Abstract
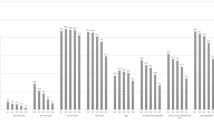
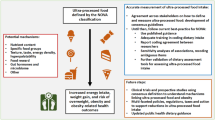
Dietary factors may play a key role in the etiology of obesity. The Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) provides a comprehensive overview of the nutrients content of the diet. This study aimed to investigate the association between INQ and obesity in male adolescents. We hypothesize that receiving a high-quality diet reduces the risk of overweight or obese. This study was carried out on 214 obese/overweight as the case group and 321 normal-weight male adolescents as the control group. Dietary intakes of the participants were collected using a food frequency questionnaire (FFQ). The FFQ-derived dietary data were used to calculate the INQ scores. After adjustments for age and height, an inverse association was found between obesity and INQ of iron, vitamin B6, and magnesium, and a positive association was found between obesity and INQ of zinc (all P < 0.05). After further adjustments for nutritional knowledge and calorie intake, an inverse association was observed between obesity and INQ of vitamin C, iron, vitamin B6, pantothenic acid, selenium, and magnesium (all P < 0.05). The positive association of obesity and INQ of zinc remained significant after adjustments. A higher intake of vitamin C, iron, vitamin B6, pantothenic acid, selenium, and magnesium and a lower intake of zinc may be protective against adolescent obesity. More longitudinal studies are required to investigate the relationship between these nutrients and obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han J, Law lor DA, Kimm SY (2010) Childhood obesity. Lancet 375(9727):1737–1748
Poobalan A, Aucott L (2016) Obesity among young adults in developing countries: a systematic overview. Curr Obes Rep 5(1):2–13
Aasheim ET, Hofsø D, Hjelmesæth J, Birkeland KI, Bøhmer T (2008) Vitamin status in morbidly obese patients: a cross-sectional study. Am J Clin Nutr 87(2):362–369
Welbourn R et al (2016) Why the NHS should do more bariatric surgery; how much should we do? Bmj 353:i1472
Haidar YM, Cosman BC (2011) Obesity epidemiology. Clinics Colon Rectal Surg 24(4):205–210
Nguyen DM, El-Serag HB (2010) The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 39(1):1–7
Caballero B (2007) The global epidemic of obesity: an overview. Epidemiol Rev 29(1):1–5
Ebbeling CB, Pawlak DB, Ludwig DS (2002) Childhood obesity: public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 360(9331):473–482
Hamilton D, Dee A, Perry IJ (2018) The lifetime costs of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence: a systematic review. Obes Rev 19(4):452–463
Gholamalizadeh M et al (2018) Influence of fat mass-and obesity-associated genotype, body mass index, and dietary intake on effects of iroquois-related homeobox 3 gene on body weight. Chin Med J 131(17):2113–2112
Kalantari N, Keshavarz Mohammadi N, Izadi P, Doaei S, Gholamalizadeh M, Eini-Zinab H, Salonurmi T, Rafieifar S, Janipoor R, Azizi Tabesh G (2018) A haplotype of three SNPs in FTO had a strong association with body composition and BMI in Iranian male adolescents. PloS One 13(4):e0195589
Slattery ML (2008) Defining dietary consumption: is the sum greater than its parts? Oxford University Press
Coulston AM (2001) The search continues for a tool to evaluate dietary quality. Oxford University Press
Vahid F, Hekmatdoost A, Mirmajidi S, Doaei S, Rahmani D, Faghfoori Z (2019) Association between index of nutritional quality and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the role of vitamin D and B group. Am J Med Sci 358(3):212–218
Sorenson AW, Wyse BW, Wittwer AJ, Hansen RG (1976) An index of nutritional quality for a balanced diet. New help for an old problem. J Am Diet Assoc 68(3):236–242
Vahid F et al (2020) A pro-inflammatory diet increases the likelihood of obesity and overweight in adolescent boys: a case–control study. Diabetol Metab Syndr 12:1–8
Mirmiran P, Hosseini Esfahani F, Mehrabi Y, Hedayati M, Azizi F (2010) Reliability and relative validity of an FFQ for nutrients in the Tehran lipid and glucose study. Public Health Nutr 13(5):654–662
Vasheghani-Farahani A, Tahmasbi M, Asheri H, Ashraf H, Nedjat S, Kordi R (2011) The Persian, last 7-day, long form of the international physical activity questionnaire: translation and validation study. Asian J Sports Med 2(2):106–116
Vahid F et al (2018) The association between index of nutritional quality (INQ) and gastric cancer and evaluation of nutrient intakes of gastric cancer patients: a case-control study. Int J Cancer Manag 11(1)
Mehrdad M, Vahid F, Eftekhari MH (2020) Nutritional quality’s key role in the odds of overweight in adults with rs9939609 polymorphism of FTO gene- the role of manganese and vitamin D. The Am J Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjms.2020.06.027
Abdollahpour I, Nedjat S, Salimi Y, Mansournia MA, Vahid F, Weinstock-Guttman B (2020) The role of dietary antioxidant index and index of nutritional quality in MS onset: finding from an Iranian population-based incident case–control study. Nutr Neurosci: 1–8
Hosseini B, Saedisomeolia A, Allman-Farinelli M (2017) Association between antioxidant intake/status and obesity: a systematic review of observational studies. Biol Trace Elem Res 175(2):287–297
Johnston CS, Beezhold BL, Mostow B, Swan PD (2007) Plasma vitamin C is inversely related to body mass index and waist circumference but not to plasma adiponectin in nonsmoking adults. J Nutr 137(7):1757–1762
Bae Y-J (2012) Evaluation of nutrient intake and anthropometric parameters related to obesity in Korean female adolescents according to dietary diversity score: from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2007-2009. Kor J Commun Nutr 17(4):419–428
Tussing-Humphreys LM, Liang H, Nemeth E, Freels S, Braunschweig CA (2009) Excess adiposity, inflammation, and iron-deficiency in female adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc 109(2):297–302
Chen M-D, Lin P-Y, Sheu WH-H (1997) Zinc status in plasma of obese individuals during glucose administration. Biol Trace Elem Res 60(1–2):123–129
Weisstaub G, Hertrampf E, López de Romaña D, Salazar G, Bugueño C, Castillo-Duran C (2007) Plasma zinc concentration, body composition and physical activity in obese preschool children. Biol Trace Elem Res 118(2):167–174
Ozata M, Mergen M, Oktenli C, Aydin A, Yavuz Sanisoglu S, Bolu E, Yilmaz MI, Sayal A, Isimer A, Ozdemir IC (2002) Increased oxidative stress and hypozincemia in male obesity. Clin Biochem 35(8):627–631
Morais JBS, Severo JS, Beserra JB, de Oiveira ARS, Cruz KJC, de Sousa Melo SR, do Nascimento GVR, de Macedo GFS, do Nascimento Marreiro D (2019) Association between cortisol, insulin resistance and zinc in obesity: a mini-review. Biol Trace Elem Res 191(2):323–330
Azab SF, Saleh SH, Elsaeed WF, Elshafie MA, Sherief LM, Esh AMH (2014) Serum trace elements in obese Egyptian children: a case–control study. Ital J Pediatr 40(1):20
Singh R, Beegom R, Rastogi SS, Gaoli Z, Shoumin Z (1998) Association of low plasma concentrations of antioxidant vitamins, magnesium and zinc with high body fat per cent measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis in Indian men. Magnes Res 11(1):3–10
ul Hassan SA et al (2017) Comparison of serum magnesium levels in overweight and obese children and normal weight children. Cureus 9(8)
Jose B, Jain V, Vikram NK, Agarwala A, Saini S (2012) Serum magnesium in overweight children. Indian Pediatr 49(2):109–112
Lelovics Z (2004) Relation between calcium and magnesium intake and obesity. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 13
Jastrzębska-Mierzyńska M, Ostrowska L, Hady HR, Dadan J (2012) Assessment of dietary habits, nutritional status and blood biochemical parameters in patients prepared for bariatric surgery: a preliminary study. Videosurg Other Miniinvas Techniq 7(3):156–165
Kim H-N, Song S-W, Choi W-S (2016) Association between serum zinc level and body composition: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutrition 32(3):332–337
García OP et al (2012) Zinc, vitamin A, and vitamin C status are associated with leptin concentrations and obesity in Mexican women: results from a cross-sectional study. Nutr Metab 9(1):59
Gibson RS, Skeaff M, Williams S (2000) Interrelationship of indices of body composition and zinc status in 11-yr-old New Zealand children. Biol Trace Elem Res 75(1–3):65–77
Huerta MG, Roemmich JN, Kington ML, Bovbjerg VE, Weltman AL, Holmes VF, Patrie JT, Rogol AD, Nadler JL (2005) Magnesium deficiency is associated with insulin resistance in obese children. Diabetes Care 28(5):1175–1181
Zafon C, Lecube A, Simo R (2010) Iron in obesity. An ancient micronutrient for a modern disease. Obes Rev 11(4):322–328
Nead KG, Halterman JS, Kaczorowski JM, Auinger P, Weitzman M (2004) Overweight children and adolescents: a risk group for iron deficiency. Pediatrics 114(1):104–108
Yoon J-SHJ (2011) Diet quality and food patterns of obese adult women from low income classes-based on 2005. KNHANES 11(6):706–715
Kim JY et al (2006) Dietary intakes and serum lipids and iron indices in obese children. Korean J Commun Nutr 11(5):575
Baltaci AKRM (2012) Leptin and zinc relation: in regulation of food intake and immunity. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 16(3):611
Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Baltaci SB (2019) The role of zinc in the endocrine system. Pak J Pharm Sci 32(1)
McKeown NM, Jacques PF, Zhang XL, Juan W, Sahyoun NR (2008) Dietary magnesium intake is related to metabolic syndrome in older Americans. Eur J Nutr 47(4):210–216
He K, Liu K, Daviglus ML, Morris SJ, Loria CM, van Horn L, Jacobs DR Jr, Savage PJ (2006) Magnesium intake and incidence of metabolic syndrome among young adults. Circulation 113(13):1675–1682
Błażewicz A, Klatka M, Astel A, Korona-Glowniak I, Dolliver W, Szwerc W, Kocjan R (2015) Serum and urinary selenium levels in obese children: a cross-sectional study. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:116–122
Garcia-Diaz DF et al (2014) Vitamin C in the treatment and/or prevention of obesity. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 60(6):367–379
Aeberli I, Molinari L, Spinas G, Lehmann R, l’Allemand D, Zimmermann MB (2006) Dietary intakes of fat and antioxidant vitamins are predictors of subclinical inflammation in overweight Swiss children. Am J Clin Nutr 84(4):748–755
McClung JP (2019) Iron, zinc, and physical performance. Biol Trace Elem Res 188(1):135–139
Scott SP, Murray-Kolb LE, Wenger MJ, Udipi SA, Ghugre PS, Boy E, Haas JD (2018) Cognitive performance in Indian school-going adolescents is positively affected by consumption of iron-biofortified pearl millet: a 6-month randomized controlled efficacy trial. J Nutr 148(9):1462–1471
Hutchinson C (2016) A review of iron studies in overweight and obese children and adolescents: a double burden in the young? Eur J Nutr 7(55):2179–2197
Komolova M, Bourque SL, Nakatsu K, Adams MA (2008) Sedentariness and increased visceral adiposity in adult perinatally iron-deficient rats. Int J Obes 32(9):1441–1444
McClung JP, Andersen NE, Tarr TN, Stahl CH, Young AJ (2008) Physical activity prevents augmented body fat accretion in moderately iron-deficient rats. J Nutr 138(7):1293–1297
Haas JDTBI (2001) Iron deficiency and reduced work capacity: a critical review of the research to determine a causal relationship. J Nutr 131(2):676S–690S
Funding
This study is related to the project NO. 1398/10596 from Student Research Committee, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. All colleagues in this university are warmly appreciated for their support and contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study has been approved by local ethics review boards at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences; all participants signed a written informed consent before the start of the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholamalizadeh, M., Rastgoo, S., Doaei, S. et al. Index of Nutritional Quality (INQ) and the Risk of Obesity in Male Adolescents: a Case-Control Study. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 1701–1706 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02297-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02297-3