Abstract
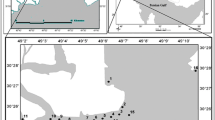
This study aims to investigate the pollution rate of heavy metals on the western seaboard of Bandarabbas in southeast Iran using a new pollution index. The bulk of the analysis was conducted on sediments, followed by selection of a few samples to perform experiments on chemical partitioning studies as well as biological accessibility. On this basis, the proportions of natural and anthropogenic elements were calculated. Finally, with regard to chemical separation results, the pollution rate was calculated based on Muller's geo-chemical index, enrichment factor, pollution index, and a new "Risk" index. Chemical separation showed the anthropogenic origin of elements are as follows: Ni(27.5%) > Zn(6.5%) > Pb(2%) > Al (0.2%). The newly developed pollution index is indicative of "low environmental pollution "for Ni.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viarengo A (1989) Heavy metals in marine invertebrates: mechanisms of regulation and toxicity at the cellular level. Rev Aquat 1(2):295–317
Kennish MJ (1997) Estuarine and marine pollution: heavy metals. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 253
Clarck RB (1992) Marine pollution. Oxford, Oxford University Press, pp 172–184
Luoma SN (1990) Processes affecting metal concentrations in estuarine and coastal marine sediments. In: Furrness RW, Rainbow PS (eds) Heavy metals in the marine environment. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 51–66
Heyvaert AC, Reuter JE, Sloton DG, Goldman CR (2000) Paleo-limnological reconstruction of historical atmospheric lead and Hg deposition at Lake Tahoe, California–Nevada. J Environ Sci Tech 34:3588–3597
Yang H, Rose NL (2003) Distribution of Hg in the lake sediments across the UK. Sci Total Environ 304:391–404
Caccia VG, Millero FJ, Palanques A (2003) The distribution of trace metals in Florida Bay sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1420–1433
Adams WJ, Kimerle RA, Barnett RA Jr (1992) Sediment quality and aquatic life assessment. Environ Sci Tech 26:1865–1875
Burton GA Jr, Scott KJ (1992) Sediment toxicity evaluation, their niche in ecological assessment. Environ Sci Tech 26:2068–2075
Sinex SA, Wright DA (1988) Distribution of trace metals in the sediments and biota of Chesapeake Bay. Mar Pollut Bull 19:425–431
Bryan GW, Langstone WJ (1992) Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: a review. Environ Pollut 76:89–131
Allen JRL, Rae JE (1986) Time sequence of metal pollution, Severn Estuary, southwestern UK. Mar Pollut Bull 17:427–431
Barcellos C, Rezende CE, Pfeiffer WC (1991) Zn and Cd production and pollution in a Brazilian coastal region. Mar Pollut Bull 22(11):558–561
Farmer JG (1991) The perturbation of historical pollution records in aquatic systems. Environ Geochem Health 13(2):76–83
Coker WB, Kettles IM, Shilts WW (1995) Comparison of mercury concentrations in modern lake sediments and glacial drift in the Canadian Shield in the region of Ottawa/Kingston to Georgian Bay, Ontario, Canada. Water, Air and Soil Poll 80:1025–1029
Birch GF, Evenden D, Teutsch ME (1996) Dominance of point source in heavy metal distributions in sediments of a major Sydney estuary (Australia). Environ Geo 28(4):169–174
Lottermoser BG (1998) Heavy metal pollution of coastal river sediments, north-eastern New South Wales, Australia: lead isotope and chemical evidence. Environ Geol 36(1–2):118–126
Gallasso JL, Siegel FR, Kravitz JH (2000) Heavy metals in eight 1965 cores from the Novaya Zemlya Trough, Kara Sea, Russian Arctic. Mar Pollut Bull 40(10):839–852
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300(1–3):229–243
Al-Masri MS, Aba A, Khalil H, Al-Hares Z (2002) Sedimentation rates and pollution history of a dried lake: Al-Oteibeh Lake. Sci Total Environ 293(1–3):177–189
Feng H, Han X, Zhang W, Yu L (2004) A preliminary study of heavy metal contamination in Yangtze River intertidal zone due to urbanization. Mar Pollut Bull 49(11-12):910–915
Pekey H (2006) The distribution and sources of heavy metals in Izmit Bay surface sediments affected by a polluted stream. Mar Pollu Bull 52(10):1197–1208
Owen RB, Sandhu N (2000) Heavy metal accumulation and anthropogenic impacts on Tolo Harbour, Hongkong. Mar Poll Bull 40(2):174–180
Spencer KL (2002) Spatial variability of metals in the inter-tidal sediments of the Medway Estuary, Kent, UK. Mar Pollut Bull 44:933–944
De Carlo EH, Anthony SA (2002) Spatial and temporal variability of trace element concentrations in an urban subtropical watershed, Honolulu, Hawaii. Appl Geochem 17:475–492
Arellano JM, Ortiz JB, Capeta da Silva D, Gonzalez de Cannales MI, Sarasquete C, Blasco J (1999) Levels of copper, zinc, manganese and iron in two fish species from salt marshes of Cadis Bay(southwest Iberian Peninsuala). Boletin del Instituto Espanol de Oceanografia 15(1–4):458–488
Cohen T, Hee S, Ambrose R (2001) Trace metals in fish and invertebrates of three California coastal wetlands. Mar Pollut Bull 42(3):232–242
Hutchinson GE (1957) A treatise on limnology. V.1, Geography, physics and chemistry. Wiley, New York, p 1015
Ruttner F (1963) Fundamentals of limnology. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, p 295
Mortimer CH (1971) The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. Part III and IV. J Ecol 30:147–207
Sain KS, Neufeld RD (1942) A dynamic model of biogeochemical cycle of heavy and trace metals in natural aquatic systems. Paper presented at the Second International Symposium on Environmental Biogeochemistry. Burlington, Ontario, Canada, 20
Coker WB, Shilts WW (1979) Lacustrine geochemistry around the north shore of Lake Superior: implications for the evaluation of the effects of acid precipitation. In Current Research, Part C, Geological Survey of Canada, Paper 79-1°C: 1–15
Butman B, Bothner MH (1998) Predicting the long-term fate of sediments and contaminants in Massachusetts Bay. US Geological Survey Fact Sheet, 172–97
Förstner U, Wittman G (1981) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment, 2nd edn. Springer, NY, pp 110–270
Holm NG (1988) Arsenic regeneration from estuarine sediments of the Bothnian Bay, Sweden. J Chem Geol 68:89–98
Chester R, Hughes RM (1967) A chemical technique for the separation of ferromanganese minerals, carbonate minerals and adsorbed trace elements from pelagic sediments. Chem Geol 2:249–262
Lee SV, Cundy AB (2001) Heavy metal contamination and mixing processes in sediments from the Humber Estuary, Eastern England. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 53(5):619–636
Karbassi AR, Amirnezhad R (2004) Geochemistry of heavy metals and sedimentation rate in a bay adjacent to the Caspian Sea. Int J Environ Sci Tech 1(3):199–206
MOOPAM–ROPME (1999) Manual of oceanographic observations and pollutant analysis methods. MOOPAM, Kuwait
Chen Z (2004) Low concentration of heavy metals in the Yangtze estuarine sediments, China: a diluting setting. Estuarine Coast Shel Sci 60(1):91–100
Davis JC (1973) Statistics and data analysis in geology. Wiley International, New York
Karbassi AR, Monavari SM, Nabi Bidhendi Gh R, Nouri J (2008) Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environ Monit Assess 147:107–116
Karbassi AR (1997) Geochemistry of Ni, Zn, Cu, Pb, Co, Cd, V, Mn, Fe, Al & Ca in sediments of North Western part of the Persian Gulf. Intl J Env Studies 54:205–212
Bowen HJM (1979) Environmental chemistry of the elements. Academic press, London, p 333
Wedepohl KH (1971) Environmental influences on the chemical composition of shales and clays. In: Ahrens LH, Press F, Runcorn SK, Urey HC (eds) Physics and chemistry of the Earth, 8. Oxford, Pergamon, pp 307–331
Priju CP, Narayana AC (2007) Heavy and trace metals in Vembanad Lake sediments. Int J Environ Res 1(4):280–289
Praveena SM, Ahmed A, Radojevic M, Abdullah MH, Aris AZ (2008) Heavy metals in mangrove surface sediment of Mengkabong lagoon, Sabah: multivariate and geo-accumulation index approaches. Int J Environ Res 2(2):139–148
Ratheesh Kumar CS, Joseph MM, Gireesh Kumar TR, Renjith KR, Manju MN, Chandramohanakumar N (2010) Spatial variability and contamination of heavy metals in the inter-tidal system of a tropical environment. Int J Environ Res 4(4):691–700
Acknowledgment
Thanks to all who assisted in this research and especially to Mr. Nasser Aghajeri and Mr. Akbarzadeh in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea Ecological Research Institute for performing the tests and sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farsad, F., Karbassi, A., Monavari, S.M. et al. Development of a New Pollution Index for Heavy Metals in Sediments. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1828–1842 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8983-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8983-3