Abstract
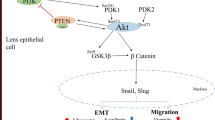
Zinc is one of the most abundant essential elements in the human body, which is an essential, coenzyme-like component of many enzymes, and is indispensable to their functions. However, high levels of zinc ions can lead to cell damage. In the present study, we explored the effects of high concentrations of zinc chloride (ZnCl2) on lens epithelial cell proliferation and migration and further investigated the effects of different concentrations of ZnCl2 on caspase-9 and caspase-12, transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). We found that ZnCl2 could inhibit human lens epithelial (HLE) B-3 cell migration and induce apoptosis/necrosis. In addition, ZnCl2 can efficiently decrease the expressions of caspase-9 and caspase-12, increase the expression of TNF-α at both gene and protein levels, and thus induces cell death. Taken together, our results indicate that ZnCl2 can inhibit HLE B-3 cell migration and proliferation by decreasing the expression of TGF-β1 and increasing the expression of TNF-α and finally lead to HLE B-3 cell death.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vallee BL (1988) Zinc: biochemistry, physiology, toxicology and clinical pathology. Biofactors 1:31–36
Feng P, Li TL, Guan ZX et al (2002) Direct effect of zinc on mitochondrial apoptogenesis in prostate cells. Prostate 52:311–318
Morris DR, Levenson CW (2012) Ion channels and zinc: mechanisms of neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. J Toxicol 2012:785647
Chang I, Cho N, Koh JY et al (2003) Pyruvate inhibits zinc-mediated pancreatic islet cell death and diabetes. Diabetologia 46:1220–1227
Strasser A, O’Connor L, Dixit VM (2000) Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 69:217–245
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Heyninck K, Beyaert R (2001) Crosstalk between NF-kappaBactivating and apoptosis-inducing proteins of the TNF-receptor complex. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 4:259–265
Balkwill F (2009) Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:361–371
Chang KL, Hung TC, Hsieh BS et al (2006) Zinc at pharmacologic concentrations affects cytokine expression and induces apoptosis of human peripheralblood mononuclear cells. Nutrition 22:465–474
Argun M, Tök L, Uğuz AC et al (2012) Melatonin and amfenac modulate calcium entry, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in ARPE-19 cell culture exposed to blue light irradiation (405 nm). Eye (Lond). doi:10.1038/eye.2014.50
Nazıroğlu M, Yoldaş N, Uzgur EN et al (2013) Role of contrast media on oxidative stress, Ca(2+) signaling and apoptosis in kidney. J Membr Biol 246:91–100
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Denault JB, Eckelman BP, Shin H et al (2007) Caspase 3 attenuates XIAP (X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein)-mediated inhibition of caspase 9. Biochem J 405:11–19
Radisky DC, Kenny PA, Bissell MJ (2007) Fibrosis and cancer: do myofibroblasts come also from epithelial cells via EMT? J Cell Biochem 101:830–839
Kalluri R, Neilson EG (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest 112:1776–1784
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Wormstone IM (2002) Posterior capsule opacification: a cell biological perspective. Exp Eye Res 74:337–347
Nelson CM, VanDuijn MM, Inman JL et al (2006) Tissue geometry determines sites of mammary branching morphogenesis in organotypic cultures. Science 314:298–300
Taylor MA, Parvani JG, Schiemann WP (2010) The pathophysiology of epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by transforming growth factor-β in normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 15:169–190
Awasthi N, Guo S, Wagner BJ (2009) Posterior capsular opacification: a problem reduced but not yet eradicated. Arch Ophthalmol 127:555–562
Liu J, Hales AM, Chamberlain CG et al (1994) Induction of cataract-like changes in rat lens epithelial explants by transforming growth factor /3. Invest Ophthalmol Us Sci 35:388–401
Taibi A, Mandavawala KP, Noel J et al (2013) Zebrafish churchill regulates developmental gene expression and cell migration. Dev Dyn 242:614–621
Grahn BH, Paterson PG, Gottschall-Pass KT et al (2001) Zinc and the eye. J Am Coll Nutr 20:106–118
Guo DD, Bi HS, Wang DG et al (2013) Zinc oxide nanoparticles decrease the expression and activity of plasma membrane calcium ATPase, disrupt the intracellular calcium homeostasis in rat retinal ganglion cells. Int J Biochem Cell B 45:1849–1859
Jansen S, Arning J, Beyersmann D (2003) Effects of the Ca ionophore a23187 on zinc-induced apoptosis in C6 glioma cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 96:133–142
Uguz AC, Cig B, Espino J et al (2012) Melatonin potentiates chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in rat pancreatic tumor cells. J Pineal Res 53:91–98
Kim SJ, Eum HA, Billiar TR et al (2013) Role of heme oxygenase 1 in TNF/TNF receptor-mediated apoptosis after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Shock 39:380–388
Truong-Tran AQ, Carter J, Ruffin RE et al (2001) The role of zinc in caspase activation and apoptotic cell death. Biometals 14:315–330
Maret W, Jacob C, Vallee BL et al (1999) Inhibitory sites in enzymes: zinc removal and reactivation by thionein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1936–1940
Kown MH, Van Der Steenhoven T, Blankenberg FG et al (2000) Zinc-mediated reduction of apoptosis in cardiac allografts. Circulation 102:228–232
Sakurai M, Takahashi G, Abe K et al (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced in motor neurons by transient spinal cord ischemia in rabbits. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 130:640–645
Palsamy P, Bidasee KR, Shinohara T (2014) Valproic acid suppresses Nrf2/Keap1 dependent antioxidant protection through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and Keap1 promoter DNA demethylation in human lens epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 121C:26–34
Bian Q, Fernandes AF, Taylor A et al (2008) Expression of K6W-ubiquitin in lens epithelial cells leads to upregulation of a broad spectrum of molecular chaperones. Mol Vis 14:403–412
Huber KL, Hardy JA (2012) Mechanism of zinc-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Protein Sci 21:1056–1065
Rudolf E, Cervinka M (2006) Cytoskeletal changes in non-apoptotic cell death. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 49:123–128
Sensi SL, Ton-That D, Sullivan PG et al (2003) Modulation of mitochondrial function by endogenous Zn2+ pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6157–6162
Kondoh M, Tasaki E, Araragi S et al (2002) Requirement of caspase and p38MAPK activation in zinc-induced apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Eur J Biochem 269:6204–6211
Mann JJ, Fraker PJ (2005) Zinc pyrithione induces apoptosis and increases expression of Bim. Apoptosis 10:369–379
Wilson MR, Foucaud L, Barlow PG et al (2007) Nanoparticle interactions with zinc and iron: implications for toxicology and inflammation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 225:80–89
Kou X, Jing Y, Deng W et al (2013) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha attenuates starvation-induced apoptosis through upregulation of ferritin heavy chain in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 13:438
Zhou P, Lu Y, Sun XH (2012) Effects of a novel DNA methyltransferase inhibitor Zebularine on human lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis 18:22–28
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong province (ZR2010HM032).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Guo, D., Wu, Q. et al. Zinc Chloride Inhibits Human Lens Epithelial Cell Migration and Proliferation Involved in TGF-β1 and TNF-α Signaling Pathways in HLE B-3 Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 159, 425–433 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9979-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9979-6