Abstract
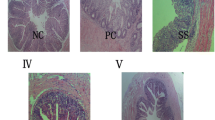
This study aimed to investigate the effects of selenium (Se)-enriched Bacillus subtilis (Se-BS) on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune status, and gut health in broilers. A total of 240 one-day-old Arbor Acres broilers were randomly allotted to four groups and fed with basal diet (control group), 0.30 mg/kg Se (SS group), 3 × 109 CFU/g B. subtilis (BS group), and 0.30 mg/kg Se + 3 × 109 CFU/g B. subtilis (Se-BS group) for 42 days. The results showed that Se-BS supplementation increased body weight (BW), average daily gain, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and the contents of interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, and immunoglobulin (Ig) G in plasma, the index and wall thickness of the duodenum, the villus height and crypt depth of the jejunum, and GPx-1 and thioredoxin reductase 1 mRNA levels in liver and intestine and decreased feed conversion ratio (FCR) and plasma malondialdehyde (MDA) content compared with the control group on day 42 (P < 0.05). Compared with groups SS and BS, Se-BS supplementation increased BW, the activities of GPx, CAT, and POD, and the contents of IL-2, IL-4, and IgG in plasma, the index and wall thickness of the duodenum, the crypt depth and secretory IgA content of the jejunum, and GPx-1 mRNA levels in liver and intestine and decreased FCR and plasma MDA content on day 42 (P < 0.05). In conclusion, Se-BS supplementation effectively improved the growth performance antioxidant capacity, immune status, and gut health of broilers.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bakhshalinejad R, Hassanabadi A, Swick RA (2019) Dietary sources and levels of selenium supplements affect growth performance, carcass yield, meat quality and tissue selenium deposition in broilers. Anim Nutr 5:256–263
Chen F, Hou L, Zhu L, Yang C, Zhu F, Qiu H, Qin S (2020) Effects of selenide chitosan sulfate on glutathione system in hepatocytes and specific pathogen-free chickens. Poult Sci 99:3979–3986
Hou L, Qiu H, Zhu L, Gao S, Chen F (2022) Selenide chitosan sulfate improved the hepatocyte activity, growth performance, and anti-oxidation capacity by activating the thioredoxin reductase of chickens in vitro and in vivo. Biol Trace Elem Res 200:3798–3807
Hou L, Qiu H, Sun P, Zhu L, Chen F, Qin S (2020) Selenium-enriched Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves the meat quality of broiler chickens via activation of the glutathione and thioredoxin systems. Poult Sci 99:6045–6054
Ye R, Huang J, Wang Z, Chen Y, Dong Y (2021) Trace element selenium effectively alleviates intestinal diseases. Int J Mol Sci 22:11708. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111708
Huang J, Xie L, Song A, Zhang C (2022) Selenium status and its antioxidant role in metabolic diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:7009863. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7009863
Barchielli G, Capperucci A, Tanini D (2022) The role of selenium in pathologies: an updated review. Antioxidants (Basel) 11:251. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020251
Tinggi U (2008) Selenium: its role as antioxidant in human health. Environ Health Prev Med 13:102–108
Khan MT, Mahmud A, Zahoor I, Javed K (2017) Organic and inorganic selenium in Aseel chicken diets: Effect on hatching traits. Poult Sci 96:1466–1472
Oladokun S, Koehler A, MacIsaac J, Ibeagha-Awemu EM, Adewole DI (2021) Bacillus subtilis delivery route: effect on growth performance, intestinal morphology, cecal short-chain fatty acid concentration, and cecal microbiota in broiler chickens. Poult Sci 100:100809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.10.063
Guo M, Li M, Zhang C, Zhang X, Wu Y (2020) Dietary administration of the bacillus subtilis enhances immune responses and disease resistance in chickens. Front Microbiol 11:1768. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01768
Qiu K, Li CL, Wang J, Qi GH, Gao J, Zhang HJ, Wu SG (2021) Effects of dietary supplementation with bacillus subtilis, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, serum immunity, and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Front Nutr 8:786878. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.786878
Yang J, Huang K, Wang J, Wu D, Liu Z, Yu P, Wei Z, Chen F (2021) Combined use of Bacillus subtilis yb-114,246 and Bacillus licheniformis yb-214,245 improves body growth performance of Chinese Huainan partridge shank chickens by enhancing intestinal digestive profiles. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13:327–342
Yang J, Wang J, Huang K, Liu Q, GuofangLiu XuX, Zhang H, Zhu M (2021) Selenium-enriched Bacillus subtilis yb-114246 improved growth and immunity of broiler chickens through modified ileal bacterial composition. Sci Rep 11:21690. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00699-4
Yang J, Zhang M, Zhou Y (2019) Effects of selenium-enriched Bacillus sp. compounds on growth performance, antioxidant status, and lipid parameters breast meat quality of Chinese Huainan partridge chicks in winter cold stress. Lipids Health Dis 18:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-019-1015-6
Hu Y, Dun Y, Li S, Zhao S, Peng N, Liang Y (2014) Effects of Bacillus subtilis KN-42 on growth performance, diarrhea and faecal bacterial flora of weaned piglets. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 27:1131–1140
NRC (1994) Nutrient requirements of poultry, 9th rev. National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington, DC
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2020) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/5140
Bakhshalinejad R, Akbari MoghaddamKakhki R, Zoidis E (2018) Effects of different dietary sources and levels of selenium supplements on growth performance, antioxidant status and immune parameters in Ross 308 broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci 59:81–91
Lauridsen C (2019) From oxidative stress to inflammation: redox balance and immune system. Poult Sci 98:4240–4246
Wang Y, Wang H, Zhan X (2016) Effects of different dl-selenomethionine and sodium selenite levels on growth performance, immune functions and serum thyroid hormones concentrations in broilers. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 100:431–439
Dalia AM, Loh TC, Sazili AQ, Jahromi MF, Samsudin AA (2017) The effect of dietary bacterial organic selenium on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and Selenoproteins gene expression in broiler chickens. BMC Vet Res 13:254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-018-1578-x
Ren Z, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Huang K (2011) Preparation of selenium/zinc-enriched probiotics and their effect on blood selenium and zinc concentrations, antioxidant capacities, and intestinal microflora in canine. Biol Trace Elem Res 141:170–183
Lv CH, Wang T, Regmi N, Chen X, Huang K, Liao SF (2015) Effects of dietary supplementation of selenium-enriched probiotics on production performance and intestinal microbiota of weanling piglets raised under high ambient temperature. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 99:1161–1171
Keerqin C, Rhayat L, Zhang ZH, Gharib-Naseri K, Kheravii SK, Devillard E, Crowley TM, Wu SB (2021) Probiotic Bacillus subtilis 29,784 improved weight gain and enhanced gut health status of broilers under necrotic enteritis condition. Poult Sci 100:100981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2021.01.004
Larsen N, Thorsen L, Kpikpi EN, Stuer-Lauridsen B, Cantor MD, Nielsen B, Brockmann E, Derkx PM, Jespersen L (2014) Characterization of Bacillus spp. strains for use as probiotic additives in pig feed. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1105–1118
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2021MC150), Shandong Science and Technology Small and Medium Enterprises Innovation Ability Improvement Project (2021tsgc1303), Qingdao Science and Technology Benefit the People Demonstration and Guidance Project (22-3-7-xdny-11-nsh), and Shandong Modern Agricultural Technology and Industry System, China (SDAIT-11-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Materials preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Huiling Qiu, Shansong Gao, Lele Hou, and Fu Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Huiling Qiu, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, H., Gao, S., Hou, L. et al. Selenium-enriched Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, Immune Status, and Gut Health of Broiler Chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 5756–5763 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03610-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03610-6