & Bogers, A. J. J. C. (2006). DNA microarray analysis for human congenital heart disease. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 44, 1–10.
Bancroff, J. D., Cook, H. C., & Turner, B. (1994). Manual of histological techniques and their diagnostic application. London: Churchill Livingstone.
Kranenburg, A. R., de Boer, W. I., Alagappan, V. K. T., Sterk, P. J., & Sharma, H. S. (2005). Enhanced bronchial expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and receptors (flk-1 and flt-1) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax, 60, 106–113.
Peters, T. H. F., Sharma, H. S., & Bogers, A. J. J. C. (2003). Computerized image analysis in the quantitative assessment of interstitial fibrosis late after correction of tetralogy of Fallot. Cardiovascular Engineering, 8, 114–120.
Shehata, S. M. K., Tibboel, D., Sharma, H. S., & Mooi, W. J. (1999). Impaired structural remodeling of pulmonary arteries in newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: A histological study on 29 patients. Journal of Pathology, 189, 112–118.
Kranenburg, A. R., de Boer, W. I., van Krieken, J. H. J. M., Mooi, W. J., Walters, J. E., Saxena, P. R., et al. (2002). Enhanced expression of fibroblast growth factor-1 and receptor FGFR-1 during vascular remodeling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 27, 517–525.
Murray, P. A., & Vatner, S. F. (1981). Reduction of maximal coronary vasodilator capacity in conscious dogs with severe right ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation Research, 48, 25–33.
Hultgren, P. B., & Bove, A. A. (1981). Myocardial blood flow and mechanics in volume overload-induced left ventricular hypertrophy in dogs. Cardiovascular Research, 15, 522–528.
Isoyama, S., Ito, N., Kuroha, M., & Takishima, T. (1989). Complete reversibility of physiological coronary vascular abnormalities in hypertrophied hearts produced by pressure overload in the rat. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 84, 288–294.
Toyota, E., Warltier, D. C., Brock, T., Ritman, E., Kolz, C., O’Malley, P., et al. (2005). Vascular endothelial growth factor is required for coronary collateral growth in the rat. Circulation, 112(14), 2108–2113.
Ghorbel, M. T., Cherif, M., Jenkins, E., Mokhtari, A., Kenny, D., Angelini, G. D., et al. (2009). Transcriptomic analysis of patients with tetralogy of Fallot reveals the effect of chronic hypoxia on myocardial gene expression. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 140(2), 337–345.
Rakusan, K., Cicutti, N., Spatenka, J., & Samánek, M. (1997). Geometry of the capillary net in human hearts. International Journal of Microcirculation: Clinical and Experimental, 17, 29–32.
Stalmans, I., Lambrechts, D., De Smet, F., Jansen, S., Wang, J., Maity, S., et al. (2003). VEGF: a modifier of the del22q11 (DiGeorge) syndrome? Nature Medicine, 9(2), 173–182.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Frank Staal and Michael Moorhouse for their help with the GeneChip data analysis. Financial support from the Netherlands Heart Foundation (NHS 96.082) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, T.H.F., Sharma, V., Yilmaz, E. et al. DNA Microarray and Quantitative Analysis Reveal Enhanced Myocardial VEGF Expression with Stunted Angiogenesis in Human Tetralogy of Fallot. Cell Biochem Biophys 67, 305–316 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9710-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9710-9