Abstract
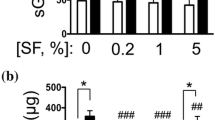
Objective Determining the activity of lysosomal exoglycosidases in tissue cultures of synoviocytes derived from the knee joints of patients with injured anterior cruciate ligaments (ACL), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Methods The following exoglycosidases in cultured synoviocytes were analyzed with p-nitrophenyl derivatives of appropriate sugars as substrates: hexosaminidase (HEX) and its isoenzyme A (HEX-A), β-glucuronidase (GluA), β-galactosidase (GAL), α-mannosidase (MAN), and α-fucosidase (FUC). Results In our cell cultures, fibroblast-like synovial cells (FLS) dominated. In the group of patients with ACL-injuries, and in the groups of patients with JIA and RA, the activity of the investigated exoglycosidases was significantly higher in the intra- rather than in the extracellular compartment. Hexosaminidase was the predominant exoglycosidase. Stimulation of synoviocytes by IL-1β in cell cultures significantly increased the activity of HEX, HEX-A, and GluA in both compartments, as well as of GAL, MAN, and FUC in the intracellular compartment. Stimulation by IL-1β rheumatoidal synoviocytes increased by 128–201% the activity of HEX and HEX A in intracellular compartments and 33–72% in extracellular compartment. Conclusions The profile of lysosomal exoglycosidases in a cell culture of human synoviocytes is similar, but not identical, to those in the knee joint. Hexosaminidase is the dominant glycosidase in cultured unstimulated and IL-1β-stimulated human synoviocytes. The HEX inhibitors may be new drugs for the treatment of inflamed knee joints.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainola, M. M., Mandelin, J. A., Liljestrom, M. P., Hukkanen, M. V., & Konttinen, Y. T. (2005). Pannus invasion and cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis: Involvement of MMP-3 and interleukin -1beta. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 23, 644–650.
Sohar, N., Hammer, H., & Sohar, I. (2002). Lysosomal peptidases and glycosidases in rheumatoid arthritis. Biological Chemistry, 383, 865–869.
Tanaka, S., Hamanishi, C., Kikuchi, H., & Fukuda, K. (1998). Factors related to degradation of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis: A review. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 27, 392–399.
Ortutay, Z., Polga’r, A., Gömör, B., et al. (2003). Synovial fluid exoglycosidases are predictors of rheumatoid arthritis and are effective in cartilage glycosaminoglycan depletion. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 48, 2163–2172.
Zwierz, K., Gindzieński, A., Ostrowska, L., & Stankiewicz-Choroszucha, B. (1989). Metabolism of glycoconjugates in human gastric mucosa. Acta Medica Hungarica, 46, 275–288.
Marciniak, J., Zalewska, A., Popko, J., & Zwierz, K. (2006). Optimization of an enzymatic method for the determination of lysosomal N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase in synovial fluid. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 44, 933–937.
Zwierz, K., Zalewska, A., & Zoch-Zwierz, W. (1999). Isoenzymes of N-acetyl-β-hexosaminidase. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 46, 739–751.
Czartoryska, B. (1977). Lysosomal exoglycosidases in catabolism of glycoheteropolymers. Postepy Biochemii, 23, 229–266.
Itakura, T., Kuroki, A., Ishibashi, Y., et al. (2006). Inefficiency in GM2 ganglioside elimination by human lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase beta-subunit gene transfer to fibroblastic cell line derived from Sandhoff disease model mice. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 29, 1564–1569.
Pennybacker, M., Liessem, B., Moczall, H., Tifft, C. J., Sandhoff, K., & Proia, R. L. (1996). Identification of domains in human beta-hexosaminidase that determine substrate specificity. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 17377–17382.
Sharma, R., Bukovac, S., Callahan, J., & Mahuran, D. (2003). A single site in human beta-hexosaminidase A binds both 6-sulfate-groups of hexosamines and the sialic acid moiety of GM2 ganglioside. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1637, 113–118.
Li, C., Qian, J., & Lin, J. S. (2006). Purification and characterization of alpha-L-fucosidase from human primary hepatocarcinoma tissue. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 12, 3770–3775.
Winchester, B. (2005). Lysosomal metabolism of glycoproteins. Glycobiology, 15, 1R–15R.
Stypułkowska, A., Zwierz, P., & Zwierz, K. (2004). Endoglycosidases and glycoamidases. Postepy Biochemii, 50, 82–88.
Shikhman, A. R., Brinson, D. C., & Lotz, M. (2000). Profile of glycosaminoglycan-degrading glycosidases and glycoside sulfatases secreted by human articular chondrocytes in homeostasis and inflammation. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 43, 1307–1314.
Dinarello, C. A. (1989). Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Advances in Immunology, 44, 153–205.
Gubler, U., Chua, A. O., Stern, A. S., et al. (1986). Recombinant human interleukin 1 alpha: Purification and biological characterization. Journal of Immunology, 36, 2492–2497.
Popko, J., Marciniak, J., Zalewska, A., Maldyk, P., Rogalski, M., & Zwierz, K. (2006). The activity of exoglycosidases in the synovial membrane and knee fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 35, 189–192.
Hofer, M., & Southwood, T. R. (2002). Classification of childhood arthritis. Best Practice and Research. Clinical Rheumatology, 16, 379–396.
Arnett, F. C., Edworthy, S. M., Bloch, D. A., et al. (1988). The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 31, 315–324.
Vergne, P., Liagre, B., Bertin, P., et al. (1998). Methotrexate and cyclooxygenase metabolism in cultured human rheumatoid synoviocytes. The Journal of Rheumatology, 25, 433–440.
Fraser, J. R. E., & Catt, K. J. (1961). Human synovial-cell culture use of a new method in a study of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet, 2, 1437–1439.
Zwierz, K., Gindzienski, A., Glowacka, D., & Porowski, T. (1981). The degradation of glycoconjugates in the human gastric mucous membrane. Acta Medica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 38, 145–152.
Pugh, D., & Walker, P. G. (1961). The localization of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase in tissues. The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 9, 242–250.
Berenbaum, F., Le Gars, L., Toussirot, E., et al. (2000). Marked elevation of serum N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 18, 63–66.
Clarris, B. J., Fraser, J. R., Ash, P., Leizer, T., & Hamilton, J. A. (1987). Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 alpha stimulate the N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase activity of human synovial cells. Rheumatology International, 7, 271–275.
Lecomte, V., Knott, I., Burton, M., Remacle, J., & Raes, M. (1994). Cathepsin B and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase in human synovial cells in culture: Effects of interleukin-1. Clinica Chimica Acta, 228, 143–159.
Solavagione, E., Bourbouze, R., Percheron, F., Hecquet, C., & Adolphe, M. (1987). Partial characterization of intracellular and secreted glycosidases from rabbit articular chondrocytes in culture. Biochimie, 69, 239–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popko, J., Marciniak, J., Ilendo, E. et al. Profile of Exoglycosidases in Synovial Cell Cultures Derived from Human Synovial Membrane. Cell Biochem Biophys 51, 89–95 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-008-9018-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-008-9018-3