Abstract
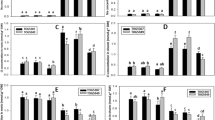
To investigate the effects of amiloride, which is an inhibitor of Na+/H+ antiporter (NHX), on Na+ accumulation and transport at the whole plant level, in this study, 3-week-old Zygophyllum xanthoxylum plants were exposed to 25, 50 and 100 mM NaCl with or without 0.5 mM amiloride. After 72 h of treatment, dry weight, tissue water content, Na+ and K+ concentrations, and transcript levels of ZxNHX were determined. The results indicated that, under salt conditions, leaf Na+ concentration, total Na+ quantity and root net Na+ uptake rate in plants treated with amiloride are significantly lower than those in control plants. Amiloride remarkably increased Na+ proportion in stem and decreased Na+ proportion in leaf of Z. xanthoxylum. Furthermore, our results showed that the transcript levels of ZxNHX are down-regulated by amiloride. It is clear that the inhibition of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter by amiloride could disrupt Na+ accumulation of leaf, and reduce Na+ uptake by root and Na+ transport from stem to leaf, thus resulting in the growth inhibition of Z. xanthoxylum exposed to salt.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKT:
-
Arabidopsis K+ transporter
- CCC:
-
Cation-Cl− cotransporter
- EtBr:
-
Ethidium bromide
- HAK:
-
High-affinity K+ transporter
- HKT:
-
High-affinity K+ transporter
- KT:
-
K+ transporter
- KUP:
-
K+ uptake transporter
- LCT:
-
Low-affinity cation transporter
- NSCC:
-
Non-selective cation channel
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- SOS:
-
Salt overly sensitive
- VIC:
-
Voltage-independent channel
References
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Liu H, Wang QQ, Yu MM et al (2008) Transgenic salt-tolerant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) constitutively expressing an Arabidopsis thaliana vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene, AtNHX3, accumulates more soluble sugar but less salt in storage roots. Plant Cell Environ 31:1325–11334
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Letter 581:2247–2254
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B et al (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30:529–539
Aharon GS, Apse MP, Duan SL et al (2003) Characterization of a family of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Soil 253:245–256
Pardo JM, Cubero B, Leidi EO et al (2006) Alkali cation exchangers: roles in cellular homeostasis and stress tolerance. J Biol Chem 57:1181–1199
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA et al (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Xue ZY, Zhi DY, Xue GP et al (2004) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic wheat (Tritivum aestivum L.) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene with improved grain yields in saline soils in the field and a reduced level of leaf Na+. Plant Sci 167:849–859
Yin XY, Yang AF, Zhang KW et al (2004) Production and analysis of transgenic maize with improved salt tolerance by the introduction of AtNHX1 gene. Acta Bot Sin 46:854–861
Lü SY, Jing YX, Shen SH et al (2005) Antiporter gene from Hordum brevisubulatum (Trin.) link and its overexpression in transgenic tobaccos. J Integr Plant Biol 47:343–349
He CX, Yan JQ, Shen GX et al (2005) Expression of an Arabidopsis vacuolar sodium/proton antiporter gene in cotton improves photosynthetic performance under salt conditions and increases fiber yield in the field. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1848–1854
Chen H, An R, Tang JH et al (2007) Over-expression of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in an upland rice. Plant Breeding 19:215–225
Zhao JS, Zhi DY, Xue ZY et al (2007) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic progeny of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 164:1377–1383
Barkla BJ, Zingarelli L, Blumwald E et al (1995) Tonoplast Na+/H+ antiport activity and its energization by the vacuolar H+-ATPase in the halophytic plant Mesmbryanthemum crystallinum L. Plant Physiol 109:549–556
Darley CP, van Wuytswinkel OCM, van der Woude K et al (2000) Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae NHX1 genes encode amiloride sensitive electroneutral Na+/H+ exchangers. Biochem J 351:241–249
Parks GE, Dietrich MA, Scumaker KS (2002) Increased vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange activity in Salicornia bigelovii Torr. in response to NaCl. J Exp Bot 53:1055–1065
Venema K, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM et al (2002) The Arabidopsis Na+/H+ exchanger AtNHX1 catalyze low affinity Na+ and K+ transport reconstituted liposomes. J Biol Chem 277:2413–2418
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Quintero FJ et al (2004) Regulation of vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange in Aribidopsis thaliana by the salt-overly-sensitive (SOS) pathway. Biol Chem 279:207–215
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C et al (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Shi H, Lee BH, Wu SJ et al (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–85
Guo KM, Babourina O, Rengel Z (2009) Na+/H+ antiporter activity of the SOS1 gene: lifetime imaging analysis and electrophysiological studies on Arabidopsis seedlings. Physiol Plant 137:155–165
Blumwald E, Poole RJ (1985) Na+/H+ antiport in isolated tonoplast vesicles from storage tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 78:163–167
Blumwald E, Cragoe EJ, Poole RJ (1987) Inhibition of Na+/H+ antiport activity in sugar beet tonoplast by analogs of amiloride. Plant Physiol 85:30–33
Ballesteros E, Blumwald E, Donaire JP et al (1997) Na+/H+ antiport activity in tonoplast vesicles isolated from sunflower roots induced by NaCl stress. Physiol Plant 99:328–334
Maathuis FJM, Sanders D (2001) Sodium uptake in Arabidopsis roots is regulated by cyclic nucleotides. Plant Physiol 127:1617–1625
Gong JM, Waner DA, Horie T et al (2004) Microarray-based rapid cloning of an ion accumulation deletion mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15404–15409
Qi CH, Chen M, Song J et al (2009) Increase in aquaporin activity is involved in leaf succulence of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa, under salinity. Plant Sci 176:200–205
Wang SM, Zhang JL, Flowers TJ (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the Halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiol 145:559–571
Wang CM, Zhang JL, Liu XS et al (2009) Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant Cell Environ 32:486–496
Liu JQ, Pu JC, Liu XM (1987) Comparative studies on water relations and xeromorphic structures of some plant species in the middle part of the desert zone in China. Acta Botanica Sinica 29:662–673
Liu JQ, Li ZJ, Pu JC et al (1988) Comparative studies on relationships between proline accumulation and photosynthesis, respiration and chlorophyll content of some plant species in the middle part of the desert zone in China. Acta Botanica Sinica 30:85–95
Wang SM, Wan CG, Wang YR et al (2004) The Characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539
Ma Q, Lou JQ, Wang SM (2010) Effects of Na+ on photosynthetic characteristics of Zygophyllum xanthonylon seedlings under osmotic stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica doi:1004-5759(2009)06-00-0
Kleyman T, Cragoe E (1988) Amiloride and its analoguesas tools in the study of ion transport. J Memb Biol 105:1–21
Anil VS, Krishnamurthy H, Mathew MK (2007) Limiting cytosolic Na+ confers salt tolerance to rice cells in culture: a two-photon microscopy study of SBFI-loaded cells. Physiol Plant 129:607–621
Gaxiola RA, Rao R, Sherman A et al (1999) The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1480–1485
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:140–151
Li YF, Wong FL, Tsai SN et al (2006) Tonoplast-located GmCLC1 and GmNHX1 from soybean enhance NaCl tolerance in transgenic bright yellow (BY)-2 cells. Plant Cell Environ 29:1122–1137
Qiao WH, Zhao XY, Li W et al (2007) Overexpression of AeNHX1, a root-specific vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from Agropyron elongatum, confers salt tolerance to Arabidopsis and Festuca plants. Plant Cell Rep 26:1663–1672
Tajdoost S, Farboodnia T, Heidary R (2007) Amiloride inhibition of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter enhance salt stress in Zea mays L. seedlings. Pak J Biol Sci 10:2020–2024
Amtmann A, Fischer M, Marsh EL et al (2001) The wheat cDNA LCT1 generates hypersensitivity to sodium in a salt-sensitive yeast strain. Plant Physiol 126:1061–1071
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Zhang JL, Flowers TJ, Wang SM (2010) Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant Soil 326:45–60
Berthomieu P, Conéjéro G, Nublat A et al (2003) Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na+ recirculation by the phloem is crucial for salt tolerance. EMBO J 22:2004–2014
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG et al (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1029–1030
Sunarpi HT, Motoda J et al (2005) Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter-induced Na+ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells. Plant J 44:928–938
Byrt CS, Platten JD, Spielmeyer W et al (2007) HKT1; 5-like cation transporters linked to Na+ exclusion loci in wheat, Nax2 and Kna1. Plant Physiol 143:1918–1928
Huang S, Spielmeyer W, Lagudah ES et al (2008) Comparative mapping of HKT genes in wheat, barley, and rice, key determinants of Na+ transport, and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 59:927–937
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM et al (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Kant S, Kant P, Raveh E et al (2006) Evidence that differential gene expression between the halophyte, Thellungiella halophila, and Arabidopsis thaliana is responsible for higher levels of the compatible osmolyte praline and tight control of Na+ uptake in T. halophila. Plant Cell Environ 29:1220–1234
Martínez-Atienza J, Jiang X, Garciadeblas B et al (2007) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143:1001–1012
Chung JS, Zhu JJ, Bressan RA et al (2008) Reactive oxygen species mediate Na+-induced SOS1 mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant J 53:554–565
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Technology R & D Program (grant No. 2008BADB3B01), the National High Tech Project of China (grant No. 2006AA10Z126) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 30770347). The authors wish to thank an anonymous reviewer for his/her valuable suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, GQ., Wang, Q., Bao, AK. et al. Amiloride Reduces Sodium Transport and Accumulation in the Succulent Xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum Under Salt Conditions. Biol Trace Elem Res 139, 356–367 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8662-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8662-9