Abstract
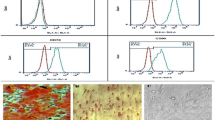
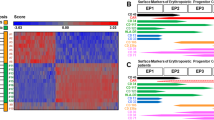
We investigated the role of homeobox B4 (HOXB4) mRNA/protein expression induced by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and/or all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in proliferation and committed differentiation of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) into colony-forming-units of T-lymphocyte (CFU-TL) and erythroid (CFU-E) progenitors in vitro. Twelve cord blood samples were collected from the fetal placenta umbilical vein and cultured in vitro. The proliferation and differentiation of cord blood HSCs into CFU-TL and CFU-E were continuously disrupted with HCMV-AD169 and/or 6 × 10−8 mol/l of ATRA. HOXB4 mRNA/protein expression in CFU-TL and CFU-E was detected in control, ATRA, HCMV and ATRA + HCMV groups on days 3, 7, and 12 of culture by fluorescent qRT-PCR/western blot. We found that HOXB4 mRNA/protein expression was detectable on day 3, increased on day 7 and was highest on day 12. HOXB4 mRNA/protein expression in HCMV group was downregulated compared with control group (P < 0.05). However, the levels were significantly upregulated in HCMV + ATRA group compared with HCMV group (P < 0.05). We concluded that the abnormal HOXB4 mRNA/protein expression induced by HCMV could play a role in hematopoietic damage. ATRA, at the concentration used, significantly up-regulated HOXB4 mRNA/protein expression in normal lymphocyte and erythrocyte progenitor cells as well as in HCMV-infected cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhuravskaya, T., Maciejewski, J. P., Netski, D. M., Bruening, E., Mackintosh, F. R., & St Jeor, S. (1997). Spread of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) after infection of human hematopoietic progenitor cells: Model of HCMV latency. Blood, 90, 2482–2491.
Cheung, A. K., Abendroth, A., Cunningham, A. L., & Slobedman, B. (2006). Viral gene expression during the establishment of human cytomegalovirus latent infection in myeloid progenitor cells. Blood, 108, 3691–3699.
Cheung, A. K., Gottlieb, D. J., Plachter, B., Cunningham, A. L., Abendroth, A., & Slobedman, B. (2009). The role of the human cytomegalovirus UL111A gene in down-regulating CD4+ T-cell recognition of latently infected cells: implications for virus elimination during latency. Blood, 114, 4128–4137.
Buske, C., Feuring-Buske, M., Abramovich, C., et al. (2002). Deregulated expression of HOXB4 enhances the primitive growth activity of human hematopoietic cells. Blood, 100, 862–868.
Magli, M. C., Barba, P., Celetti, A., De Vita, G., Cillo, C., & E Boncinelli, E. (1991). Coordinate regulation of HOX genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 88, 6348–6352.
Brun, A. C., Bjornsson, J. M., Magnusson, M., et al. (2004). Hoxb4-deficient mice undergo normal hematopoietic development but exhibit a mild proliferation defect in hematopoietic stem cells. Blood, 103, 4126–4133.
Heise, M. T., White, L. J., Simpson, D. A., et al. (2003). An attenuating mutation in nsP1 of the Sindbis-group virus S.A.AR86 accelerates nonstructural protein processing and up-regulates viral 26S RNA synthesis. Journal of Virology, 77, 1149–1156.
Madi, N., Al-Nakib, W., Mustafa, A. S., Saeed, T., Pacsa, A., & Nampoory, M. R. (2007). Detection and monitoring of cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant patients by quantitative real-time PCR. Medical Principles and Practice, 16, 268–273.
Jurak, I., & Brune, W. (2006). Induction of apoptosis limits cytomegalovirus cross-species infection. EMBO Journal, 25, 2634–2642.
Behzad-Behbahani, A., Entezam, M., Mojiri, A., et al. (2008). Incidence of human herpes virus-6 and human cytomegalovirus infections in donated bone marrow and umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology, 26, 252–255.
Oshima, M., Endoh, M., Endo, T. A., et al. (2011). Genome-wide analysis of target genes regulated by HoxB4 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells developing from embryonic stem cells. Blood, 117, e142–e150.
Bowles, K. M., Vallier, L., Smith, J. R., Alexander, M. R., & Pedersen, R. A. (2006). HOXB4 overexpression promotes hematopoietic development by human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells, 24, 1359–1369.
Zhu, J., Zhang, Y., Joe, G. J., et al. (2005). NF-Ya activates multiple hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) regulatory genes and promotes HSC self-renewal. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 11728–11733.
Beslu, N., Krosl, J., Laurin, M., et al. (2004). Molecular interactions involved in HOXB4-induced activation of HSC self-renewal. Blood, 104, 2307–2314.
Miyake, N., Brun, A. C., Magnusson, M., Miyake, K., Scadden, D. T., & Karlsson, S. (2006). HOXB4-induced self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells is significantly enhanced by p21 deficiency. Stem Cells, 24, 653–661.
Chen, L. Y., Dai, G., Wu, G. J., et al. (2000). Influence of human cytomegalovirus infection on the expression of HOX genes in human embryo lung cells. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 25, 440–442.
Reeves, M. B. (2011). Chromatin-mediated regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression. Virus Research, 157, 134–143.
Sinclair, J. (2010). Chromatin structure regulates human cytomegalovirus gene expression during latency, reactivation and lytic infection. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1799, 286–295.
Kirito, K., Fox, N., & Kaushansky, K. (2003). Thrombopoietin stimulates Hoxb4 expression: An explanation for the favorable effects of TPO on hematopoietic stem cells. Blood, 102, 3172–3178.
Yurochko, A. D., & Huang, E. S. (1999). Human cytomegalovirus binding to human monocytes induces immunoregulatory gene expression. The Journal of Immunology, 162, 4806–4816.
Niu, C. S., Li, M. W., Ni, Y. F., Chen, J. M., Mei, J. M., Li, J., et al. (2010). Effect of all-trans retinoic acid on the proliferation and differentiation of brain tumor stem cells. Journal of Experimental Clinical Cancer Research, 29, 113.
Bel-Vialar, S., Itasaki, N., & Krumlauf, R. (2002). Initiating Hox gene expression in the early chick neural tube differential sensitivity to FGF and RA signaling subdivides the Hoxb genes in two distinct groups. Development, 129, 5103–5115.
Evans, T. (2005). Regulation of hematopoiesis by retinoid signaling. Experimental Hematology, 33, 1055–1061.
Sammons, J., Ahmed, N., Khokher, M. A., & Hassan, H. T. (2000). Mechanisms mediating the inhibitory effect of all-trans retinoic acid on primitive hematopoietic stem cells in human long-term bone marrow culture. Stem Cells, 18, 214–219.
Botto, S., Streblow, D. N., DeFilippis, V., et al. (2011). IL-6 in human cytomegalovirus secretome promotes angiogenesis and survival of endothelial cells through the stimulation of survivin. Blood, 117, 352–361.
Kirchmeyer, M., Koufany, M., Sebillaud, S., Netter, P., Jouzeau, J. Y., & Bianchi, A. (2008). All-trans retinoic acid suppresses interleukin-6 expression in interleukin-1-stimulated synovial fibroblasts by inhibition of ERK1/2 pathway independently of RAR activation. Arthritis Research and Therapy, 10, R141.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Health Bureau of Sichuan Province for financial support (Grant No. 20060040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen-jun, L., qu-lian, G., Hong-ying, C. et al. Studies on HOXB4 Expression During Differentiation of Human Cytomegalovirus-infected Hematopoietic Stem Cells into Lymphocyte and Erythrocyte Progenitor Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 63, 133–141 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9349-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9349-y