Abstract
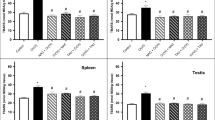
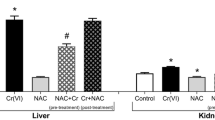
Acute exposure to hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] compounds can cause hepatotoxicity. Reactive intermediates and free radicals generated during reduction process may be responsible for Cr(VI) toxicity. In this study, the effects of pretreatment or posttreatment of taurine on Cr(VI)-induced oxidative stress and chromium accumulation in liver tissue of Swiss Albino mice were investigated. Single intraperitoneal (ip) potassium dichromate treatment (20 mgCr/kg), as Cr(VI) compound, significantly elevated the level of lipid peroxidation as compared with control group (p < 0.05). This was accompanied by significant decreases in nonprotein sulfhydryls (NPSHs) level, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) enzyme activities as well as a significant chromium accumulation in the tissue (p < 0.05). Taurine administration (1 g/kg, ip) before or after Cr(VI) exposure resulted in reduction of lipid peroxidation (p < 0.05) showed rebalancing effect on tissue NPSH levels either in pretreatment or in posttreatment (p < 0.05). Enzyme activities of SOD and CAT were restored by taurine pretreatment (p < 0.05), whereas posttreatment had less pronounced effects on these parameters. On the other hand, taurine treatment, before or after exposure, could exert only slight decreases in tissue Cr levels (p > 0.05). In view of the results, taurine seems to exert some beneficial effects against Cr(VI)-induced oxidative stress in liver tissue.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (1988) Chromium. Environmental Health Criteria, vol. 61. WHO, Geneva
Barceloux DG (1999) Chromium. Clin Toxicol 37:173–194
De Flora S, Wetterhahn KE (1989) Mechanisms of chromium metabolism and genotoxicity. Life Chem Rep 7:169–244
Costa M, Klein CB (2006) Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Crit Rev Toxicol 36:155–163
Codd R, Dillon CT, Levina A, Lay PA (2001) Studies on the genotoxicity of chromium: from test tube to the cell. Coord Chem Rev 216–217:537–582
Huang YL, Chen CY, Sheu JY, Chuang IC, Pan JH, Lin TH (1999) Lipid peroxidation in workers exposed to hexavalent chromium. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 56:235–247
Mattagajasingh SN, Misra HP (1995) Alterations in the prooxidant and antioxidant status of human leukemic T-lymphocyte MOLT4 cells treated with potassium chromate. Mol Cell Biochem 142:61–70
Bagchi D, Stohs SJ, Downs BW, Bagchi M, Preuss HG (2002) Cytotoxicity and oxidative mechanisms of different forms of chromium. Toxicology 180:5–22
Meert KL, Ellis J, Aronow R, Perrin E (1994) Acute ammonium dichromate poisoning. Ann Emerg Med 24:748–750
Kolacinski Z, Kostrzewski P, Kruszewska S, Razniewska G, Mielczarska J (1999) Acute potassium dichromate poisoning: a toxicokinetic case study. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37:785–791
Loubieres Y, de Lassence A, Bernier M, Vieillard-Baron A, Schmitt JM, Page B, Jardin F (1999) Acute, fatal, oral chromic acid poisoning. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37:333–336
Goyer RA, Clarkson TW (2001) Toxic effects of metals. In: Klaassen CD (ed) Casarett and Doull’s Toxicology: the basic science of poisons. 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 811–867
Laborda R, Diaz-Mayans J, Nunez A (1986) Nephrotoxic and hepatotoxic effects of chromium compounds in rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 36:332–336
Kumar A, Barthwal R (1991) Hexavalent chromium effects on hematological indices in rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 46:761–768
Dartsch PC, Hildenbrand S, Kimmel R, Schmahl FW (1998) Investigations on the nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity of trivalent and hexavalent chromium compounds. Int Arch Occup Environ Health S71:40–45
Liu KJ, Shi X (2001) In vivo reduction of chromium(VI) and its related free radical generation. Mol Cell Biochem 222:41–47
Shi X, Chiu A, Chen CT, Halliwell B, Castranova V, Vallyathan V (1999) Reduction of chromium(VI) and its relationship to carcinogenesis. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 2:87–104
Huxtable RJ, Sebring LA (1986) Towards a unifying theory for the actions of taurine. TIPS 7:481–485
Redmond HP, Stapleton PP, Neary P, Bouchier-Hayes D (1998) Immunonutrition: the role of taurine. Nutrition 14:599–604
Kerai MDJ, Waterfield CJ, Kenyon SH, Asker DS, Timbrell JA (1998) Taurine: protective properties against ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis and lipid peroxidation during chronic ethanol consumption in rats. Amino Acids 15:53–76
Waters E, Wang JH, Redmond HP, Wu QD, Kay E, Bouchier-Hayes D (2001) Role of taurine in preventing acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280:G1274–G1279
Hu YH, Lin CL, Huang YW, Liu PE, Hwang DF (2007) Dietary amino acid taurine ameliorates liver injury in chronic hepatitis patients. Amino Acids DOI 10.1007/s00726-007-0565-5
Ueno S, Susa N, Furukawa Y, Sugiyama M (1995) Formation of paramagnetic chromium in liver of mice treated with dichromate(VI). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 135:165–171
Azuma J, Hamaguchi T, Ohta H, Takihara K, Awata N, Sawamura A, Harada H, Tanaka Y, Kishimoto S (1987) Calcium overload-induced myocardial damage caused by isoproterenol and by adriamycin: possible role of taurine in its prevention. Adv Exp Med Biol 217:167–179
Hamaguchi T, Azuma J, Awata N, Ohta H, Takihara K, Harada H, Kishimoto S, Sperelakis N (1988) Reduction of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by taurine. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 59:21–30
Korang K, Milakofsky L, Hare TA, Hofford JM, Vogel WH (1996) Levels of taurine, amino acids and related compounds in plasma, vena cava, aorta and heart of rats after taurine administration. Pharmacology 52:263–270
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Rungby J, Ernst E (1992) Experimentally induced lipid peroxidation after exposure to chromium, mercury or silver: interactions with carbon tetrachloride. Pharmacol Toxicol 70:205–207
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Crapo JD, McCord JM, Fridovich I (1978) Preparation and assay of superoxide dismutases. Methods Enzymol 53:382–393
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Phifer EC (1995) Determination of chromium and molybdenum in medical foods by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry. J AOAC Int 78:1497–1501
Sipowicz MA, Anderson LM, Utermahlen WE Jr, Issaq HJ, Kasprzak KS (1997) Uptake and tissue distribution of chromium(III) in mice after a single intraperitoneal or subcutaneous administration. Toxicol Lett 93:9–14
Nakashima T, Taniko T, Kuriyama K (1982) Therapeutic effect of taurine administration on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury. Jpn J Pharmacol 32:583–589
Balkan J, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Kanbağlı O, Çevikbaş U, Aykaç-Toker G, Uysal M (2001) Taurine has a protective effect against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis by decreasing oxidative stress. Hum Exp Toxicol 20:251–254
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2007) Taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicol in Vitro 21:1419–1428
Jagadeesan G, Pillai SS (2007) Hepatoprotective effects of taurine against mercury induced toxicity in rats. J Environ Biol 28:753–756
Mas MR, Comert B, Oncu K, Atay Vural S, Akay C, Tasci I, Ozkomur E, Serdar M, Mas N, Alcigir G, Yener N (2004) The effect of taurine treatment on oxidative stress in experimental liver fibrosis. Hepatol Res 28:207–215
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Hojo Y, Nishiguchi K, Kawazoe S, Mizutani T (1999) Comparison of susceptibility of liver and kidney to lipid peroxidation induction by Cr(IV), Cr(V), Cr(VI) compounds. J Health Sci 45:329–332
das Neves RP, Santos TM, Pereira Mde L, de Jesus JP (2002) Comparative histological studies on liver of mice exposed to Cr(VI) and Cr(V) compounds. Hum Exp Toxicol 21:365–369
Bagchi D, Vuchetich PJ, Bagchi M, Hassoun EA, Tran MX, Tang L, Stohs SJ (1997) Induction of oxidative stress by chronic administration of sodium dichromate [chromium VI] and cadmium chloride [cadmium II] to rats. Free Radic Biol Med 22:471–478
Goulart M, Batoréu MC, Rodrigues AS, Laires A, Rueff J (2005) Lipoperoxidation products and thiol antioxidants in chromium exposed workers. Mutagenesis 20:311–315
Hojo Y, Okado A, Kawazoe S, Mizutani T (2000) Direct evidence for in vivo hydroxyl radical generation in blood of mice after acute chromium(VI) intake: electron spin resonance spin-trapping investigation. Biol Trace Elem Res 76:75–84
Kehrer JP (2000) The Haber–Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicology 149:43–50
Halliwell B (1991) Reactive oxygen species in living systems: source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am J Med 91(Suppl 3C):14S–22S
Gutteridge JMC (1995) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage. Clin Chem 41:1819–1828
Meister A (1995) Glutathione metabolism. Methods Enzymol 251:3–7
Sen CK (1997) Nutritional biochemistry of cellular glutathione. Nutr Biochem 8:660–672
De Mattia G, Bravi MC, Laurenti O, De Luca O, Palmeri A, Sabatucci A, Mendico G, Ghiselli A (2004) Impairment of cell and plasma redox state in subjects professionally exposed to chromium. Am J Ind Med 46:120–125
Wiegand HJ, Ottenwalder H, Bolt HM (1984) The reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by glutathione: an intracellular redox pathway in the metabolism of the carcinogen chromate. Toxicology 33:341–348
OEHHA (1999) Public Health Goal for Chromium in Drinking Water. Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, California Environmental Protection Agency, Sacramento
Gunaratnam M, Pohlscheidt M, Grant MH (2002) Pretreatment of rats with the inducing agents phenobarbitone and 3-methylcholantrene ameliorates the toxicity of chromium (VI) in hepatocytes. Toxicology in Vitro 16:509–516
Hojo Y, Satomi Y (1991) In vivo nephrotoxicity induced in mice by chromium(VI). Involvement of glutathione and chromium(V). Biol Trace Elem Res 31:21–31
Standeven AM, Wetterhahn KE (1991) Possible role of glutathione in chromium(VI) metabolism and toxicity in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 68:469–476
Cupo DY, Wetterhahn KE (1985) Modification of Cr(VI)-induced DNA damage by glutathione and cytochromes P-450 in chicken embryo hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82:6755–6759
Snyder RD (1988) Role of active oxygen species in metal-induced DNA strand breakage in human diploid fibroblasts. Mutat Res 193:237–246
Michiels C, Raes M, Toussaint O, Remacle J (1994) Importance of Se-glutathione peroxidase, catalase and Cu/Zn-SOD for cell survival against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 17:235–248
Shainkin-Kestenbaum R, Caruso C, Berlyne GM (1991) Effect of chromium on oxygen free radical metabolism, inhibition of superoxide dismutase and enhancement of 6-hydroxydopamine oxidation. J Trace Elem Electrolytes Health Dis 5:197–201
Koh YH, Yoon SJ, Park JW (1999) Inactivation of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase by the lipid peroxidation products malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. J Biochem Mol Biol 32:440–444
Gürer H, Özgüneş H, Saygın E, Ercal N (2001) Antioxidant effect of taurine against lead-induced oxidative stress. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41:397–402
Appenroth D, Winnefeld K, Schröter H, Rost M (1994) The ambiguous effect of ascorbic acid on chromate induced proteinuria in rats. Arch Toxicol 68:138–141
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2000) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Ogasawara M, Nakamura T, Koyama I, Nemoto M, Yoshida T (1994) Reactivity of taurine with aldehydes and its physiological role. Adv Exp Med Biol 359:71–78
Warskulat U, Borsch E, Reinehr R, Heller-Stilb B et al (2006) Chronic liver disease is triggered by taurine transporter knockout in the mouse. FASEB J 20:574–576
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J (1988) The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem J 256:251–255
Shi X, Flynn DC, Porter DW, Leonard SS, Vallyathan V, Castranova V (1997) Efficacy of taurine based compounds as hydroxyl radical scavengers in silica induced peroxidation. Ann Clin Lab Sci 27:365–374
Sutherland JE, Zhitkovich A, Kluz T, Costa M (2000) Rats retain chromium in tissues following chronic ingestion of drinking water containing hexavalent chromium. Biol Trace Elem Res 74:41–53
Hwang DF, Wang LC, Cheng HM (1998) Effect of taurine on toxicity of copper in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 36:239–244
Hwang DF, Wang LC (2001) Effect of taurine on toxicity of cadmium in rats. Toxicology 167:173–180
Boşgelmez İİ, Güvendik G (2004) Effects of taurine on oxidative stress parameters and chromium levels altered by acute hexavalent chromium exposure in mice kidney tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 102:209–225
Oudit GY, Trivieri MG, Khaper N, Husain T, Wilson GJ, Liu P, Sole MJ, Backx PH (2004) Taurine supplementation reduces oxidative stress and improves cardiovascular function in an iron-overload murine model. Circulation 109:1877–1885
Farooq Q, Malik AU, Ahmad N (1970) Complexes of chromium(II) chloride with some sulphur-containing amino acids. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 26:411–414
Vinokurov EG, Bondar VV (2003) Prediction of stability constants for Cr(III) and Cr(II) complexes. Russ J Coord Chem 29:66–72
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. A. Boşgelmez for helpful suggestions and comments on the preparation of the manuscript; S. Çalış for perfect technical assistance; Dr. M. Doğan, Dr. B. Salih, and S. Petin for their supports in total chromium determinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boşgelmez, İ.İ., Söylemezoğlu, T. & Güvendik, G. The Protective and Antidotal Effects of Taurine on Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mice Liver Tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res 125, 46–58 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8154-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8154-3