Abstract
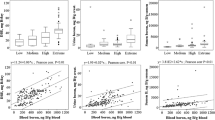
The possible changes in semen quality were studied in men living in a boron mining area. The subjects in the boron group had exposure to boron at an average level of 6.5 mg/day, as determined by urinary analysis. The results obtained by the boron group were compared to those obtained for the control group whose subjects were living in the same geographical area but away from the boron region; average exposure level was 1.4 mg/day for this group. The semen samples were analyzed according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization. Boron levels were established in the water samples obtained from various locations in the study region. In the boron mining fields where the subjects in the boron group live, water samples contained boron in the range of 1.4–6.5 mg/L, while the values were <0.01 mg/L for the water samples obtained from the region where the subjects of the control group reside. No negative effects were found in the sperm samples obtained from the subjects of the boron group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oliva A, Spira A, Multigner L (2001) Contribution of environmental factors to the risk of male infertility. Hum Reprod 16:1768–1776
Chapin RE, Ku WW (1994) The reproductive toxicity of boric acid. Environ Health Perspect 102:87–91
Ku WW, Chapin RE, Wine RN, Gladen BC (1993) Testicular toxicity of boric acid (BA): relationship of dose to lesion development and recovery in the F344 rat. Reprod Toxicol 7:305–319
Liu P, Hu W, Xu J, Robbins WA, Xun L, Wu G, Wei F (2006) Influence of boron exposure on male semen quality. China Environ Sci 26:43–47
Şaylı BS, Tüccar E, Elhan AH (1998) An assessment of fertility in boron-exposed Turkish subpopulations. Reprod Toxicol 12:297–304
Şaylı BS (2001) An assessment of fertility in boron-exposed Turkish subpopulations: 3. Evaluation of fertility among sibs and in ‘borate families’. Biol Trace Elem Res 81:255–267
World Health Organization (1996) Trace elements in human nutrition and health. WHO, Geneva
Brown TF, McCormick ME, Morris DR, Zeringue LK (1989) Effects of dietary boron on mineral balance in sheep. Nutr Res 9:503–512
Hegsted M, Keenan MJ, Siver F, Wozniak P (1991) Effect of boron on vitamin D deficient rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 28:243–255
Hunt CD, Herbel JL, Nielsen FH (1997) Metabolic responses of postmenopausal women to supplemental dietary boron and aluminum during usual and low magnesium intake: boron, calcium, and magnesium absorption and retention and blood mineral concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr 65:803–813
Hunt CD, Idso JP (1999) Dietary boron as a physiological regulator of the normal inflammatory response: a review and current research progress. J Trace Elem Med Biol 12:221–233
Fort DJ, Propst TL, Stover EL, Strong PL, Murray FJ (1998) Adverse reproductive and developmental effects in Xenopus from insufficient boron. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:237–259
Fort DJ, Stover EL, Strong PL, Murray FJ, Keen CL (1999) Chronic feeding of a low boron diet adversely affects reproduction and development in Xenopus laevis. J Nutr 129:2055–2060
Armstrong TA, Flowers WL, Spears JW, Nielsent FH (2002) Long-term effects of boron supplementation on reproductive characteristics and bone mechanical properties in gilts. J Anim Sci 80:154–161
Korkmaz M, Sayli U, Sayli BS, Bakirdere S, Titretir S, Ataman OY, Keskin S (2007) Estimation of human daily boron exposure in a boron-rich area. Br J Nutr 98:571–575
World Health Organization (1999) Laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and sperm–cervical mucus interaction, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Simsek A, Velioglu SY, Coskun LA (2003) Boron concentrations in selected foods from borate-producing regions in Turkey. J Sci Food Agric 83:586–592
Sutherland B, Leslie R, Woodhouse PS, Janet CK (1999) Boron balance in humans. J Trace Elem Exp Med 12:271–284
Pahl VM, Culver BD, Strong I, Murray JF, Vaziri DN (2001) The effect of pregnancy on renal clearance of boron in humans: a study based on normal dietary intake of boron. Toxicol Sci 60:252–256
Korkmaz M, Uzgoren E, Bakırdere S, Aydın F, Ataman OY (2007) Effects of dietary boron on cervical cytopathology and on micronucleus frequency in exfoliated buccal cells. Environ Toxicol 22:17–25
Devirian AT, Volpe LS (2003) The physiological effect of dietary boron. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 43:219–231
Eskenazi B, Kidd SA, Marks AR, Sloter E, Block G, Wyrobek AJ (2005) Antioxidant intake is associated with semen quality in healthy men. Hum Reprod 20:1006–1012
Flowers WL, Spears JW, Nielsen FH (2007) Effect of boron supplementation on semen quality estimates in mature boars. J Anim Sci 85:538
Naghii MR, Saman S (1997) The effect of boron on plasma testosterone and plasma lipids in rats. Nutr Res 17:523–532
World Health Organization (1992) Laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and semen–cervical mucus interaction, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Whorton MD, Haas J, Trent L (1994) Reproductive effects of inorganic borates on male employees: birth rate assessment. Environ Health Perspect 102:129–131
Whorton MD, Haas J, Trent L, Wong O (1994) Reproductive effects of sodium borates on male employees: birth rate assessment. Occup Environ Med 51:761–767
Scialli AR, Bonde JP, Brüske-Hohlfeld I, Culver BD, Li Y, Sullivan FM (2010) An overview of male reproductive studies of boron with an emphasis on studies of highly exposed Chinese workers. Reprod Toxicol 29:10–24
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by the National Boron Institute (BOREN), Turkey through the grant 2005/AR/GE 6. We would like to express our appreciation to Dr. Zafer Ayhan of Atalar Laboratory and Güven Laboratory, Balıkesir for his help in the semen analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korkmaz, M., Yenigün, M., Bakırdere, S. et al. Effects of Chronic Boron Exposure on Semen Profile. Biol Trace Elem Res 143, 738–750 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8928-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8928-2