Abstract
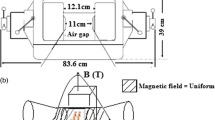
Electromagnetic pulse (EMP) was a potentially harmful factor to the human body, and a biological dosimetry to evaluate effects of EMP is necessary. Little is known about effects of EMP on concentration of macro and trace elements in serum so far. In this study, Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 50-kV/m EMP-exposed group (n = 10), 100-kV/m EMP-exposed group (n = 10), 200-kV/m EMP-exposed group (n = 40), and the sham-exposed group (n = 20). The macro and trace element concentrations in serum were examined at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after EMP exposure at different electric field intensities. Compared with the sham-exposed groups, the concentration of sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), selenium (Se), and manganese (Mn) in rat serum was not changed significantly within 48 h after 200 pulses of EMP exposure at electric field intensity of 50, 100, and 200 kV/m although the K level was decreased and the Ca level was increased with the electric field intensity of EMP increasing. In addition, there was a tendency that the Zn level was decreased with the time going on within 48 h after EMP exposure. Under our experimental conditions, EMP exposure cannot affect the concentration of macro and trace elements in rat serum. There was no time–effect or dose–effect relationship between EMP exposure and serum element levels. The macro and trace elements in serum are not suitable endpoints of biological dosimetry of EMP.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMP:
-
Electromagnetic pulse
- Na:
-
Sodium
- K:
-
Potassium
- Mg:
-
Magnesium
- Ca:
-
Calcium
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- Cu:
-
Copper
- Fe:
-
Iron
- Se:
-
Selenium
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- GTEM:
-
Gigahertz transverse electromagnetic
References
Chen YB, Li J, Liu JY, Zeng LH, Wan Y, Li YR, Ren D, Guo GZ (2011) Effect of electromagnetic pulses (EMP) on associative learning in mice and a preliminary study of mechanism. Int J Radiat Biol 87(12):1147–1154
Ding GR, Li KC, Wang XW, Zhou YC, Qiu LB, Tan J, Xu SL, Guo GZ (2009) Effect of electromagnetic pulse exposure on brain micro vascular permeability in rats. Biomed Environ Sci 22(3):265–268
Jiang DP, Li J, Zhang J, Xu SL, Kuang F, Lang HY, Wang YF, An GZ, Li JH, Guo GZ (2013) Electromagnetic pulse exposure induces overexpression of beta amyloid protein in rats. Arch Med Res 44(3):178–184
Wang XW, Ding GR, Shi CH, Zeng LH, Liu JY, Li J, Zhao T, Chen YB, Guo GZ (2010) Mechanisms involved in the blood-testis barrier increased permeability induced by EMP. Toxicology 276(1):58–63
Yang MJ, Liu JY, Wang YF, Lang HY, Miao X, Zhang LY, Zeng LH, Guo GZ (2013) Effects of electromagnetic pulse on polydactyly of mouse fetuses. Theriogenology 80(1):18–23
Brodziak-Dopierala B, Kwapulinski J, Kusz D, Gajda Z, Sobczyk K (2009) Interactions between concentrations of chemical elements in human femoral heads. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57(1):203–210
Naziroglu M (2011) TRPM2 cation channels, oxidative stress and neurological diseases: where are we now? Neurochem Res 36(3):355–366
Naziroglu M (2012) Molecular role of catalase on oxidative stress-induced Ca(2+) signaling and TRP cation channel activation in nervous system. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 32(3):134–141
Prasad AS (1998) Zinc in human health: an update. J Trace Elem Exp Med 11:63–87
Fatmi W, Kechrid Z, Naziroglu M, Flores-Arce M (2013) Selenium supplementation modulates zinc levels and antioxidant values in blood and tissues of diabetic rats fed zinc-deficient diet. Biol Trace Elem Res 152(2):243–250
Erikson KM, Syversen T, Aschner JL, Aschner M (2005) Interactions between excessive manganese exposures and dietary iron-deficiency in neurodegeneration. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19(3):415–421
Rana SV (2008) Metals and apoptosis: recent developments. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22(4):262–284
Naziroglu M, Celik O, Ozgul C, Cig B, Dogan S, Bal R, Gumral N, Rodriguez AB, Pariente JA (2012) Melatonin modulates wireless (2.45 GHz)-induced oxidative injury through TRPM2 and voltage gated Ca(2+) channels in brain and dorsal root ganglion in rat. Physiol Behav 105(3):683–692
Naziroglu M, Tokat S, Demirci S (2012) Role of melatonin on electromagnetic radiation-induced oxidative stress and Ca2+ signaling molecular pathways in breast cancer. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 32(6):290–297
Ozorak A, Naziroglu M, Celik O, Yuksel M, Ozcelik D, Ozkaya MO, Cetin H, Kahya MC, Kose SA (2013) Wi-Fi (2.45 GHz)- and mobile phone (900 and 1800 MHz)-induced risks on oxidative stress and elements in kidney and testis of rats during pregnancy and the development of offspring. Biol Trace Elem Res 156(1–3):221–9
Li KC, Hui YP, Ma SR, Ding GR, Guo Y, Liu JY, Li YR, Guo GZ (2011) Inhibition of bone formation by high intensity pulsed electromagnetic field in MC3T3-E1 cells. Prog Electromagn Res 112:139–153
Bonhomme-Faivre L, Mace A, Bezie Y, Marion S, Bindoula G, Szekely AM, Frenois N, Auclair H, Orbach-Arbouys S, Bizi E (1998) Alterations of biological parameters in mice chronically exposed to low-frequency (50 Hz) electromagnetic fields. Life Sci 62(14):1271–1280
Burchard JF, Nguyen DH, Block E (1999) Macro- and trace element concentrations in blood plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of dairy cows exposed to electric and magnetic fields. Bioelectromagnetics 20(6):358–364
Gulczynska E, Gadzinowski J, Wilczynski J, Zylinska L (2006) Prenatal MgSO4 treatment modifies the erythrocyte band 3 in preterm neonates. Pharmacol Res 53(4):347–352
Kayan M, Naziroglu M, Barak C (2010) Effects of vitamins C and E combination on element levels in blood of smoker and nonsmoker radiology X-ray technicians. Biol Trace Elem Res 136(2):140–148
Karakoc Y, Buruk MS, Aktan B, Kirvar R, Erdogan S, Sahbaz MA, Aksoy S, Gulyasar T (2011) Effects of chronic light/dark cycle on iron zinc and copper levels in different brain regions of rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 144(1–3):1003–1007
Akdag MZ, Dasdag S, Aksen F, Isik B, Yilmaz F (2006) Effect of ELF magnetic fields on lipid peroxidation, sperm count, p53, and trace elements. Med Sci Monit 12(11):BR366–BR371
Ghodbane S, Amara S, Arnaud J, Garrel C, Faure H, Favier A, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2011) Effect of selenium pre-treatment on plasma antioxidant vitamins A (retinol) and E (alpha-tocopherol) in static magnetic field-exposed rats. Toxicol Ind Health 27(10):949–955
Ebisch IM, Thomas CM, Peters WH, Braat DD, Steegers-Theunissen RP (2007) The importance of folate, zinc and antioxidants in the pathogenesis and prevention of subfertility. Hum Reprod Update 13(2):163–174
Favier AE (1992) The role of zinc in reproduction: hormonal mechanisms. Biol Trace Elem Res 32:363–382
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30800928).
Conflict of Interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kangchu Li and Shirong Ma contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Ma, S., Ren, D. et al. Effects of Electromagnetic Pulse on Serum Element Levels in Rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 158, 81–86 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9903-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9903-0