Abstract
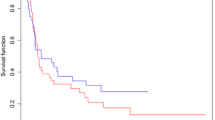
We compared the curative and side-effects in esophageal carcinoma treated by conventional fraction (CF) and late course accelerated hyperfraction (LCAF) three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy. Ninety-eight patients were randomly assigned to two different radiotherapy model groups. Fifty patients were treated using CF three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy at a total dose of 60–68 Gy; 2 Gy/F; 5 fractions/week (median 64 Gy), 48 patients were treated with LCAF (First CF-treated at the dose 40 Gy. Later, LCAF-treated 1.5 Gy/F; 2 fractions/day; 21–27 Gy; a total dose of 61–67 Gy; median 64 Gy). The data showed that the 1-, 2- and 3-year-survival rates in LCAF group were 79.2, 56.3, and 43.8%, compared to 74, 54, and 36% in CF group (P = 0.476). The 1-, 2- and 3-year-local control rates in LCAF group were 81.3, 62.5, and 50%, compared to 78, 58, and 42% in CF group (P = 0.454). In CF group, the incidence of radiation-induced esophagitis was lower than that in LCAF group (72 vs. 93.8%; P = 0.008) and there was no significant difference between rates of radiation-induced pneumonitis in CF and LCAF groups (10 vs. 6.25%; P = 0.498). It was concluded that the 1-, 2- and 3-year-local control and survival rates of esophageal carcinoma patients treated with LCAF were slightly better than CF radiotherapy; however, the radiation side-effects in LCAF group were greater than those in CF group.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin, D. M., Bray, F., Ferlay, J., & Pisani, P. (2005). Global cancer statistics 2002. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 55, 74–108.
Parkin, D. M., Laara, E., & Muir, C. S. (1988). Estimates of the worldwide frequency of sixteen major cancers in 1980. International Journal of Cancer, 41, 184–197.
Weibo, Y., Zihao, Y., Guozhen, X., & Yimin, H. (2008). Radiation Oncology (4th ed., pp. 555–563). Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press.
Withers, H. R., Taylor, J. M., & Maeiejewski, B. (1988). The hazard of accelerated tumor colonogen repopulation during radiotherapy. Acta Oncologica, 27, 131–146.
Trott, K. R. (1990). Cell repopulation and overall treatment time. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 19, 1071–1075.
Chun, H., Jun, W., Daoan, Z., Xiangran, Y., & Shuchai, Z. (1997). 100 cases of esophageal neoplasms treated with later course accelerated hyperfraction radiotherapy. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 6, 16–18.
Xuehui, S., Gendi, W., Xinwei, L., & Xuejun, M. (1997). The long-term effect of later course accelerated hyperfraction radiotherapy for esophageal neoplasms. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 6, 12–15.
Xiaofang, S., Buduo, M., Mingli, C., Xueming, S., Huaigu, G., & Mingzhu, S. (1998). Phase-III clinical trial of later course accelerated hyperfraction radiotherapy for esophageal neoplasms. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 7, 86–89.
Kuaile, Z., Yang, W., & Xuehui, S. (2001). Clinical analysis of later course accelerated hyperfraction radiotherapy for esophageal neoplasms. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 10, 14–16.
Yang, W., Xuehui, S., Shaoqin, H., Weiqiang, Y., Ying, W., & Xiaomao, G. (2003). The analysis on long-term follow-up result and prognosis of hyperfraction radiotherapy for esophageal neoplasms. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 12, 4–8.
Zefen, X., Zhong, Z., Hongzhi, Z., Jianrong, D., Jun, L., & Wei, H. (2004). The evaluation of the tumor dose distribution in the conventional radiotherapy for esophageal neoplasms by 3-dimentional treatment plan system. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 12, 273–277.
Lan, W., Chun, H., Shuchai, Z., Zifeng, C., & Yankun, C. (2006). The dosiological study on conventional radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 5, 176–180.
Chun, H., Xiangran, Y., Jun, W., Guoxin, M., Aiqin, X., & Xin, Z. (2005). The dosiological study on later course accelerated hyperfraction radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 14, 398–400.
Bedford, J. L., Viviers, L., Guzel, Z., Childs, P. J., Webb, S., & Tait, D. M. (2000). A quantitative treatment planning study evaluating the potential of dose escalation in conformal radiotherapy of the oesophagus. Radiotherapy & Oncology, 57, 183–193.
Lan, W., Chun, H., Xin, Z., Jun, W., Aiqin, X., & Guoxin, M. (2008). The curative effect of 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 35, 424–427.
Daoli, N., Huiling, H., Chunli, R., & Zhifeng, Q. (2004). The analysis on clinical curative effect of 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 13, 193–195.
Yiqin, Z., Jincheng, L., Zhenyu, Z., & Qing, W. (2005). Preliminary results of clinical study on 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 14, 31–34.
Ren, L., Wenbin, S., Shuchai, Z., Yuqiang, W., Juan, L., & Jingwei, S. (2008). Preliminary analysis of 120 cases of esophageal cancer treated with 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and later course accelerated hyperfraction radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Clinical Focus, 23, 328–330.
Xindong, S., Jingming, Y., Xiaoli, F., Ruimei, R., Minghuan, L., & Guoli, Z. (2006). Randomized clinical study of surgery versus radiotherapy alone in the treatment of resectable esophageal cancer in the chest. Chinese Journal of Oncology, 28, 784–787.
Baozhi, R., Lei, H., Peijun, Z., Changping, S., & Fanhua, K. (2006). Late course accelerated three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for esophageal carcinoma with long term result and prognostic analysis. Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, 15, 93–96.
Kuaile, Z., Xuehui, S., Guoliang, J., & Yang, W. (2004). Late-course accelerated hyperfractionated radiotherapy for localized esophageal carcinoma. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 60, 123–129.
Acknowledgment
We thank Changzhou Natural Science Foundation for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lu Xu-Jing and Wang Jian-Hua contributed equally to this study as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JH., Lu, XJ., Zhou, J. et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Conventional Fraction and Late Course Accelerated Hyperfraction Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys 62, 107–112 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9267-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9267-4