Abstract
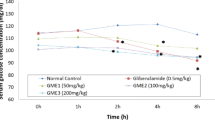
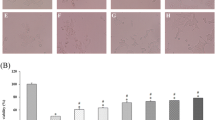
In order to obtain the additional benefit of anti-diabetic activity and protective effects of liver injury for diabetes, the anti-diabetic effect and acute oral toxicity of a combination of chromium(III) malate complex (Cr2(LMA)3) and propolis were assessed. The anti-diabetic activity of the combination of the Cr2LMA3 and propolis was compared with Cr2(LMA)3 and propolis alone in alloxan-induced diabetic mice by daily oral gavage for a period of 2 weeks. Acute oral toxicity of the combination of the Cr2LMA3 and propolis was tested using ICR mice at the dose of 1.0–5.0 g/kg body mass by a single oral gavage and observed for a period of 2 weeks. The results of the anti-diabetic activity of the combination from the aspects of blood glucose level, liver glycogen level, and the activities of aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, and alkaline phosphatase indicated that the increased anti-diabetic activity and the protective efficacy of liver injury for diabetes were observed. In acute toxicity study, LD50 (median lethal dose) value for the combination was greater than 5.0 g/kg body mass. The combination of Cr2LMA3 and propolis might represent the nutritional supplement with potential therapeutic value to control blood glucose and exhibit protective efficacy of liver injury for diabetes and non-toxicity in acute toxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rayfield E, Ault M, Keusch G et al (1982) Infection and diabetes: the case for glucose control. Am J Med 72:439–450
Bahaa KAA-S (2011) Immunomodulatory effects of black seeds and garlic on alloxan-induced diabetes in albino rat. Allergol Immunopath. doi:10.1016/j.aller.2011.07.002
Ferracini M, Martins JO, Campos MR et al (2010) Impaired phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages from diabetic rats is related to the deficient coupling of LTs to the Fc gamma R signaling cascade. Mol Immunol 47:1974–1980
Halliwell B, Gutteridge J (1985) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford, London
Mansour HA, Newairy A-SA, Yousef MI et al (2002) Biochemical study on the effects of some Egyptian herbs in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Toxicology 170:221–228
Sharma S, Agrawal RP, Choudhary M et al (2011) Beneficial effect of chromium supplementation on glucose, HbA1C and lipid variables in individuals with newly onset type-2 diabetes. J Trace Elem Med Biol. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2011.03.003
Anderson RA (2003) Chromium and insulin resistance. Nutr Res Rev 16:267–275
Sreekanth R, Pattabhi V, Rajan SS (2008) Molecular basis of chromium insulin interactions. Biochem Bioph Res Co 369:725–729
Trent LK, Tiedingcancel DJSM (1995) Effects of chromium picolinate on body composition. J Sport Med Phys Fit 35:273–280
Dogukan A, Tuzcu M, Juturu V et al (2010) Effects of chromium histidinate on renal function, oxidative stress, and heat-shock proteins in fat-fed and streptozotocin-treated rats. J Renal Nutr 20:112–120
Jennings DS, Brevard PB, Flohr JA et al (1997) Chromium nicotinate supplementation: effects on body composition and strength in female collegiate athletes participating in off-season training. J Am Diet Assoc 97:A65
Li F, Wu X-Y, Zhao T et al (2011) Anti-diabetic properties of chromium citrate complex in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 25:218–224
Wu X-Y, Li F, Xu W-D et al (2011) Anti-hyperglycemic activity of chromium(III) malate complex in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1031–1043
Sulaiman GM, Sammarrae KWA, Ad’hiah AH et al. Chemical characterization of Iraqi propolis samples and assessing their antioxidant potentials (2011) Food Chem Toxicol doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.06.060
Orsolic N, Knezevic AH, Sver L et al (2004) Immunomodulatory and antimetastatic action of propolis and related polyphenolic compounds. J Ethnopharmacol 94:307–315
Girgin G, Baydar T, Ledochowski M et al (2009) Immunomodulatory effects of Turkish propolis: changes in neopterin release and tryptophan degradation. Immunobiology 214:129–134
Fuliang HU, Hepburn HR, Xuan H et al (2005) Effects of propolis on blood glucose, blood lipid and free radicals in rats with diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol Res 51:147–152
Çetin E, Kanbur M, Silici S et al (2010) Propetamphos-induced changes in haematological and biochemical parameters of female rats: protective role of propolis. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1806–1810
Nair SA, Shylesh BS, Gopakumar B et al (2006) Anti-diabetes and hypoglycaemic properties of Hemionitis arifolia (Burm.) Moore in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 106:192–197
Buccolo G, David M (1973) Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by use of enzyme. Clin Chem 19:476–482
Carroll NV, Longly RW, Joseph HR (1956) Determination of glycogen in liver and muscle by use of anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem 220:583–593
Yang X-P, Li S-Y, Dong F et al (2006) Insulin-sensitizing and cholesterol-lowering effects of chromium (d-Phenylalanine)3. J Inorg Biochem 100:1187–1193
Król E, Krejpcio Z (2010) Chromium(III) propionate complex supplementation improves carbohydrate metabolism in insulin-resistance rat model. Food Chem Toxicol 48:2791–2796
Król E, Krejpcio Z (2011) Evaluation of anti-diabetic potential of chromium(III) propionate complex in high-fat diet fed and STZ injected rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:3217–3223
Matsushige K, Basnet P, Hasa K et al (1996) Propolis protects pancreatic beta-cells against the toxicity of streptozotocin (STZ). Phytomedicine 3:203–209
Kim D-S, Kim T-W, Park I-K et al (2002) Effects of chromium picolinate supplementation on insulin sensitivity, serum lipids, and body weight in dexamethasone-treated rats. Metabolism 51:589–594
Lukivskaya O, Patsenker E, Buko VU (2007) Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on liver mitochondrial function in rats with alloxan-induced diabetes: link with oxidative stress. Life Sci 80:2397–2402
Ghosh R, Sharatchandra K, Rita S et al (2004) Hypoglycemic activity of Ficus hispida (bark) in normal and diabetic albino rats. Ind J Phamacol 36:222–225
Kolankaya D, Selmanog LuG et al (2002) Protective effects of Turkish propolis on alcohol-induced serum lipid changes and liver injury in male rats. Food Chem 78:213–217
Bhadauria M, Nirala SK, Shukla S (2008) Multiple treatment of propolis extract ameliorates carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2703–2712
Ferrannini E, Lanfranchi A, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F et al (1990) Influence of long-term diabetes on liver glycogen metabolism in the rat. Metabolism 39:1082–1088
Hems DA, Harmon CS, Whitton PD (1975) Inhibition by parathyroid hormone of glycogen synthesis in the perfused rat liver. FEBS Lett 58:167–169
Bhadauria M, Nirala SK (2009) Reversal of acetaminophen induced subchronic hepatorenal injury by propolis extract in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharm 27:17–25
Wang ZQ, Zhang XH, Cefalu WT (2000) Chromium picolinate and biotin enhance glycogen synthesis and glycogen synthase gene expression in human skeletal muscle culture. Diabet Res Clin Pr 50(Supplement 1):395
Loomis TA, Hayes AW (1996) Academic Press (San Diego) California; Vol. 4th Edition
Staniek H, Krejpcio Z, Iwanik K (2010) Evaluation of the acute oral toxicity class of tricentric chromium(III) propionate complex in rat. Food Chem Toxicol 48:859–864
Shara M, Yasmin T, Kincaid AE et al (2005) Safety and toxicological evaluation of a novel niacin-bound chromium (III) complex. J Inorg Biochem 99:2161–2183
Mohammadzadeh S, Shariatpanahi M, Hamedi M et al (2007) Chemical composition, oral toxicity and antimicrobial activity of Iranian propolis. Food Chem 103:1097–1103
Burdock GA (1998) Review of the biological properties and toxicity of bee propolis (propolis). Food Chem Toxicol 36:347–363
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20103227110004) and Graduate innovative projects in Jiangsu University (CX10B_019X). All authors thank Dr. Mohammed Takase for the language revising and polishing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, XY., Li, F., Zhao, T. et al. Enhanced Anti-Diabetic Activity of a Combination of Chromium(III) Malate Complex and Propolis and its Acute Oral Toxicity Evaluation. Biol Trace Elem Res 148, 91–101 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9347-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9347-3