Abstract
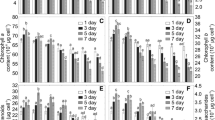
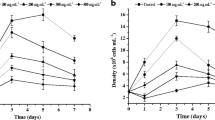
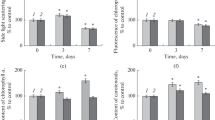
The growth response of the marine alga Dunaliella tertiolecta to different concentrations of lead and aluminum was investigated. Both metals had a stimulatory effect at low concentration and an inhibitory effect at high concentration (hormesis). The IC25 values of lead are 8.43, 7.29, and 6.74 mg L−1 for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. The corresponding values for aluminum are 30.54, 22.42, and 18.16 mg L−1. Although it seems that the two metals are not directly toxic to the alga at the concentrations found in the environment, as implied by the IC25 values and the environmental concentrations of the metals, low concentrations of both metals, alone and in combination, affected the ultrastructure. The growth of batch-grown cells exposed to 0.5 mg L−1 lead and aluminum, alone and combined, during the 24-h exponential phase was investigated. The same cells were also examined under an electron microscope to determine the biological effects of the two metals on the ultrastructure. The most obvious effects of lead were disrupted thylakoidal membranes, accumulated polyphosphate bodies and vacuoles, and lead precipitates on the cell surface. These ultrastructural alterations were partially present in aluminum-treated and lead–aluminum-treated cells. In joint exposure, the most important change was the lysis of the cell membrane. Aluminum and lead seem to act synergistically on the cell membrane leading to cell membrane lysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel KS, Shrivas K, Hoffmann P, Jakubowski N (2006) A survey of lead pollution in Chhattisgarh State, Central India. Environ Geochem Health 28:11–17
Jain SK, Vasudevan P, Jha NK (1989) Removal of some heavy metals from polluted water by aquatic plants: studies on duckweed and water velvet. Biol Wastes 28:115–126
Yap CK, Ismail A, Omar H, Tan SG (2004) Toxicities and tolerances of Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in a primary producer (Isochrysis galbana) and in a primary consumer (Perna viridis). Environ Int 29:1097–1104
Simpson AM, Hatton W, Brockbank M (1988) Aluminum; its use and control in potable water. Environ Technol Lett 9:907–916
Sollars CJ, Bragg S, Simpson AM, Perry R (1989) Aluminum in European drinking water. Environ Technol Lett 10:131–150
Souad C, Farida Z, Nadra L, François B, Bougle D, Azeddine S (2006) Trace elements level in infant hair and diet, and in the local environment of the Moroccan city of Marrakech. Sci Total Environ 370:337–342
Lindemann J, Holtkamp E, Herrmann R (1990) The impact of Al on green algae isolated from two hydrochemically different headwater streams, Bavaria, Germany. Environ Pollut 67:61–77
Jensen TE, Baxter M, Rachlin JW, Jani V (1982) Uptake of heavy metals by Plectonema boryanum (Cyanophyceae) into cellular components, especially polyphosphate bodies: An X-ray energy dispersive study. Environ Pollut A 27:119–127
Jensen TE, Rachlin JW, Jani V, Warkentine B (1982) An X-ray energy dispersive study of cellular compartmentalization of lead and zinc in Chlorella saccharophila (Chloropyhta), Navicula insertia and Nitzschia closterium (Bacillariophyta). Environ Exp Bot 22:319–328
Rai LC, Gaur JP, Kumar HD (1981) Phycology and heavy metal pollution. Biol Rev 56:99–151
Visiviki I, Rachlin JW (1994) Acute and chronic exposure of Dunaliella salina and Chlamydomonas bullosa to copper and cadmium: effects on ultrastructure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 26:154–162
Chan K, Wong SLL (1987) Ultrastructural changes of Chaetomorpha brachygona growing in metal environment. Cytologia 52:97–105
Wong SL, Nakamoto L, Wainwright JF (1994) Identification of toxic metals in affected algal cells in assays of wastewaters. J Appl Phycol 6:405–414
Shehata SA, Lasheen MR, Kobbia IA, Ali GH (1999) Toxic effects of certain metal mixtures on some physiological and morphological characteristics of freshwater algae. Water Air Soil Pollut 100:119–135
Okay O, Gaines A (1996) Toxicity of 2, 4- D acid to phytoplankton. Wat Res 30:688–696
USEPA (1993) Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater organisms in Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory. EPA-600/4-90/027F. USEPA, Cincinnati, OH, p 293
Leblond JB, Duffy, LK (2001) Toxicity assessment of total dissolved solids in effluent of Alaska mines using 22-h chronic microtox and Selenastrum capricornitium assay. Sci Total Environ 271:49–59
Saçan MT, Balcıoğlu IA (2006) A case study on algal response to raw and treated effluents from an aluminum plating plant and a pharmaceutical plant. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:234–243
Hayat MA (1972) Basic electron microscopy techniques. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, p 119
Hoshaw RW, Maluf LY (1981) Ultrastructure of the green flagellate, Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chloropyhceae, Volvocales) with comparative notes on three other species. Phycologia 20:199–206
Dunstan WM (1975) Stimulation and inhibition of phytoplankton growth by low molecular weight hydrocarbons. Mar Biol 31:305–310
Delistrary D (1986) Growth and photosynthetic responses of a freshwater alga, Selenastrum capricornitum, to oil shale by-product water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 36:114–121
Sarabia R, Torreblanca A, Del Ramo JJ, Diaz-Mayans J (1998) Review: effect of low mercury concentration on hatching in the Artemia strain La Mata parthenogenetic diploid. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Mol Integr Physiol 120:93–97
Sauve S, Brousseau P, Pellerin J, Morin Y, Senecal L, Goudreau P, Fournier M (2002) Phagocytic activity of marine and freshwater bivalves: in vitro exposure of hemocytes to metals (Ag, Cd, Hg and Zn). Aquat Toxicol 58:189–200
Srivastava N, Sahai R (1987) Effects of distillery waste on the performance of Cicerarictinum L. Environ Pollut 43:91–102
Joy CM (1990) Toxicity testing with freshwater algae in River Periyar (India). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:915–922
Schmitt-Jansen M, Altenburger R (2005) Toxic effects of isoproturon on peripyhton communities—a microcosm study. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 62:539–545
Mooney HM, Patching JM (1998) Electron microscopy of the marine microalga Dunaliella tertiolecta exposed to triphenyltin. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 20:200–204
Rachlin JW, Jensen TE, Baxter M, Jani V (1982) Utilization of morphometric analysis in evaluating response of Plectonema boryanum (Cyanophyceae) to exposure to eight heavy metals. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11:323–333
Smith MA (1983) The effect of heavy metals on the cytoplasmic fine structure of Skeletonema costatum (Bacillariophyta). Protoplasma 116:24–33
Sicko-Goad L, Stoermer EF (1979) A morphometric study of lead and copper effects on Diatoma tenue var elongatum (Bacillariophyta). J Phycol 15:316–321
Nishikawa K, Yamakoshi Y, Uemura I, Tominaga N (2003) Ultrastructural changes in Chlamydomonas acidophila (Chlorophyta) induced by heavy metals and polyphosphate metabolism. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44:253–259
Rachlin JW, Jensen TE, Warkentina BE (1985) Morphometric analysis of response of Ananaena flos-aquae and Anabaena variabilis (Cyanophyceae) to selected concentrations of zinc. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 14:395–402
Sauvant MP, Pepin D, Bohatier J, Groliere CA (2000) Effect of chelators on the acute toxicity and bioavailability of aluminum to Tetrahymena pyriformis. Aquat Toxicol 47:259–275
Rachlin JW, Jensen TE, Warkentine B (1984) The toxicological response of the alga Anabena flos-aquae (Cyanophyceae) to cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 13:143–151
Rai LC, Jensen TE, Rachlin JW (1990) A morphometric and X-ray energy dispersive approach to monitoring pH-altered cadmium toxicity in Anabena flos-aquae. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:479–487
Folsom BR, Popescu NA, Wood JM (1986) Comparative study of aluminum and copper transport and toxicity in an acid-tolerant freshwater green alga. Environ Sci Technol 20:616–620
Santana-Casiana JM, Gonzales-Davila M, Laglera LM, Perez-Pena J, Brand L, Millero FJ (1997) The influence of zinc, aluminum and cadmium on the uptake kinetics of iron by algae. Mar Chem 59:95–111
Schnitzer M, Kenndorf H (1981) Reactions of fulvic acids with metal ions. Water Air Soil Pollut 15:97–108
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the technicians of the Electron Microscopy Unit of Marmara University for the use of the JEM-1200 Ex-II electron microscope and for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saçan, M.T., Oztay, F. & Bolkent, S. Exposure of Dunaliella tertiolecta to Lead and Aluminum: Toxicity and Effects on Ultrastructure. Biol Trace Elem Res 120, 264–272 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-8016-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-007-8016-4