Abstract
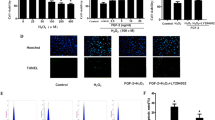
Chronic excessive fluoride intake is known to be toxic, and effects of long-term fluorosis on different organ systems have been examined. However, there are few studies about the effects of fluorosis on cardiovascular systems. Here, we studied the fluoride-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and determined the underlying molecular mechanisms including the cell viability, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, the changes of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), and the cell apoptosis. Sodium fluoride (NaF) at concentrations of 0, 2, 4, 8, and 16 mg/L was administered to cultured H9c2 cells for up to 48 h. After the treatment, H9c2 cells were collected and the associated parameters were measured by flow cytometry. Our study found that fluoride not only inhibited H9c2 cell proliferation but also induced cell apoptosis. With the increment of NaF concentration, the apoptotic rates and ROS generation were increased, while the ΔΨm was decreased. In summary, these data suggested that NaF-induced H9c2 cell apoptosis is mediated by direct increased intracellular ROS and downregulated ΔΨm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre-Sierra A, Alonso A, Camargo JA (2013) Fluoride bioaccumulation and toxic effects on the survival and behavior of the endangered white-clawed crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes (Lereboullet). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:244–250
Mukhopadhyay D, Chattopadhyay A (2014) Induction of oxidative stress and related transcriptional effects of sodium fluoride in female zebrafish liver. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93:64–70
Adali MK, Varol E, Aksoy F, Icli A, Ersoy IH, Ozaydin M, Erdogan D, Dogan A (2013) Impaired heart rate recovery in patients with endemic fluorosis. Biol Trace Elem Res 152:310–315
Trevors JT, Saier MH Jr (2009) Where is the global environmental bailout? Water Air Soil Pollut 198:1–3
Ayoob S, Gupta A (2006) Fluoride in drinking water: a review on the status and stress effects. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 55:433–487
Wang Y, Gu ZW (1996) Modern occupational medicine. People's medical publishing house, Beijing
Cicek E, Aydin G, Akdogan M, Okutan H (2005) Effects of chronic ingestion of sodium fluoride on myocardium in a second generation of rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 24:79–87
Basha MP, Sujitha NS (2011) Chronic fluoride toxicity and myocardial damage: antioxidant offered protection in second generation rats. Toxicol Int 18:99–104
Zhan WC, He DJ (1988) Ultrastructural findings in liver, kidneys, thyroid gland and myocardium of rabbits following sodium fluoride administration. J Guiyang Med Coll 13:129–132
Bian J, Lin X, Yang X, Fan T, Zhu Q (2010) Changes of certain oxidative, anti-oxidative and vascular function indexes of New Zealand rabbit exposed by high-fluoride. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 39:751–754
Shen XY, Ruan Q, Zhang ZG, Xu XL (2003) Influence of fluorosis on hemodynamics of rats. Chin J Control Endemic Dis 18:208–209
Cheng RY, Nie QL, Sun HF, Zhang YJ, Wu LH, Ma YQ, Yan XY (2013) Fluoride-induced oxidative stress in rat myocardium through the Bax/Bcl-2 signalling pathway. Fluoride 46(4):198–203
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2008) Terminalia arjuna protects mouse hearts against sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress. J Med Food 11:733–740
Ly JD, Grubb DR, Lawen A (2003) The mitochondrial membrane potential (∆ψm) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis 8:115–128
Kroemer G, Zazami N, Susin SA (1997) Immunol Today 18:44–51
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Kowaltowski AJ, Netto LE, Vercesi AE (1998) The thiol-specific antioxidant enzyme prevents mitochondrial permeability transition. Evidence for the participation of reactive oxygen species in this mechanism. J Biol Chem 273:12766–12769
Cai J, Jones DP (1998) Superoxide in apoptosis. Mitochondrial generation triggered by cytochrome c loss. J Biol Chem 273:11401–11404
Kim CN, Wang X, Huang Y, Ibrado AM, Liu L, Fang G, Bhalla K (1997) Overexpression of Bcl-X (L) inhibits Ara-C-induced mitochondrial loss of cytochrome C and other perturbations that activate the molecular cascade of apoptosis. Cancer Res 57:3115–3120
Duranteau J, Chandel NS, Kulisz A, Shao Z, Schumacker PT (1998) Intracellular signaling by reactive oxygen species during hypoxia in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem 273:11619–11624
Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y, Kang YJ (2002) Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium: mitochondrial cytochrome c-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway. Diabetes 51:1938–1948
Sun Z, Niu R, Wang B, Jiao Z, Wang J, Zhang J, Wang S, Wang J (2011) Fluoride-induced apoptosis and gene expression profiling in mice sperm in vivo. Arch Toxicol 85:1441–1452
Ge Y, Niu R, Zhang J, Wang J (2011) Proteomic analysis of brain proteins of rats exposed to high fluoride and low iodine. Arch Toxicol 85:27–33
Yan X, Feng C, Chen Q, Li W, Wang H, Lv L, Smith GW, Wang J (2009) Effects of sodium fluoride treatment in vitro on cell proliferation, apoptosis and caspase-3 and caspase-9 mRNA expression by neonatal rat osteoblasts. Arch Toxicol 83:451–458
Dubey N, Khan AM, Raina R (2013) Sub-acute deltamethrin and fluoride toxicity induced hepatic oxidative stress and biochemical alterations in rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:334–338
Shivashankara AR, Shivarajashankara YM, Bhat PG, Rao SH (2002) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in liver of rats in chronic fluoride toxicity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:612–616
Hassan HA, Yousef MI (2009) Mitigating effects of antioxidant properties of black berry juice on sodium fluoride induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47:2332–2337
Ranjan R, Swarup D, Patra RC (2009) Oxidative stress indices in erythrocytes, liver, and kidneys of fluoride-exposed rabbits. Fluoride 42:88–93
Dönmez N, Çinar A (2003) Effects of chronic fluorosis on electrocardiogram in sheep. Biol Trace Elem Res 92:115–121
Miyamoto H, Doita M, Nishida K, Yamamoto T, Sumi M, Kurosaka M (2006) Effects of cyclic mechanical stress on the production of inflammatory agents by nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus derived cells in vitro. Spine 31:4–9
Sohal RS, Weindruch R (1996) Oxidative stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science 273:59–63
Beatty S, Koh H, Phil M et al (2000) The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol 45:115–134
Sang H, Zhang L, Li J (2012) Anti-benzopyrene-7, 8-diol-9, 10-epoxide induces apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in human bronchiolar epithelium cells independent of the mitochondria permeability transition pore. Food Chem Toxicol 50:2417–2423
Khan M, Ding C, Rasul A, Yi F, Li T, Gao H, Gao R, Zhong L, Zhang K, Fang X, Ma T (2012) Isoalantolactone induces reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in pancreatic carcinomapanc-1 cells. Int J Biol Sci 8:533–547
Barbier O, Arreola-Mendoza L, Del Razo LM (2010) Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 188:319–333
Carmody RJ, Cotter TG (2001) Signalling apoptosis: a radical approach. Redox Reports 6:77–90
Chandra J, Samali A, Orrenius S (2000) Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 29:323–333
Shih CM, Ko WC, Wu JS, Wei YH, Wang LF, Chang EE, Lo TY, Cheng HH, Chen CT (2004) Mediating of caspase-independent apoptosis by cadmium through the mitochondria-ROS pathway in MRC-5 fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem 91:384–397
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the China National Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 31240009, 31302158); Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (Grant No. 2012–079); Shanxi Province Science and Technology Bureau Program (Grant Nos. 2011021030-1, No. 2013011059-1) and Shanxi Province Soft Science (Grant No. 2013041084-03)
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Yang, X., Hao, X. et al. Sodium Fluoride Induces Apoptosis in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes by Altering Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Intracellular ROS Level. Biol Trace Elem Res 166, 210–215 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0273-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0273-z