Abstract
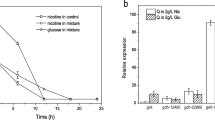
Nicotine-degrading Pseudomonas sp. JY-Q is a preferred strain utilized in reconstituted tobacco process for tobacco waste treatment. However, its efficiency of nicotine metabolism still requires to be improved via genomic technology such as promoter engineering based on genomic information. Concerning upstream module of nicotine metabolic pathway, we found that two homologous genes of nicotine dehydrogenase (nicA2 and nox) coexisted in strain JY-Q. However, the transcriptional amount of nox was 20-fold higher than that of nicA2. Thus, the nicA2 expression required improvement. Combinatorial displacement was accomplished for two predicted endogenous promoters, named as PnicA2 and Pnox for nicA2 and nox, respectively. The mutant with Pnox as the promoters for both nicA2 and nox exhibited the best nicotine metabolic capacity which increased by 66% compared to the wild type. These results suggested that endogenous promoter replacement is also feasible for function improvement of metabolic modules and strain enhancement of biodegradation capacity to meet real environment demand.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han, H., Ling, Z., Khan, A., Virk, A. K., Kulshrestha, S., & Li, X. (2019). Improvements of thermophilic enzymes: From genetic modifications to applications. Bioresource Technology, 279, 350–361.
Oh, Y. H., Choi, J. W., Kim, E. Y., Song, B. K., Jeong, K. J., Park, K., Kim, I. K., Woo, H. M., Lee, S. H., & Park, S. J. (2015). Construction of synthetic promoter-based expression cassettes for the production of cadaverine in recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176(7), 2065–2075.
Liu, Y., Li, Q., Zhu, H., & Yang, J. (2009). High soluble expression of D-amino acid oxidase in Escherichia coli regulated by a native promoter. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 158(2), 313–322.
Fowler, Z. L., Gikandi, W. W., & Koffas, M. A. (2009). Increased malonyl coenzyme a biosynthesis by tuning the Escherichia coli metabolic network and its application to flavanone production. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(18), 5831–5839.
Ramos, J. L., Marqués, S., & Timmis, K. N. (1997). Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid catabolic operons is achieved through an interplay of host factors and plasmid-encoded regulators. Annual Review of Microbiology, 51(1), 341–373.
Sharshar, M. M., Samak, N. A., Hao, X., Mu, T., Zhong, W., Yang, M., Peh, S., Ambreen, S., & Xing, J. (2019). Enhanced growth-driven stepwise inducible expression system development in haloalkaliphilic desulfurizing Thioalkalivibrio versutus. Bioresource Technology, 288, 121486.
Shavandi, M., Sadeghizadeh, M., Zomorodipour, A., & Khajeh, K. (2009). Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by recombinant Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A. Bioresource Technology, 100(1), 475–479.
Zhang, H., Zhao, R., Huang, C., Li, J., Shao, Y., Xu, J., Shu, M., & Zhong, W. (2019). Selective and faster nicotine biodegradation by genetically modified Pseudomonas sp. JY-Q in the presence of glucose. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103(1), 339–348.
Herring, C. D., Glasner, J. D., & Blattner, F. R. (2003). Gene replacement without selection: Regulated suppression of amber mutations in Escherichia coli. Gene, 311, 153–163.
Kim, J. Y., & Cha, H. J. (2003). Down-regulation of acetate pathway through antisense strategy in Escherichia coli: improved foreign protein production. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 83(7), 841–853.
Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Li, J., Shin, H. D., Chen, R. R., Du, G., Liu, L., & Chen, J. (2014). Modular pathway engineering of Bacillus subtilis for improved N-acetylglucosamine production. Metabolic Engineering, 23, 42–52.
Chen, X., Gao, C., Guo, L., Hu, G., Luo, Q., Liu, J., Nielsen, J., Chen, J., & Liu, L. (2018). DCEO biotechnology: Tools to design, construct, evaluate, and optimize the metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of chemicals. Chemical Reviews, 118(1), 4–72.
Hu, H., Wang, W., Tang, H., & Xu, P. (2015). Characterization of pseudooxynicotine amine oxidase of Pseudomonas putida S16 that is crucial for nicotine degradation. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 17770.
Hu, H., Wang, L., Wang, W., Wu, G., Tao, F., Xu, P., Deng, Z., & Tang, H. (2019). Regulatory mechanism of nicotine degradation in Pseudomonas putida. mBio, 10(3), e00602-19.
Li, J., Qian, S., Xiong, L., Zhu, C., Shu, M., Wang, J., Jiao, Y., He, H., Zhang, F., Linhardt, R. J., & Zhong, W. (2017). Comparative genomics reveals specific genetic architectures in nicotine metabolism of Pseudomonas sp. JY-Q. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 2085.
Lim, H. J., Kim, K., Shin, M., Jeong, J. H., Ryu, P. Y., & Choy, H. E. (2015). Effect of promoter-upstream sequence on sigma38-dependent stationary phase gene transcription. Journal of Microbiology, 53(4), 250–255.
Matsumoto, T., Tanaka, T., & Kondo, A. (2017). Engineering metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli for constructing a "microbial chassis" for biochemical production. Bioresource Technology, 245(Pt B), 1362–1368.
Nie, Z., Luo, H., Li, J., Sun, H., Xiao, Y., Jia, R., Liu, T., Chang, Y., Yu, H., & Shen, Z. (2020). High-throughput screening of T7 promoter mutants for soluble expression of cephalosporin C acylase in E. coli. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 190(1), 293–304.
Xu, M., Rao, Z., Yang, J., Xia, H., Dou, W., Jin, J., & Xu, Z. (2012). Heterologous and homologous expression of the arginine biosynthetic argC~H cluster from Corynebacterium crenatum for improvement of (L)-arginine production. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 39(3), 495–502.
Hwang, H. J., Lee, S. Y., & Lee, P. C. (2018). Engineering and application of synthetic nar promoter for fine-tuning the expression of metabolic pathway genes in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 11(1), 103.
Wang, S., Liu, G., Wang, J., Yu, J., Huang, B., & Xing, M. (2013). Enhancing cellulase production in Trichoderma reesei RUT C30 through combined manipulation of activating and repressing genes. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 40(6), 633–641.
Xiao, F., Wang, H., Shi, Z., Huang, Q., Huang, L., Lian, J., Cai, J., & Xu, Z. (2020). Multi-level metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas mutabilis ATCC31014 for efficient production of biotin. Metabolic Engineering, 61, 406–415.
Wang, L., Tang, H., Yu, H., Yao, Y., & Xu, P. (2014). An unusual repressor controls the expression of a crucial nicotine-degrading gene cluster in Pseudomonas putida S16. Molecular Microbiology, 91(6), 1252–1269.
Zhong, W., Zhu, C., Shu, M., Sun, K., Zhao, L., Wang, C., Ye, Z., & Chen, J. (2010). Degradation of nicotine in tobacco waste extract by newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. ZUTSKD. Bioresource Technology, 101(18), 6935–6941.
Liu, H., He, H., Cheng, C., Liu, J., Shu, M., Jiao, Y., Tao, F., & Zhong, W. (2015). Diversity analysis of the bacterial community in tobacco waste extract during reconstituted tobacco process. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(1), 469–476.
Li, J., Wang, J., Li, S., Yi, F., Xu, J., Shu, M., Shen, M., Jiao, Y., Tao, F., Zhu, C., Zhang, H., Qian, S., & Zhong, W. (2019). Co-occurrence of functional modules derived from nicotine-degrading gene clusters confers additive effects in Pseudomonas sp. JY-Q. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103(11), 4499–4510.
Liu, J., Ma, G., Chen, T., Hou, Y., Yang, S., Zhang, K. Q., & Yang, J. (2015). Nicotine-degrading microorganisms and their potential applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(9), 3775–3785.
Quandt, J., & Hynes, M. F. (1993). Versatile suicide vectors which allow direct selection for gene replacement in gram-negative bacteria. Gene, 127(1), 15–21.
Schafer, A., Tauch, A., Jager, W., Kalinowski, J., Thierbach, G., & Puhler, A. (1994). Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: Selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene, 145(1), 69–73.
Kovach, M. E., Elzer, P. H., Hill, D. S., Robertson, G. T., Farris, M. A., Roop 2nd., R. M., & Peterson, K. M. (1995). Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene, 166(1), 175–176.
Tang, H., Wang, L., Wang, W., Yu, H., Zhang, K., Yao, Y., & Xu, P. (2013). Systematic unraveling of the unsolved pathway of nicotine degradation in Pseudomonas. PLoS Genetics, 9(10), e1003923.
Li, J., Li, S., Xie, L., Chen, G., Shen, M., Pan, F., Shu, M., Yang, Y., Jiao, Y., Zhang, F., Linhardt, R. J., & Zhong, W. (2021). Additional Role of Nicotinic Acid Hydroxylase for the Transformation of 3-Succinoyl-pyridine by Pseudomonas sp. Strain JY-Q. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87(6), e02740–20.
Liu, T., Li, J., Qiu, L., Zhang, F., Linhardt, R. J., & Zhong, W. (2020). Combined genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the dibutyl phthalate metabolic pathway in Arthrobacter sp. ZJUTW. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 117(12), 3712–3726.
Li, J., Shen, M., Chen, Z., Pan, F., Yang, Y., Shu, M., Chen, G., Jiao, Y., Zhang, F., Linhardt, R. J., & Zhong, W. (2021). Expression and functional identification of two homologous nicotine dehydrogenases, NicA2 and Nox, from Pseudomonas sp. JY-Q. Protein Expression and Purification, 178, 105767.
Huang, C., Shan, L., Chen, Z., He, Z., Li, J., Yang, Y., Shu, M., Pan, F., Jiao, Y., Zhang, F., Linhardt, R. J., & Zhong, W. (2021). Differential Effects of Homologous Transcriptional Regulators NicR2A, NicR2B1, and NicR2B2 and Endogenous Ectopic Strong Promoters on Nicotine Metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. Strain JY-Q. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87(3), e02457–20.
Tang, Q., Lu, T., & Liu, S. J. (2018). Developing a synthetic biology toolkit for Comamonas testosteroni, an emerging cellular chassis for bioremediation. ACS Synthetic Biology, 7(7), 1753–1762.
Liu, D., Mao, Z., Guo, J., Wei, L., Ma, H., Tang, Y., Chen, T., Wang, Z., & Zhao, X. (2018). Construction, model-based analysis, and characterization of a promoter library for fine-tuned gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. ACS Synthetic Biology, 7(7), 1785–1797.
Wei, L., Xu, N., Wang, Y., Zhou, W., Han, G., Ma, Y., & Liu, J. (2018). Promoter library-based module combination (PLMC) technology for optimization of threonine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(9), 4117–4130.
Liu, C., Zhang, B., Liu, Y. M., Yang, K. Q., & Liu, S. J. (2018). New intracellular shikimic acid biosensor for monitoring shikimate synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. ACS Synthetic Biology, 7(2), 591–601.
Jin, L. Q., Jin, W. R., Ma, Z. C., Shen, Q., Cai, X., Liu, Z. Q., & Zheng, Y. G. (2019). Promoter engineering strategies for the overproduction of valuable metabolites in microbes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103(21-22), 8725–8736.
Availability of Data and Materials
GenBank accession number of strain JY-Q is CP011525. Data and materials supporting this study have been provided in the text.
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for Publication
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31970104, 31800118, 21938012, 31670115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jun Li: Conceptualization, resources, data curation, software, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft, project administration, writing—review and editing. Fengmei Yi: Data curation, software, formal analysis, writing—original draft, visualization, methodology. Guoqing Chen, Zeyu Chen, Zeling Zhang, Xiaotong Mei: Software, investigation. Fanda Pan, Yang Yang, Ming Shu: Investigation, methodology. Weihong Zhong: Conceptualization, resources, supervision, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 188 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yi, F., Chen, G. et al. Function Enhancement of a Metabolic Module via Endogenous Promoter Replacement for Pseudomonas sp. JY-Q to Degrade Nicotine in Tobacco Waste Treatment. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193, 2793–2805 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03566-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03566-0