Abstract
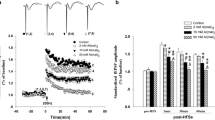
The neurotoxic effects of aluminum (Al) are associated with the impairment of synaptic plasticity, the biological basis of learning and memory, the major form of which is long-term potentiation (LTP). The canonical glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β)/β-catenin signaling–mediated brain–derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) pathway has been suggested to play important roles in memory. Thus, Al may affect LTP through this pathway. In this study, a Sprague-Dawley rat model of neurotoxicity was established through intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of aluminum maltol (Al(mal)3), which was achieved by preimplantation of a cannula into the lateral ventricle. The rats in the control and Al-treated groups received a daily injection of SB216763, an inhibitor of GSK-3β. Electrophysiology and western blot analysis were used to investigate the regulatory effect of the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling-mediated BDNF pathway on LTP impairment induced by Al(mal)3. The results confirmed that i.c.v. injection of Al(mal)3 significantly suppressed the field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) amplitude, as indicated by a decrease in BDNF protein expression, which was accompanied by dose-dependent decreases in β-catenin protein expression and the phosphorylation of GSK-3β at Ser9. Rats that received SB216763, a GSK-3β inhibitor, exhibited higher fEPSP amplitudes than control rats. Furthermore, SB216763 treatment upregulated the hippocampal protein expression of BDNF and β-catenin while increasing the ratio of p-GSK-3β/GSK-3β. From the perspective of the identified β-catenin–BDNF axis, Al impairs hippocampal LTP, possibly through the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling–mediated BDNF pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Niu Q (2018) Overview of the relationship between aluminum exposure and health of human being. Adv Exp Med Biol 1091:1–31
Yokel RA (2002) Brain uptake, retention, and efflux of aluminum and manganese. Environ Health Perspect 110(Suppl 5(Suppl 5)):699–704
Yumoto S, Nagai H, Matsuzaki H, Matsumura H, Tada W, Nagatsuma E, Kobayashi K (2001) Aluminium incorporation into the brain of rat fetuses and sucklings. Brain Res Bull 55(2):229–234
Kawahara M, Kato-Negishi M (2011) Link between aluminum and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: the integration of the aluminum and amyloid cascade hypotheses. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:276393
Flaten TP (2001) Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Res Bull 55(2):187–196
Colomina MT, Peris-Sampedro F (2017) Aluminum and Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Neurobiol 18:183–197
Lu X, Liang R, Jia Z, Wang H, Pan B, Zhang Q, Niu Q (2014) Cognitive disorders and tau-protein expression among retired aluminum smelting workers. J Occup Environ Med 56(2):155–160
Walton JR (2009) Functional impairment in aged rats chronically exposed to human range dietary aluminum equivalents. Neurotoxicology 30(2):182–193
Yu L, Jiang R, Su Q, Yu H, Yang J (2014) Hippocampal neuronal metal ion imbalance related oxidative stress in a rat model of chronic aluminum exposure and neuroprotection of meloxicam. Behav Brain Funct 10:6
Dudek SM, Bear MF (1993) Bidirectional long-term modification of synaptic effectiveness in the adult and immature hippocampus. J Neurosci 13(7):2910–2918
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere CA, Regan CM, Walsh DM, Sabatini BL, Selkoe DJ (2008) Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer's brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 14(8):837–842
Bannerman DM, Sprengel R, Sanderson DJ, McHugh SB, Rawlins JNP, Monyer H, Seeburg PH (2014) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety. Nat Rev Neurosci 15(3):181–192
Malenka RC, Bear MF (2004) LTP and LTD: an embarrassment of riches. Neuron 44(1):5–21
Whitlock JR, Heynen AJ, Shuler MG, Bear MF (2006) Learning induces long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Science 313(5790):1093–1097
Zhang H, Yang X, Qin X, Niu Q (2016) Caspase-3 is involved in aluminum-induced impairment of long-term potentiation in rats through the Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Neurotox Res 29(4):484–494
Bambah-Mukku D, Travaglia A, Chen DY, Pollonini G, Alberini CM (2014) A positive autoregulatory BDNF feedback loop via C/EBPβ mediates hippocampal memory consolidation. J Neurosci 34(37):12547–12559
Panja D, Kenney JW, D’Andrea L, Zalfa F, Vedeler A, Wibrand K, Fukunaga R, Bagni C, Proud CG, Bramham CR (2014) Two-stage translational control of dentate gyrus LTP consolidation is mediated by sustained BDNF-TrkB signaling to MNK. Cell Rep 9(4):1430–1445
Diógenes MJ, Costenla AR, Lopes LV, Jerónimo-Santos A, Sousa VC, Fontinha BM, Ribeiro JA, Sebastião AM (2011) Enhancement of LTP in aged rats is dependent on endogenous BDNF. Neuropsychopharmacology 36(9):1823–1836
Leal G, Bramham CR, Duarte CB (2017) BDNF and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Vitam Horm 104:153–195
Gibon J, Barker PA (2017) Neurotrophins and proneurotrophins: focus on synaptic activity and plasticity in the brain. Neuroscientist 23(6):587–604
Lu B, Nagappan G, Lu Y (2014) BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. Handb Exp Pharmacol 220:223–250
Lu B, Nagappan G, Guan X, Nathan PJ, Wren P (2013) BDNF-based synaptic repair as a disease-modifying strategy for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(6):401–416
Park H, Poo MM (2013) Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(1):7–23
Li H, Xue X, Li Z, Pan B, Hao Y, Niu Q (2020) Aluminium-induced synaptic plasticity injury via the PHF8-H3K9me2-BDNF signalling pathway. Chemosphere 244:125445
King MK, Pardo M, Cheng Y, Downey K, Jope RS, Beurel E (2014) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors: rescuers of cognitive impairments. Pharmacol Ther 141(1):1–12
Jiang P, Li G, Zhou X, Wang C, Qiao Y, Liao D, Shi D (2019) Chronic fluoride exposure induces neuronal apoptosis and impairs neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity: role of GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Chemosphere 214:430–435
Goold RG, Gordon-Weeks PR (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and the regulation of axon growth. Biochem Soc Trans 32(Pt 5):809–811
Li X, Jope RS (2010) Is glycogen synthase kinase-3 a central modulator in mood regulation? Neuropsychopharmacology 35(11):2143–2154
Eldar-Finkelman H (2002) Glycogen synthase kinase 3: an emerging therapeutic target. Trends Mol Med 8(3):126–132
Benedetti F, Poletti S, Radaelli D, Bernasconi A, Cavallaro R, Falini A, Lorenzi C, Pirovano A, Dallaspezia S, Locatelli C, Scotti G, Smeraldi E (2010) Temporal lobe grey matter volume in schizophrenia is associated with a genetic polymorphism influencing glycogen synthase kinase 3-β activity. Genes Brain Behav 9(4):365–371
Peineau S, Taghibiglou C, Bradley C, Wong TP, Liu L, Lu J, Lo E, Wu D, Saule E, Bouschet T, Matthews P, Isaac JTR, Bortolotto ZA, Wang YT, Collingridge GL (2007) LTP inhibits LTD in the hippocampus via regulation of GSK3beta. Neuron 53(5):703–717
Yu DF, Shen ZC, Wu PF, Guan XL, Chen T, Jin Y, Hu ZL, Ni L, Wang F, Chen JG, Long LH (2016) HFS-triggered AMPK activation phosphorylates GSK3β and induces E-LTP in rat hippocampus in vivo. CNS Neurosci Ther 22(6):525–531
Ma T, Tzavaras N, Tsokas P, Landau EM, Blitzer RD (2011) Synaptic stimulation of mTOR is mediated by Wnt signaling and regulation of glycogen synthetase kinase-3. J Neurosci 31(48):17537–17546
Fortress AM, Frick KM (2016) Hippocampal Wnt signaling: memory regulation and hormone interactions. Neuroscientist 22(3):278–294
Fortress AM, Schram SL, Tuscher JJ, Frick KM (2013) Canonical Wnt signaling is necessary for object recognition memory consolidation. J Neurosci 33(31):12619–12626
Garza JC, Guo M, Zhang W, Lu XY (2012) Leptin restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a chronic unpredictable stress model of depression and reverses glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Mol Psychiatry 17(8):790–808
Chen BY, Wang X, Wang ZY, Wang YZ, Chen LW, Luo ZJ (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, possibly by triggering the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Neurosci Res 91(1):30–41
Zhang W, Shi Y, Peng Y, Zhong L, Zhu S, Zhang W, Tang SJ (2018) Neuron activity-induced Wnt signaling up-regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the pain neural circuit. J Biol Chem 293(40):15641–15651
Yi H, Hu J, Qian J, Hackam AS (2012) Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated by the Wnt signaling pathway. Neuroreport 23(3):189–194
Martin RB (1986) The chemistry of aluminum as related to biology and medicine. Clin Chem 32(10):1797–1806
Coghlan MP, Culbert AA, Cross DAE, Corcoran SL, Yates JW, Pearce NJ, Rausch OL, Murphy GJ, Carter PS, Roxbee Cox L, Mills D, Brown MJ, Haigh D, Ward RW, Smith DG, Murray KJ, Reith AD, Holder JC (2000) Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene transcription. Chem Biol 7(10):793–803
Hooper C, Markevich V, Plattner F, Killick R, Schofield E, Engel T, Hernandez F, Anderton B, Rosenblum K, Bliss T, Cooke SF, Avila J, Lucas JJ, Giese KP, Stephenson J, Lovestone S (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition is integral to long-term potentiation. Eur J Neurosci 25(1):81–86
Stepanichev MY, Kudryashova IV, Yakovlev AA, Onufriev MV, Khaspekov LG, Lyzhin AA, Lazareva NA, Gulyaeva NV (2005) Central administration of a caspase inhibitor impairs shuttle-box performance in rats. Neuroscience 136(2):579–591
Paxinos G, Watson C, Pennisi M, Topple A (1985) Bregma, lambda and the interaural midpoint in stereotaxic surgery with rats of different sex, strain and weight. J Neurosci Methods 13(2):139–143
Liang RF et al (2012) Aluminium-maltolate-induced impairment of learning, memory and hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats. Ind Health 50(5):428–436
Singh S, Mishra A, Bharti S, Tiwari V, Singh J, Parul, Shukla S (2018) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β regulates equilibrium between neurogenesis and gliogenesis in rat model of Parkinson’s disease: a crosstalk with Wnt and notch signaling. Mol Neurobiol 55(8):6500–6517
Wang J, Lin F, Cai F, Yan W, Zhou Q, Xie L (2013) Microcystin-LR inhibited hippocampal long-term potential via regulation of the glycogen synthase kinase-3β pathway. Chemosphere 93(2):223–229
Buchta AM et al (2005) Neurotoxicity of exposures to aluminium welding fumes in the truck trailer construction industry. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19(3):677–685
Zawilla NH, Taha FM, Kishk NA, Farahat SA, Farghaly M, Hussein M (2014) Occupational exposure to aluminum and its amyloidogenic link with cognitive functions. J Inorg Biochem 139:57–64
Wang L, Hu J, Zhao Y, Lu X, Zhang Q, Niu Q (2014) Effects of aluminium on β-amyloid (1-42) and secretases (APP-cleaving enzymes) in rat brain. Neurochem Res 39(7):1338–1345
Birch AM, Kelly ÁM (2013) Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of nerve growth factor improves recognition memory in the rat. Neuropharmacology 75:255–261
Khan MB, Ahmad M, Ahmad S, Ishrat T, Vaibhav K, Khuwaja G, Islam F (2015) Bacopa monniera ameliorates cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration induced by intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin in rat: behavioral, biochemical, immunohistochemical and histopathological evidences. Metab Brain Dis 30(1):115–127
Pan B, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Li L, Xue X, Li H, Niu Q (2020) Role of mGluR 1 in synaptic plasticity impairment induced by maltol aluminium in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 78:103406
McLachlan DR et al (1991) Would decreased aluminum ingestion reduce the incidence of Alzheimer's disease? Cmaj 145(7):793–804
Shuchang H et al (2008) Protective effects of gastrodia elata on aluminium-chloride-induced learning impairments and alterations of amino acid neurotransmitter release in adult rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci 26(6):467–473
Luo J (2009) GSK3beta in ethanol neurotoxicity. Mol Neurobiol 40(2):108–121
Shim SS, Stutzmann GE (2016) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3: an emerging target in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 33(23):2065–2076
Takashima A (2012) GSK-3β and memory formation. Front Mol Neurosci 5:47
Dewachter I, Ris L, Jaworski T, Seymour CM, Kremer A, Borghgraef P, de Vijver H, Godaux E, van Leuven F (2009) GSK3beta, a centre-staged kinase in neuropsychiatric disorders, modulates long term memory by inhibitory phosphorylation at serine-9. Neurobiol Dis 35(2):193–200
Tapia-Arancibia L, Aliaga E, Silhol M, Arancibia S (2008) New insights into brain BDNF function in normal aging and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res Rev 59(1):201–220
Oliva CA, Vargas JY, Inestrosa NC (2013) Wnts in adult brain: from synaptic plasticity to cognitive deficiencies. Front Cell Neurosci 7:224
Nagahara AH, Tuszynski MH (2011) Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(3):209–219
Andero R, Choi DC, Ressler KJ (2014) BDNF-TrkB receptor regulation of distributed adult neural plasticity, memory formation, and psychiatric disorders. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 122:169–192
Yang JW, Ru J, Ma W, Gao Y, Liang Z, Liu J, Guo JH, Li LY (2015) BDNF promotes the growth of human neurons through crosstalk with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via GSK-3β. Neuropeptides 54:35–46
Hiester BG, Galati DF, Salinas PC, Jones KR (2013) Neurotrophin and Wnt signaling cooperatively regulate dendritic spine formation. Mol Cell Neurosci 56:115–127
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank our colleagues for their help and work on the study.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81703202 and 81872599).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
All experiments complied with the rulings of the Institute of Laboratory Animal Research, Division on Earth and Life Sciences, National Institute of Health, USA (Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals). The research protocol was performed in accordance with the regulations of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanxi Medical University.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
First authors: Huifang Zhang and Yingchao Han
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Han, Y., Zhang, L. et al. The GSK-3β/β-Catenin Signaling–Mediated Brain–Derived Neurotrophic Factor Pathway Is Involved in Aluminum-Induced Impairment of Hippocampal LTP In Vivo. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 4635–4645 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02582-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02582-9