Abstract
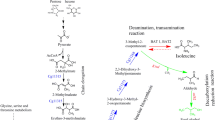
D-Arabitol is an important functional sugar alcohol, which can be used in the preparation of foods, chemicals, and medicines. Despite biological production of D-arabitol from low-cost substrates has recently been the focus of research, low yield of this technology has limited its large-scale exploitation. Optimization of this bioprocess could be a promising option to improve the yield of D-arabitol. In this study, one-factor-at-a-time (OFAT) strategy and Box-Behnken design (BBD) were used to increase D-arabitol production by Metschnikowia reukaufii CICC 31,858 through optimizing the fermentation conditions and medium composition. The OFAT optimization provided the optimal conditions for temperature, agitation speed, and fermentation time of 30℃, 220 rpm, and 6 days, respectively. Likewise, the optimum concentrations of peptone, ammonium sulfate, KH2PO4, MgSO4·7H2O, and fumaric acid in the fermentation medium were (g/L) 7.5, 1, 2, 0.5, and 7.5, respectively. Under these optimum conditions, 80.43 g/L of D-arabitol was produced from 200 g/L of glucose, with a productivity of 0.56 g/L/h. The BBD optimization with three important components of fermentation medium (KH2PO4, MgSO4·7H2O, and fumaric acid) showed that the predicted titer of D-arabitol varied from 47.21 to 89.27 g/L, and the actual titer of D-arabitol ranged from 47.36 to 89.83 g/L. The optimum concentrations (g/L) of KH2PO4, MgSO4·7H2O, and fumaric acid in the fermentation medium were found to be 1.0, 0.5, and 4.7 g/L, respectively. Under the optimum conditions, 92.45 g/L of D-arabitol was finally produced with the yield and productivity of 0.46 g/g and 0.64 g/L/h, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Roberts, A. (2016). The safety and regulatory process for low calorie sweeteners in the United States. Physiology and Behavior, 164, 439–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.02.039
Felipe Hernández-Pérez, A., Jofre, F. M., De Souza Queiroz, S., Vaz De Arruda, P., Chandel, A. K., & Felipe, M. D. G. D. A. (2020). In Biotechnological production of sweeteners. Biotechnological Production of Bioactive Compounds (pp. 261–292). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64323-0.00009-6
Ravikumar, Y., Ponpandian, L. N., Zhang, G., Yun, J., & Qi, X. (2021). Harnessing L-arabinose isomerase for biological production of D-tagatose: Recent advances and its applications. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 107, 16–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.11.020
Kordowska-Wiater, M. (2015). Production of arabitol by yeasts: Current status and future prospects. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 119(2), 303–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12807
Zhang, G., Lin, Y., He, P., Li, L., Wang, Q., & Ma, Y. (2014). Characterization of the sugar alcohol-producing yeast Pichia anomala. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 41(1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1364-5
Ravikumar, Y., Razack, S. A., Ponpandian, L. N., Zhang, G., Yun, J., Huang, J., & Qi, X. (2022). Microbial hosts for production of D-arabitol Current state-of-art and future prospects. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 120(April 2021), 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.12.029
Guo, Q., Zabed, H., Zhang, H., Wang, X., Yun, J., Zhang, G., … Qi, X. (2019). Optimization of fermentation medium for a newly isolated yeast strain (Zygosaccharomyces rouxii JM-C46) and evaluation of factors affecting biosynthesis of D-arabitol. Lwt, 99(June 2018), 319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.09.086
Qi, X., Luo, Y., Wang, X., Zhu, J., Lin, J., Zhang, H., & Sun, W. (2015). Enhanced d-arabitol production by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii JM-C46: Isolation of strains and process of repeated-batch fermentation. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 42(5), 807–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1603-z
Saha, B. C., Sakakibara, Y., & Cotta, M. A. (2007). Production of D-arabitol by a newly isolated Zygosaccharomyces rouxii. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34(7), 519–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-007-0211-y
Sánchez-Fresneda, R., Guirao-Abad, J. P., Argüelles, A., González-Párraga, P., Valentín, E., & Argüelles, J. C. (2013). Specific stress-induced storage of trehalose, glycerol and d-arabitol in response to oxidative and osmotic stress in Candida albicans. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 430(4), 1334–1339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.10.118
Song, W., Lin, Y., Hu, H., Xie, Z., & Zhang, J. (2011). Isolation and identification of a novel Candida sp H2 producing D-arabitol and optimization of D-arabitol production. Wei sheng wu xue bao = Acta microbiologica Sinica, 51(3), 332–339. https://doi.org/10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.2011.03.005
Zheng, S., Jiang, B., Zhang, T., & Chen, J. (2020). Combined mutagenesis and metabolic regulation to enhance d-arabitol production from Candida parapsilosis. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 47(4–5), 425–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-020-02278-4
Koganti, S., & Ju, L. K. (2013). Debaryomyces hansenii fermentation for arabitol production. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 79, 112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.07.014
Kumdam, H., Murthy, S. N., & Gummadi, S. N. (2014). Arabitol production by microbial fermentation - biosynthesis and future applications. International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research, 1(1), 1–12.
Nozaki, H., Suzuki, S. I., Tsuyoshi, N., & Yokozeki, K. (2003). Production of D-arabitol by Metschnikowia reukaufii AJ14787. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 67(9), 1923–1929. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.67.1923
Van Eck, J. H., Prior, B. A., & Brandt, E. V. (1993). The water relations of growth and polyhydroxy alcohol production by ascomycetous yeasts. Journal of General Microbiology, 139(5), 1047–1054. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-139-5-1047
Gancedo, C., Gancedo, J. M., & Sols, A. (1968). Glycerol metabolism in yeasts: Pathways of utilization and production. European Journal of Biochemistry, 5(2), 165–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00353.x
Cheng, H., Lv, J., Wang, H., Wang, B., Li, Z., & Deng, Z. (2014). Genetically engineered Pichia pastoris yeast for conversion of glucose to xylitol by a single-fermentation process. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(8), 3539–3552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5501-x
Narisetty, V., Astray, G., Gullón, B., Castro, E., Parameswaran, B., & Pandey, A. (2017). Improved 1,3-propanediol production with maintained physical conditions and optimized media composition: Validation with statistical and neural approach. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 126, 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.07.003
Yang, M., An, Y., Zabed, H. M., Guo, Q., Yun, J., Zhang, G., & Qi, X. (2019). Random mutagenesis of Clostridium butyricum strain and optimization of biosynthesis process for enhanced production of 1,3-propanediol. Bioresource Technology, 284, 188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.098
Zabed, H. M., Zhang, Y., Guo, Q., Yun, J., Yang, M., Zhang, G., & Qi, X. (2019). Co-biosynthesis of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and 1,3-propanediol by a newly isolated Lactobacillus reuteri strain during whole cell biotransformation of glycerol. Journal of Cleaner Production, 226(2019), 432–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.071
Chen, X. F., Huang, C., Yang, X. Y., Xiong, L., Chen, X. D., & Ma, L. L. (2013). Evaluating the effect of medium composition and fermentation condition on the microbial oil production by Trichosporon cutaneum on corncob acid hydrolysate. Bioresource Technology, 143, 18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.05.102
Sabra, W., Groeger, C., Sharma, P. N., & Zeng, A. P. (2014). Improved n-butanol production by a non-acetone producing Clostridium pasteurianum DSMZ 525 in mixed substrate fermentation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(9), 4267–4276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5588-8
Ramachandran, S., Roopesh, K., Nampoothiri, K. M., Szakacs, G., & Pandey, A. (2005). Mixed substrate fermentation for the production of phytase by Rhizopus spp. using oilcakes as substrates. Process Biochemistry, 40(5), 1749–1754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.06.040
Liszkowska, W., & Berlowska, J. (2021). Yeast fermentation at low temperatures: Adaptation to changing environmental conditions and formation of volatile compounds. Molecules, 26(4), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041035
Beltran, G., Novo, M., Guillamón, J. M., Mas, A., & Rozès, N. (2008). Effect of fermentation temperature and culture media on the yeast lipid composition and wine volatile compounds. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 121(2), 169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.11.030
Toyoda, T., & Ohtaguchi, K. (2011). Effect of temperature on d-arabitol production from lactose by Kluyveromyces lactis. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38(9), 1179–1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0893-4
Kumdam, H., Murthy, S. N., & Gummadi, S. N. (2013). Production of ethanol and arabitol by Debaryomyces nepalensis: Influence of process parameters. AMB Express, 3, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-0855-3-23
Akinosho, H., Rydzak, T., Borole, A., Ragauskas, A., & Close, D. (2015). Toxicological challenges to microbial bioethanol production and strategies for improved tolerance. Ecotoxicology, 24(10), 2156–2174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1543-4
Fairbairn, S., McKinnon, A., Musarurwa, H. T., Ferreira, A. C., & Bauer, F. F. (2017). The impact of single amino acids on growth and volatile aroma production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8(DEC), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02554
Walker, G. M., & Stewart, G. G. (2016). Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the production of fermented beverages. Beverages, 2(4), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages2040030
Rhee, J. Il, & Sohn, O. J. (2003). Flow injection system for on-line monitoring of fumaric acid in biological processes. In Analytica Chimica Acta (Vol. 499, pp. 71–80). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2003.08.029
Rakić, T., Kasagić-Vujanović, I., Jovanović, M., Jančić-Stojanović, B., & Ivanović, D. (2014). Comparison of full factorial design, central composite design, and Box-Behnken design in chromatographic method development for the determination of fluconazole and its impurities. Analytical Letters, 47(8), 1334–1347. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2013.867503
Loman, A. A., Islam, S. M. M., & Ju, L. K. (2018). Production of arabitol from enzymatic hydrolysate of soybean flour by Debaryomyces hansenii fermentation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(2), 641–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8626-5
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972042, 32150410349), National Key R & D Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFA0910401), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20210752), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2019M661759), Foreign Experts Program of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. QNJ20200214015), and Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. JSSCBS20210929).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiaqi Huang: Conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. Yingfeng An: Investigation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. Hossain M Zabed: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Yuvaraj Ravikumar: Writing—review and editing. Mei Zhao: Writing—review and editing. Junhua Yun: Formal analysis. Guoyan Zhang: Resources, formal analysis. Yufei Zhang: Resources, formal analysis. Xiaolan Li: Investigation, formal analysis. Xianghui Qi: Conceptualization; writing, review and editing; supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable. This article does not contain data collected from humans or animals.
Consent to Participate
All authors agreed to participate.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable. The manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., An, Y., Zabed, H.M. et al. Enhanced Biosynthesis of D-Arabitol by Metschnikowia reukaufii Through Optimizing Medium Composition and Fermentation Conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 194, 3119–3135 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03910-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03910-y