Abstract
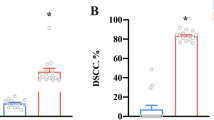
Dairy cow neutrophils activate a program leading to cell death and expulsion of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The role of NETs is to capture pathogens, degrade bacterial toxic factors, and kill bacteria, and the effect of trace elements on NETs formation in cows is ambiguous. In this study, we investigated the effect of copper (0.5 mg/L, 0.8 mg/L, and 2.0 mg/L), zinc (0.1 mg/L, 1.0 mg/L, and 2.0 mg/L), and selenium (0.01 mg/L, 0.08 mg/L, and 2.0 mg/L) on NETs formation in dairy cows. Trace element induction of NETs formation was observed by laser confocal microscopy. The percentage of NETs formed was calculated by quantifying the number of neutrophils forming NETs out of the total number of neutrophils observed under 20 high-power (200×) magnification fields. Copper, zinc, and selenium induced the formation of a network of DNA, neutrophil elastase (ELA2), and myeloperoxidase. Copper (0.8 mg/L), zinc (1.0 mg/L), and selenium (0.01 mg/L) significantly induced the formation of NETs (p < 0.05). The study provides an experimental basis for enhancing the immunity of cows before and after delivery by adding copper, zinc, and selenium.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- PMN:
-
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils
- NETs:
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps
- ELA2:
-
Neutrophils elastase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
References
Babu U, Failla ML (1990) Copper status and function of neutrophils are reversibly depressed in marginally and severely copper-deficient rats. J Nutr 120:1700–1709
Hopkins RG, Failla ML (1995) Chronic intake of a marginally low copper diet impairs in vitro activities of lymphocytes and neutrophils from male rats despite minimal impact on conventional indicators of copper status. J Nutr 125:2658–2668
Karimbakas J, Langkamp-Henken B, Percival SS (1998) Arrested maturation of granulocytes in copper deficient mice. J Nutr 128:1855–1860
Saedi MS, Smith CG, Frampton J, Chambers I, Harrison PR, Sunde RA (1988) Effect of selenium status on mRNA levels for glutathione peroxidase in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 153(2):855–861
Boyne R, Arthur JR (1979) Alterations of neutrophil function in selenium-deficient cattle. J Comp Pathol 89:151–158
Boyne R, Arthur JR (1981) Effects of selenium and copper deficiency on neutrophil function in cattle. J Comp Pathol 91:271–276
Wikse SE, Herd D, Field R, Holland P (1992) Diagnosis of copper deficiency in cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc 200:1625–1629
Sollberger G, Tilley DO, Zychlinsky A (2018) Neutrophil extracellular traps: the biology of chromatin externalization. Dev Cell 44:542–553
Hampton MB, Kettle AJ, Winterbourn CC (1998) Inside the neutrophil phagosome: oxidants, myeloperoxidase, and bacterial killing. Blood 92:3007–3017
Segal AW (2005) How neutrophils kill microbes. Annu Rev Immunol 23:197–223
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303:1532–1535
Fuchs TA, Abed U, Goosmann C, Hurwitz R, Schulze I, Wahn V, Weinrauch Y, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2007) Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 176:231–241
Beiter K, Wartha F, Albiger B, Normark S, Zychlinsky A, Henriques-Normark B (2006) An endonuclease allows Streptococcus pneumoniae to escape from neutrophil extracellular traps. Curr Biol 16:401–407
Buchanan JT, Simpson AJ, Aziz RK, Liu GY, Kristian SA, Kotb M, Feramisco J, Nizet V (2006) DNase expression allows the pathogen group A Streptococcus to escape killing in neutrophil extracellular traps. Curr Biol 16:396–400
Urban CF, Reichard U, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2006) Neutrophil extracellular traps capture and kill Candida albicans yeast and hyphal forms. Cell Microbiol 8:668–676
Chuammitri P, Ostojic J, Andreasen CB, Redmond SB, Lamont SJ, Palic D (2009) Chicken heterophil extracellular traps (HETs): novel defense mechanism of chicken heterophils. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 129:126–131
Palic D, Ostojic J, Andreasen CB, Roth JA (2007) Fish cast NETs: neutrophil extracellular traps are released from fish neutrophils. Dev Comp Immunol 31:805–816
Wartha F, Beiter K, Normark S, Henriques-Normark B (2007) Neutrophil extracellular traps: casting the NET over pathogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:52–56
Steinberg BE, Grinstein S (2007) Unconventional roles of the NADPH oxidase: signaling, ion homeostasis, and cell death. Sci STKE 2007:pe11
Narasaraju T, Yang E, Samy RP, Ng HH, Poh WP, Liew AA, Phoon MC, van Rooijen N, Chow VT (2011) Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to acute lung injury of influenza pneumonitis. Am J Pathol 179:199–210
Marcos V, Zhou-Suckow Z, Onder Yildirim A, Bohla A, Hector A, Vitkov L, Krautgartner WD, Stoiber W, Griese M, Eickelberg O, Mall MA, Hartl D (2015) Free DNA in cystic fibrosis airway fluids correlates with airflow obstruction. Mediat Inflamm 2015:408935
Schuschke DA, Percival SS, Lominadze D, Saari JT, Lentsch AB (2002) Tissue-specific ICAM-1 expression and neutrophil transmigration in the copper-deficient rat. Inflammation 26:297–303
Bao B, Prasad AS, Beck FW, Snell D, Suneja A, Sarkar FH, Doshi N, Fitzgerald JT, Swerdlow P (2008) Zinc supplementation decreases oxidative stress, incidence of infection, and generation of inflammatory cytokines in sickle cell disease patients. Transl Res 152:67–80
Ueno H, Kajihara H, Nakamura H, Okuno T, Sakazaki F, Arakawa T, Ogino H, Nakamuro K, Yodoi J (2014) Effect of selenite on T-cell mitogenesis: contribution of ROS production and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Biol Pharm Bull 37:1352–1358
Meegan JE, Yang X, Coleman DC, Jannaway M, Yuan SY (2017) Neutrophil-mediated vascular barrier injury: Role of neutrophil extracellular traps. Microcirculation 24(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/micc.12352
Meng H, Yalavarthi S, Kanthi Y, Mazza LF, Elfline MA, Luke CE, Pinsky DJ, Henke PK, Knight JS (2017) In vivo role of neutrophil extracellular traps in antiphospholipid antibody-mediated venous thrombosis. Arthritis Rheum 69:655–667
Stoiber W, Obermayer A, Steinbacher P, Krautgartner WD (2015) The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the formation of extracellular traps (ETs) in humans. Biomolecules 5:702–723
Lentsch AB, Kato A, Saari JT, Schuschke DA (2001) Augmented metalloproteinase activity and acute lung injury in copper-deficient rats. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 281:L387–L393
Lominadze D, Saari JT, Percival SS, Schuschke DA (2004) Proinflammatory effects of copper deficiency on neutrophils and lung endothelial cells. Immunol Cell Biol 82:231–238
Shankar AH, Prasad AS (1998) Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr 68:447S–463S
Kommisrud E, Osteras O, Vatn T (2005) Blood selenium associated with health and fertility in Norwegian dairy herds. Acta Vet Scand 46(4):229–240
Kornhauser C, Garcia-Ramirez JR, Wrobel K, Pérez-Luque EL, Garay-Sevilla ME, Wrobel K (2008) Serum selenium and glutathione peroxidase concentrations in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Prim Care Diabetes 2(2):81–85
Harthill M (2011) Review: micronutrient selenium deficiency influences evolution of some viral infectious diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(3):1325–1336
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972747, 31772698) and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (c2018043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures used in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Wang, H., Lian, S. et al. Effect of Copper, Zinc, and Selenium on the Formation of Bovine Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 3312–3318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02477-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02477-1