Abstract
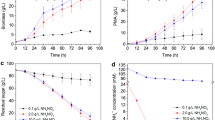
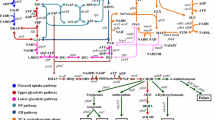
Hirsutella sinensis is considered as the only correct anamorph of Ophiocordyceps sinensis. To improve cordycepin and cordycepic acid production in H. sinensis, the biosynthetic pathways of cordycepin and cordycepic acid were predicted, and verified by cloning and expressing genes involved in these pathways, respectively. Then, 5′-nucleotidase participating in biosynthetic pathway of cordycepin, hexokinase, and glucose phosphate isomerase involved in biosynthetic pathway of cordycepic acid, were demonstrated playing important roles in the corresponding biosynthetic pathway by real-time PCR, accompanying with significantly up-regulated 15.03-, 5.27-, and 3.94-fold, respectively. Moreover, the metabolic regulation of H. sinensis was performed. As expected, cordycepin production reached 1.09 mg/g when additional substrate of 5′-nucleotidase was 4 mg/mL, resulting in an increase of 201.1 % compared with the control. In the same way, cordycepic acid production reached 26.6 and 23.4 % by adding substrate of hexokinase or glucose phosphate isomerase, leading to a rise of 77.3 and 55.1 %, respectively. To date, this is the first time to improve cordycepin and cordycepic acid production through metabolic regulation based on biosynthetic pathway analysis, and metabolic regulation is proved as a simple and effective way to enhance the output of cordycepin and cordycepic acid in submerged cultivation of H. sinensis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong, C. H., & Yao, Y. J. (2005). Nutritional requirements of mycelial growth of Cordyceps sinensis in submerged culture. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 99, 483–92.
Zhou, X., Gong, Z., Su, Y., Lin, J., & Tang, K. (2009). Cordyceps fungi: natural products, pharmacological functions and developmental products. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 61, 279–91.
Liu, Z. Y., Yao, Y. J., Qi Liang, Z., Liu, A. Y., Pegler, D. N., & Chase, M. W. (2001). Molecular evidence for the anamorph-teleomorph connection in Cordyceps sinensis. Mycological Research, 105, 827–32.
Hsieh, C., Tsai, M. J., Hsu, T. H., Chang, D. M., & Lo, C. T. (2005). Medium optimization for polysaccharide production of Cordyceps sinensis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 120, 145–57.
Liu, Y. S., Leung, P. H., & Wu, J. Y. (2008). Exopolysaccharide production in batch and semi-continuous fermentation of Cordyceps sinensis. Journal of Biotechnology, 136, S301–2.
Sheng, L., Chen, J., Li, J., & Zhang, W. (2011). An exopolysaccharide from cultivated Cordyceps sinensis and its effects on cytokine expressions of immunocytes. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 163, 669–78.
Nakamura, K., Konoha, K., Yoshikawa, N., Yamaguchi, Y., Kagota, S., Shinozuka, K., & Kunitomo, M. (2005). Effect of cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) on hematogenic lung metastatic model mice. In Vivo, 19, 137–41.
Tsai, Y. J., Lin, L. C., & Tsai, T. H. (2010). Pharmacokinetics of adenosine and cordycepin, a bioactive constituent of Cordyceps sinensis in rat. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 4638–43.
Kondrashov, A., Meijer, H. A., Barthet-Barateig, A., Parker, H. N., Khurshid, A., Tessier, S., Sicard, M., Knox, A. J., Pang, L., & De Moor, C. H. (2012). Inhibition of polyadenylation reduces inflammatory gene induction. RNA, 18, 2236–50.
Fan, H., Li, S., Xiang, J., Lai, C., Yang, F., Gao, J., & Wang, Y. (2006). Qualitative and quantitative determination of nucleosides, bases and their analogues in natural and cultured Cordyceps by pressurized liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–ESI–MS/MS). Analytica Chimica Acta, 567, 218–28.
Li, S., Li, P., Lai, C., Gong, Y., Kan, K. K., Dong, T. T., Tsim, K. W., & Wang, Y. (2004). Simultaneous determination of ergosterol, nucleosides and their bases from natural and cultured Cordyceps by pressurised liquid extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography, A, 1036, 239–43.
Guo, F. Q., Li, A., Huang, L. F., Liang, Y. Z., & Chen, B. M. (2006). Identification and determination of nucleosides in Cordyceps sinensis and its substitutes by high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 40, 623–30.
Li, Z., Yu, J., Liang, Z., & Xiao, Y. (2008). Effect of precursor and fungal elicitor on cordycepin production. Food Science, 29, 273–5.
Mao, X. B., Eksriwong, T., Chauvatcharin, S., & Zhong, J. J. (2005). Optimization of carbon source and carbon/nitrogen ratio for cordycepin production by submerged cultivation of medicinal mushroom Cordyceps militaris. Process Biochemistry, 40, 1667–72.
Das, S. K., Masuda, M., Sakurai, A., & Sakakibara, M. (2009). Effects of additives on cordycepin production using a Cordyceps militaris mutant induced by ion beam irradiation. African Journal of Biotechnology, 8, 3041–7.
Chatterjee, R., Srinivasan, K. S., & Maiti, P. C. (1957). Cordyceps sinesis (Berkeley) saccardo: structure of cordycepic acid. Journal of the American Pharmacists Association, 46, 114–8.
Mendelow, A. D., Teasdale, G. M., Russell, T., Flood, J., Patterson, J., & Murray, G. D. (1985). Effect of mannitol on cerebral blood flow and cerebral perfusion pressure in human head injury. Journal of Neurosurgery, 63, 43–8.
Li, R., Zhao, Y., & Jiang, X. L. (2011). Chemical composition of Hirsutella beakdumountainsis, a potential substitute for Cordyceps sinensis. African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 16286–92.
Albrecht, M., Misawa, N., & Sandmann, G. (1999). Metabolic engineering of the terpenoid biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli for production of the carotenoids beta-carotene and zeaxanthin. Biotechnology Letters, 21, 791–5.
Singh, V., Mani, I., Chaudhary, D. K., & Dhar, P. K. (2014). Metabolic engineering of biosynthetic pathway for production of renewable biofuels. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172, 1158–71.
Jia, X., Li, S., Xie, S., & Wen, J. (2012). Engineering a metabolic pathway for isobutanol biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 168, 1–9.
Rahman, Z., Sung, B. H., Yi, J. Y., Bui, L. M., Lee, J. H., & Kim, S. C. (2014). Enhanced production of n-alkanes in Escherichia coli by spatial organization of biosynthetic pathway enzymes. Journal of Biotechnology, 192, 187–91.
Cheon, Y., Kim, J. S., Park, J. B., Heo, P., Lim, J. H., Jung, G. Y., Seo, J. H., Park, J. H., Koo, H. M., Cho, K. M., Park, J. B., Ha, S. J., & Kweon, D. H. (2014). A biosynthetic pathway for hexanoic acid production in Kluyveromyces marxianus. Journal of Biotechnology, 182, 30–6.
Liu, Z. Q., Lin, S., Baker, P. J., Wu, L. F., Wang, X. R., Wu, H., Xu, F., Wang, H. Y., Brathwaite, M. E., & Zheng, Y. G. (2015). Transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the entomopathogenic fungus Hirsutella sinensis isolated from Ophiocordyceps sinensis. BMC Genomics, 16, 106.
Reboul, J., Vaglio, P., Rual, J. F., Lamesch, P., Martinez, M., Armstrong, C. M., Li, S. M., Jacotot, L., Bertin, N., Janky, R., Moore, T., Hudson, J. R., Hartley, J. L., Brasch, M. A., Vandenhaute, J., Boulton, S., Endress, G. A., Jenna, S., Chevet, E., Papasotiropoulos, V., Tolias, P. P., Ptacek, J., Snyder, M., Huang, R., Chance, M. R., Lee, H. M., Doucette-Stamm, L., Hill, D. E., & Vidal, M. (2003). C. elegans ORFeome version 1.1: experimental verification of the genome annotation and resource for proteome-scale protein expression. Nature Genetics, 34, 35–41.
Liu, Z. Q., Zheng, W., Huang, J. F., Jin, L. Q., Jia, D. X., Zhou, H. Y., Xu, J. M., Liao, C. J., Cheng, X. P., Mao, B. X., & Zheng, Y. G. (2015). Improvement and characterization of a hyperthermophilic glucose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus and its application in production of high fructose corn syrup. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 42, 1091–103.
Deng, L., Zhou, T. Y., Pi, L., Zhao, X. H., Han, T., Li, Y. K., & Han, F. (2013). Optimization of microwave-mssisted extraction of cordycepic acid and cordycepin from cultured Cordyceps militaris by response surface methodology. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 25, 8065–71.
Xiao, J. H., Xiao, D. M., Xiong, Q., Liang, Z. Q., & Zhong, J. J. (2009). Optimum extraction and high-throughput detection of cordycepic acid from medicinal macrofungi Cordyceps jiangxiensis, Cordyceps taii and Cordyceps gunnii. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 7, 328–33.
Zheng, P., Xia, Y., Xiao, G., Xiong, C., Hu, X., Zhang, S., Zheng, H., Huang, Y., Zhou, Y., & Wang, S. (2011). Genome sequence of the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris, a valued traditional Chinese medicine. Genome Biology, 12(11), 287–302.
Lennon, M. B., & Suhadolnik, R. J. (1976). Biosynthesis of 3′-deoxyadenosine by Cordyceps militaris: mechanism of reduction. BBA-Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis, 425, 532–6.
Stone, R. (2010). Improbable partners aim to bring biotechnology to a Himalayan kingdom. Science, 327, 940–1.
Li, R., Jiang, X. L., & Guan, H. S. (2010). Optimization of mycelium biomass and exopolysaccharides production by Hirsutella sp. in submerged fermentation and evaluation of exopolysaccharides antibacterial activity. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9, 196–203.
Yu, S. J., Zhang, Y., & Fan, M. Z. (2012). Analysis of volatile compounds of mycelia of Hirsutella sinensis, the anamorph of Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Medical Materials and Engineering, 140, 253–7.
Xiang, L., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Luo, H., Li, C., Xu, X., Sun, C., Song, J., Shi, L., & He, L. (2014). Transcriptome analysis of the Ophiocordyceps sinensis fruiting body reveals putative genes involved in fruiting body development and cordycepin biosynthesis. Genomics, 103(1), 154–9.
Suhadolnik, R., Weinbaum, G., & Meloche, H. (1964). The biosynthesis of cordycepin. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 86, 948–9.
Iwamoto, K., & Shiraiwa, Y. (2005). Salt-regulated mannitol metabolism in algae. Marine Biotechnology, 7, 407–15.
Qi, J., Zheng, N., Zhang, B., Sun, P., Hu, S., Xu, W., Ma, Q., Zhao, T., Zhou, L., Qin, M., & Li, X. (2013). Mining genes involved in the stratification of Paris polyphylla seeds using high-throughput embryo transcriptome sequencing. BMC Genomics, 14(6), 1–14.
Pathan, A. A. K., Uma Devi, K., Vogel, H., & Reineke, A. (2007). Analysis of differential gene expression in the generalist entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuillemin grown on different insect cuticular extracts and synthetic medium through cDNA-AFLPs. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 44(12), 1231–41.
Xu, A. L., Xia, J. L., Liu, K. K., Li, L., Yang, Y., Nie, Z. Y., & Qiu, G. Z. (2010). Real-time PCR analysis of metabolic pathway of PHB in Acidiphilium cryptum DX1-1. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 20, 71–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (no. 2012AA021701) and the Key Scientific and Technology Programs of Zhejiang Province (no. 2012C03005-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest exists.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 552 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Liu, ZQ., Xue, YP. et al. Biosynthetic Pathway Analysis for Improving the Cordycepin and Cordycepic Acid Production in Hirsutella sinensis . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179, 633–649 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2020-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2020-0