Abstract
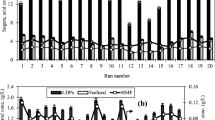
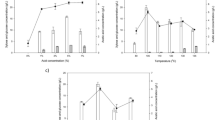
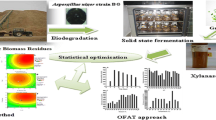
Xylose-rich sawdust hydrolysate can be an economic substrate for the enzymatic production of xylitol, a specialty product. It is important to identify the process factors influencing xylitol production. This research aimed to screen the parameters significantly affecting bioxylitol synthesis from wood sawdust by xylose reductase (XR). Enzymatic bioxylitol production was conducted to estimate the effect of different variables reaction time (2–18 h), temperature (20–70 °C), pH (4.0–9.0), NADPH (1.17–5.32 g/L), and enzyme concentration (2–6 %) on the yield of xylitol. Fractional factorial design was followed to identify the key process factors. The screening design identified that time, temperature, and pH are the most significant factors influencing bioxylitol production among the variables with the values of 12 h, 35 °C, and 7.0, respectively. These conditions led to a xylitol yield of 71 % (w/w). This is the first report on the statistical screening of process variables influencing enzyme-based bioxylitol production from lignocellulosic biomass.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rafiqul, I. S. M., & Sakinah, A. M. M. (2013). Processes for the production of xylitol—a review. Food Reviews International, 29(2), 127–156.
Li, Z., Qu, H., Li, C., & Zhou, X. (2013). Direct and efficient xylitol production from xylan by Saccharomyces cerevisiae through transcriptional level and fermentation processing optimizations. Bioresource Technology, 149, 413–419.
Deng, L. H., Tang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2014). Detoxification of corncob acid hydrolysate with SAA pretreatment and xylitol production by immobilized Candida tropicalis. Scientific World Journal. doi:10.1155/2014/214632.
Ping, Y., Ling, H. Z., Song, G., & Ge, J. P. (2013). Xylitol production from non-detoxified corncob hemicelluloses acid hydrolysate by Candida tropicalis. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 75, 86–91.
Zhang, J., Geng, A., Yao, C., Lu, Y., & Li, Q. (2012). Xylitol production from d-xylose and horticultural waste hemicellulosic hydrolysate by a new isolate of Candida athensensis SB18. Bioresource Technology, 105, 134–141.
Jacques, N., & Casaregola, S. (2008). Safety assessment of dairy microorganisms: the hemiascomycetous yeasts. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 126, 321–326.
Branco, R. F., Santos, J. C., & Silva, S. S. (2011). A novel use for sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic fraction: xylitol enzymatic production. Biomass and Bioenergy, 35, 3241–3246.
Neuhauser, W., Steininger, M., Haltrich, D., Kulbe, K. D., & Nidetzky, B. (1998). A pH-controlled fed-batch process can overcome inhibition by formate in NADH-dependent enzymatic reductions using formate dehydrogenase-catalyzed coenzyme regeneration. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 60(3), 277–282.
Nidetzky, B., Neuhauser, W., Haltrich, D., & Kulbe, K. D. (1996). Continuous enzymatic production of xylitol with simultaneous coenzyme regeneration in a charged membrane reactor. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 52(3), 387–396.
Rafiqul, I. S. M., & Sakinah, A. M. M. (2012). Kinetic studies on acid hydrolysis of Meranti wood sawdust for xylose production. Chemical Engineering Science, 71, 431–437.
Rafiqul, I. S. M., & Sakinah, A. M. M. (2012). Design of process parameters for the production of xylose from wood sawdust. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 90, 1307–1312.
Rafiqul, I. S. M., Sakinah, A. M. M., & Karim, R. (2014). Production of xylose from Meranti wood sawdust by dilute acid hydrolysis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174(2), 542–555.
Rafiqul, I. S. M., Sakinah, A. M. M., & Zularisam, A. W. (2015). Inhibition by toxic compounds in the hemicellulosic hydrolysates on the activity of xylose reductase from Candida tropicalis. Biotechnology Letters, 37(1), 191–196.
Rafiqul, I. S. M., & Sakinah, A. M. M. (2015). Biochemical properties of xylose reductase prepared from adapted strain of Candida tropicalis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175(1), 387–399.
Nidetzky, B., Brüggler, K., Kratzer, R., & Mayr, P. (2003). Multiple forms of xylose reductase in Candida intermedia: comparison of their functional properties using quantitative structure-activity relationships, steady-state kinetic analysis, and pH studies. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(27), 7930–7935.
Woodyer, R., Simurdiak, M., Donk, W. A., & Zhao, H. (2005). Heterologous expression, purification and characterization of a highly active xylose reductase from Neurospora crassa. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(3), 1642–1647.
Bezerra, M. A., Santelli, R. E., Oliveira, E. P., Villar, L. S., & Escaleira, L. A. (2008). Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta, 76, 965–977.
Bouchekara, H. R. E. H., Dahman, G., & Nahas, M. (2011). Smart electromagnetic simulations: guidelines for design of experiments technique. Progress in Electromagnetics Research B, 31, 357–379.
Graham, H. D. (1992). Stabilization of the Prussian blue color in the determination of polyphenols. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 40, 801–805.
Rafiqul, I. S. M., Sakinah, A. M. M., & Zularisam, A. W. (2015). Evaluation of sawdust hemicellulosic hydrolysate for bioproduction of xylitol by enzyme xylose reductase. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 94, 82–89.
Montgomery, D. C. (2001). Design and analysis of experiments (5th ed., pp. 427–450). New York: Wiley.
Acknowledgments
The financial support for this research work from the Universiti Malaysia Pahang (UMP) and Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia (MTUN-COE Research Grant No. RDU 121205) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafiqul, I.S.M., Sakinah, A.M.M. & Zularisam, A.W. Enzymatic Production of Bioxylitol from Sawdust Hydrolysate: Screening of Process Parameters. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 1071–1083 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1630-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1630-2