Abstract
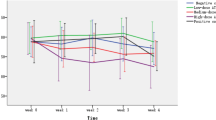
This study assessed effects of aluminum (Al) exposure on the immune function of erythrocytes in rats. Forty male Wistar rats (5 weeks old) weighed 110–120 g were randomly allocated equally into four groups according to their weights and were orally exposed to 0, 64.18, 128.36, and 256.72 mg/kg body weight aluminum trichloride in drinking water for 120 days. Levels of erythrocytes C3b receptor rate (RBC-C3bRR), erythrocytes C3b immune complex rosette rate (RBC-ICR), erythrocytes rosette forming enhancing rate (ERER) and erythrocytes rosette forming inhibitory rate (ERIR) were determined by the end of experiment. The three Al-treated groups had lower values of RBC-C3bRR and ERER, and higher values of RBC-ICR and ERIR than those in control group. The levels of RBC-C3bRR and ERER decreased, while the levels of RBC-ICR and ERIR increased with the increases of Al content in drinking water. The results suggest that the immune function of erythrocytes in rats is suppressed by Al exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reinagel ML, Taylor RP (2000) Transfer of immune complexes from erythrocyte CR1 to mouse macrophages. J Immunol 164:1977–1985
Garratty G (2010) Advances in red blood cell immunology 1960 to 2009. Transfusion 50:526–535
Hewitt CD, Savory J, Wills MR (1990) Aspects of aluminum toxicity. Clin Lab Med 10:403–422
Rengel Z (2004) Aluminum cycling in the soil-plant-animal-human continuum. Biometals 17:669–689
Fewtrell MS, Bishop NJ, Edmonds CJ, Isaacs EB, Lucas A (2009) Aluminum exposure from parenteral nutrition in preterm infants: bone health at 15-year follow-up. Pediatrics 124:1372–1379
You LG, Wu ZZ, Li YF, Zhang YF, Li MX (2003) The effect of buganyangsui formula on erythrocytes immune and regulation function in mice with Alzheimer’s disease following aluminum exposure. Chin J Trad Med Sci Tech 10:209–210
Liu FT, Li YF, Gu QY (2007) The effects of aluminum intoxication on the immune function of white and red blood cell in chicks. Chin Anim Husb Vet Med 34:70–72
Jiang JB, Wu CH, Gao H, Song JD, Li HQ (2010) Effects of astragalus polysaccharides on immunologic function of erythrocyte in chickens infected with infectious bursa disease virus. Vaccine 28:5614–5616
Yokel RA, Hicks CL, Florence RL (2008) Aluminum bioavailability from basic sodium aluminum phosphate, an approved food additive emulsifying agent, incorporated in cheese. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2261–2266
Zhang LC, Li XW, Gu QY, Zhu YZ, Zhao HS, Li YF, Zhang ZG (2010) Effects of subchronic aluminum exposure on serum concentrations of iron and iron-associated proteins in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8725-y
Li XW, Hu CW, Zhu YZ, Sun H, Li YF, Zhang ZG (2010) Effects of aluminum exposure on bone mineral, density, mineral, and trace elements in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8861-4
Siegel I, Liu TL, Gleicher N (1981) The red-cell immune system. Lancet 2:556–559
Lindorfer MA, Hahn CS, Foley PL, Taylor RP (2001) Heteropolymer-mediated clearance of immune complexes via erythrocyte CR1: mechanisms and applications. Immunol Rev 183:10–24
Gasser O, Schifferli JA (2005) Microparticles released by human neutrophils adhere to erythrocytes in the presence of complement. Exp Cell Res 307:381–387
Mudad R, Telen MJ (1996) Biologic functions of blood group antigens. Curr Opin Hematol 3:473–479
Birmingham DJ, Hebert LA (2001) CR1 and CRl-like: the primate immune adherence receptors. Immunol Rev 180:100–111
Oudin S, Libyh MT, Goossens D, Dervillez X, Philbert F, Réveil B, Bougy F, Tabary T, Rouger P, Klatzmann D, Cohen JH (2000) A soluble recombinant multimeric anti-RH (D) single-chain Fv/CR1 molecule restores the immune complex binding ability of CR1-deficient erythrocytes. J Immunol 164:1505–1513
Türkez H, Yousef MI, Geyikoglu F (2010) Propolis prevents aluminium-induced genetic and hepatic damages in rat liver. Food Chem Toxicol 48:2741–2746
Ng YC, Peters DK, Cederholm-williams SA, Walport MJ (1987) A lysine-binding protein in SLE sera inhibits the binding of immune complexes to normal erythrocyte CR1 (complement receptor type 1). Clin Exp Immunol 69:89–97
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Natural Science Fund of Heilongjiang Province of China (C200935).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhao, H., Li, X. et al. Effects of Subchronic Aluminum Exposure on the Immune Function of Erythrocytes in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 1576–1580 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8964-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-8964-6