Abstract
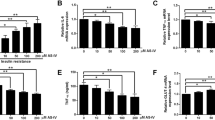
Insulin resistance (IR) is one of the leading causes of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Inflammation, as a result of the disordered immune response, plays important roles in IR and T2DM. Interleukin-4-induced gene 1 (IL4I1) has been shown to regulate immune response and be involved in inflammation progress. However, there was little known about its roles in T2DM. Here, high glucose (HG)-treated HepG2 cells were used for T2DM investigation in vitro. Our results indicated that the expression of IL4I1 was up-regulated in peripheral blood samples of T2DM-patients and HG-induced HepG2 cells. The silencing of IL4I1 alleviated the HG-evoked IR through elevating the expressions of p-IRS1, p-AKT and GLUT4, and enhancing glucose consumption. Furthermore, IL4I1 knockdown inhibited inflammatory response by reducing the levels of inflammatory mediators, and suppressed the accumulation of lipid metabolites triglyceride (TG) and palmitate (PA) in HG-induced cells. Notably, IL4I1 expression was positively correlated with aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in peripheral blood samples of T2DM-patients. The silencing of IL4I1 inhibited the AHR signaling by reducing the HG-induced expressions of AHR and CYP1A1. Subsequent experiments confirmed that 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), an agonist of AHR, reversed the suppressive effects of IL4I1 knockdown on HG-caused inflammation, lipid metabolism and IR in cells. In conclusion, we found that the silencing of IL4I1 attenuated inflammation, lipid metabolism and IR in HG-induced cells via inhibiting AHR signaling, suggesting that IL4I1 might be a potential therapy target for T2DM.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data and materials used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alvarado, D. M., Chen, B., Iticovici, M., Thaker, A. I., Dai, N., VanDussen, K. L., et al. (2019). Epithelial indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 modulates Aryl Hydrocarbon receptor and Notch Signaling to increase differentiation of secretory cells and alter Mucus-Associated Microbiota. Gastroenterology, 157(4), 1093–1108e1011.
Baker, N. A., Shoemaker, R., English, V., Larian, N., Sunkara, M., Morris, A. J., et al. (2015). Effects of Adipocyte Aryl Hydrocarbon receptor Deficiency on PCB-Induced disruption of glucose homeostasis in lean and obese mice. Environmental Health Perspectives, 123(10), 944–950.
Berbudi, A., Rahmadika, N., Tjahjadi, A. I., & Ruslami, R. (2020). Type 2 diabetes and its impact on the Immune System. Current Diabetes Review, 16(5), 442–449.
Bock, K. W. (2020). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) functions: balancing opposing processes including inflammatory reactions. Biochemical Pharmacology, 178, 114093.
Bock, K. W. (2020). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), integrating energy metabolism and microbial or obesity-mediated inflammation. Biochemical Pharmacology, 184, 114346.
Boulland, M. L., Marquet, J., Molinier-Frenkel, V., Möller, P., Guiter, C., Lasoudris, F., et al. (2007). Human IL4I1 is a secreted L-phenylalanine oxidase expressed by mature dendritic cells that inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation. Blood, 110(1), 220–227.
Castellano, F., & Molinier-Frenkel, V. (2017). An Overview of l-Amino Acid Oxidase Functions from Bacteria to Mammals: Focus on the Immunoregulatory Phenylalanine Oxidase IL4I1. Molecules, 22(12), 2151.
Chabowski, A., Żendzian-Piotrowska, M., Konstantynowicz, K., Pankiewicz, W., Mikłosz, A., Łukaszuk, B., et al. (2013). Fatty acid transporters involved in the palmitate and oleate induced insulin resistance in primary rat hepatocytes. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 207(2), 346–357.
Donath, M. Y., Dinarello, C. A., & Mandrup-Poulsen, T. (2019). Targeting innate immune mediators in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Nature Reviews Immunology, 19(12), 734–746.
Duncan, B. B., Castilhos, C. D., Bracco, P. A., Schmidt, M. I., Kang, S., Im, S., et al. (2020). Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor binding and the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the brazilian longitudinal study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Environmental Health : A Global Access Science Source, 19(1), 105.
Farzi, A., Hassan, A. M., Zenz, G., & Holzer, P. (2019). Diabesity and mood disorders: multiple links through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Molecular Aspects Of Medicine, 66, 80–93.
Finck, B. N. (2018). Targeting metabolism, insulin resistance, and diabetes to treat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes, 67(12), 2485–2493.
Gao, Z., Hwang, D., Bataille, F., Lefevre, M., York, D., Quon, M. J., et al. (2002). Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by inhibitor kappa B kinase complex. Journal Of Biological Chemistry, 277(50), 48115–48121.
Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C., & Quintana, F. J. (2018). Regulation of the Immune response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon receptor. Immunity, 48(1), 19–33.
Ibrahim, M., MacFarlane, E. M., Matteo, G., Hoyeck, M. P., Rick, K. R. C., Farokhi, S., et al. (2020). Functional cytochrome P450 1A enzymes are induced in mouse and human islets following pollutant exposure. Diabetologia, 63(1), 162–178.
Kahn, S. E., Hull, R. L., & Utzschneider, K. M. (2006). Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature, 444(7121), 840–846.
Kurita, H., Yoshioka, W., Nishimura, N., Kubota, N., Kadowaki, T., & Tohyama, C. (2009). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. Journal Of Applied Toxicology, 29(8), 689–694.
Kwon, Y., Jang, M., Lee, Y., Ha, J., & Park, S. (2021). Metabolomic analysis of the improvements in insulin secretion and resistance after sleeve gastrectomy: implications of the novel biomarkers. Obesity Surgery, 31(1), 43–52.
Lasoudris, F., Cousin, C., Prevost-Blondel, A., Martin-Garcia, N., Abd-Alsamad, I., Ortonne, N., et al. (2011). IL4I1: an inhibitor of the CD8+ antitumor T-cell response in vivo. European Journal Of Immunology, 41(6), 1629–1638.
Li, Q., Su, J., Jin, S. J., Wei, W., Cong, X. D., Li, X. X., et al. (2018). Argirein alleviates vascular endothelial insulin resistance through suppressing the activation of Nox4-dependent O(2)(-) production in diabetic rats. Free Radical Biology And Medicine, 121, 169–179.
Liu, L., Li, Y., Feng, R., & Sun, C. (2010). Direct ultrasound-assisted methylation of fatty acids in serum for free fatty acid determinations. Can J Chem, 88(9), 898–905.
Lv, Q., Wang, K., Qiao, S., Yang, L., Xin, Y., Dai, Y., et al. (2018). Norisoboldine, a natural AhR agonist, promotes Treg differentiation and attenuates colitis via targeting glycolysis and subsequent NAD(+)/SIRT1/SUV39H1/H3K9me3 signaling pathway. Cell Death And Disease, 9(3), 258.
Malik, S. A., Acharya, J. D., Mehendale, N. K., Kamat, S. S., & Ghaskadbi, S. S. (2019). Pterostilbene reverses palmitic acid mediated insulin resistance in HepG2 cells by reducing oxidative stress and triglyceride accumulation. Free Radical Research, 53(7), 815–827.
Manzella, C. R., Ackerman, M., Singhal, M., Ticho, A. L., Ceh, J., Alrefai, W. A., et al. (2020). Serotonin modulates AhR activation by interfering with CYP1A1-Mediated clearance of AhR Ligands. Cellular Physiology And Biochemistry, 54(1), 126–141.
Molinier-Frenkel, V., Mestivier, D., & Castellano, F. (2016). Alterations of the immunosuppressive IL4I1 enzyme activity induced by naturally occurring SNP/mutations. Genes And Immunity, 17(2), 148–152.
Molinier-Frenkel, V., Prévost-Blondel, A., & Castellano, F. (2019). The IL4I1 Enzyme: A New Player in the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment.Cells, 8(7), 757.
Nishiumi, S., Yoshida, M., Azuma, T., Yoshida, K., & Ashida, H. (2010). 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin impairs an insulin signaling pathway through the induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in adipocytes. Toxicological Sciences, 115(2), 482–491.
Olivero-Verbel, J., Cabarcas-Montalvo, M., & Ortega-Zúñiga, C. (2010). Theoretical targets for TCDD: a bioinformatics approach. Chemosphere, 80(10), 1160–1166.
Panahi, G., Pasalar, P., Zare, M., Rizzuto, R., & Meshkani, R. (2018). High glucose induces inflammatory responses in HepG2 cells via the oxidative stress-mediated activation of NF-κB, and MAPK pathways in HepG2 cells. Archives Of Physiology And Biochemistry, 124(5), 468–474.
Petersen, M. C., & Shulman, G. I. (2018). Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiological Reviews, 98(4), 2133–2223.
Prevost-Blondel, A., & Richard, Y. (2019). Interleukin 4-Induced Gene 1 as an Emerging Regulator of B-Cell Biology and its role in cutaneous melanoma. Critical Reviews In Immunology, 39(1), 39–57.
Rajagopalan, S., & Brook, R. D. (2012). Air pollution and type 2 diabetes: mechanistic insights. Diabetes, 61(12), 3037–3045.
Romagnani, S. (2016). IL4I1: key immunoregulator at a crossroads of divergent T-cell functions. European Journal Of Immunology, 46(10), 2302–2305.
Rothhammer, V., & Quintana, F. J. (2019). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: an environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. Nature Reviews Immunology, 19(3), 184–197.
Sadik, A., Somarribas Patterson, L. F., Öztürk, S., Mohapatra, S. R., Panitz, V., Secker, P. F., et al. (2020). IL4I1 is a metabolic Immune checkpoint that activates the AHR and promotes Tumor Progression. Cell, 182(5), 1252–1270e1234.
Scarlata, C. M., Celse, C., Pignon, P., Ayyoub, M., & Valmori, D. (2015). Differential expression of the immunosuppressive enzyme IL4I1 in human induced Aiolos+, but not natural Helios+, FOXP3 + Treg cells. European Journal Of Immunology, 45(2), 474–479.
Seok, S., Sun, H., Kim, Y. C., Kemper, B., & Kemper, J. K. (2020). Defective FXR-SHP Regulation in Obesity Aberrantly Increases miR-802 Expression, Promoting Insulin Resistance and Fatty Liver. Diabetes, 70(3), 733-744.
Shinde, R., & McGaha, T. L. (2018). The Aryl Hydrocarbon receptor: connecting immunity to the Microenvironment. Trends In Immunology, 39(12), 1005–1020.
Stanford, K. I., & Goodyear, L. J. (2014). Exercise and type 2 diabetes: molecular mechanisms regulating glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Advances In Physiology Education, 38(4), 308–314.
Wada, J., & Makino, H. (2016). Innate immunity in diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 12(1), 13–26.
Wu, Y. S., Li, Z. M., Chen, Y. T., Dai, S. J., Zhou, X. J., Yang, Y. X. (2020). Berberine Improves Inflammatory Responses of Diabetes Mellitus in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats and Insulin-Resistant HepG2 Cells through the PPM1B Pathway. J Immunol Res, 2020, 2141508.
Xia, H., Zhu, X., Zhang, X., Jiang, H., Li, B., Wang, Z., et al. (2019). Alpha-naphthoflavone attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in oleic acid-treated HepG2 hepatocytes and in high fat diet-fed mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 118, 109287.
Xu, C. X., Wang, C., Zhang, Z. M., Jaeger, C. D., Krager, S. L., Bottum, K. M., et al. (2015). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency protects mice from diet-induced adiposity and metabolic disorders through increased energy expenditure. Int J Obes (Lond), 39(8), 1300–1309.
Yaribeygi, H., Farrokhi, F. R., Butler, A. E., & Sahebkar, A. (2019). Insulin resistance: review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. Journal Of Cellular Physiology, 234(6), 8152–8161.
Zhang, X., Gan, M., Li, J., Li, H., Su, M., Tan, D., et al. (2020). Endogenous indole pyruvate pathway for Tryptophan Metabolism mediated by IL4I1. Journal Of Agriculture And Food Chemistry, 68(39), 10678–10684.
Zhao, H., Chen, L., Yang, T., Feng, Y. L., Vaziri, N. D., Liu, B. L., et al. (2019). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation mediates kidney disease and renal cell carcinoma. J Transl Med, 17(1), 302.
Zhao, R. X., He, Q., Sha, S., Song, J., Qin, J., Liu, P., et al. (2020). Increased AHR transcripts correlate with pro-inflammatory T-Helper lymphocytes polarization in both metabolically healthy obesity and type 2 Diabetic patients. Frontiers In Immunology, 11, 1644.
Zheng, J., Guo, Y., Hu, B., Zhu, L., Yang, Y., Li, S. (2020). Serum metabolomic profiles reveal the impact of BuZangTongLuo formula on metabolic pathways in diabetic mice with hindlimb ischemia. J Ethnopharmacol, 258, 112928.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (2023-YBSF-404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Zhufang Tian, Lin Xu, Junhui Du, Nan Li, Qi Wang and Hongzhi Sun. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Lin Run and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest Disclosure
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics Approval Statement
This study was approved by the ethic committee of Xi’an Jiaotong University Health Science Center and performed according to the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Run, L., Tian, Z., Xu, L. et al. Knockdown of IL4I1 Improved High Glucose-evoked Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells by Alleviating Inflammation and Lipotoxicity Through AHR Activation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 6694–6707 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04399-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04399-9