Abstract
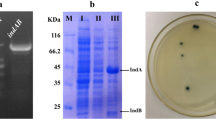
Indirubin, a red isomer of indigo, can be used for the treatment of various chronic diseases. However, the microbial production of indirubin did not receive much attention probably due to its low yield compared with indigo. In this study, the recombinant Escherichia coli containing the naphthalene dioxygenase (NDO) genes from Comamonas sp. MQ was used to produce indirubin from tryptophan. To enhance the production of indirubin, the induction conditions for NDO expression were optimized. The optimal induction conditions were carried out with 0.5 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside at 30 °C when cells were grown to OD600 ≈ 1.20. Subsequently, the effects of medium composition on indirubin production were investigated by response surface methodology, and 9.37 ± 1.01 mg/l indirubin was produced from 3.28 g/l tryptophan. Meanwhile, the indirubin production was further improved by adding 2-oxindole and isatin to the tryptophan medium after induction. About 57.98 ± 2.62 mg/l indirubin was obtained by the addition of 500 mg/l 2-oxindole after 1-h induction, which was approximately 6.2-fold to that without additional 2-oxindole. The present study provided a possible way to improve the production of indirubin and should lay the foundation for the application of microbial indirubin production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry, A., Dodge, T. C., Pepsin, M., & Weyler, W. (2002). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 127–133.
Hoessel, R., Leclerc, S., Endicott, J. A., Nobel, M. E., Lawrie, A., Tunnah, P., et al. (1999). Nature Cell Biology, 1, 60–67.
Leclerc, S., Garnier, M., Hoessel, R., Marko, D., Bibb, J. A., Snyder, G. L., et al. (2001). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 251–260.
Spink, B. C., Hussain, M. M., Katz, B. H., Eisele, L., & Spink, D. C. (2003). Biochemical Pharmacology, 66, 2313–2321.
Zhang, A. J., Qu, Y. Y., Zhang, B. J., Zhang, L. J., Zeng, C., Peng, J. X., et al. (2007). Journal of Molecular Medicine, 85, 1263–1270.
Meyer, A., Würsten, M., Schmid, A., Kohler, H. P., & Witholt, B. (2002). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 34161–34167.
Lee, J. Y., Shin, Y. S., Shin, H. J., & Kim, G. J. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 9193–9198.
Han, G. H., Gim, G. H., Kim, W., Seo, S. I., & Kim, S. W. (2012). Journal of Biotechnology, 164, 179–187.
Ensley, B. D., Ratzkin, B. J., Osslund, T. D., Simon, M. J., Wackett, L. P., & Gibson, D. T. (1983). Science, 222, 167–169.
Gillam, E. M., Notley, L. M., Cai, H., De Voss, J. J., & Guengerich, F. P. (2000). Biochemistry, 39, 13817–13824.
Doukyu, N., Toyoda, K., & Aono, R. (2003). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 60, 720–725.
Choi, H. S., Kim, J. K., Cho, E. H., Kim, Y. C., Kim, J. I., & Kim, S. W. (2003). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306, 930–936.
Rui, L., Reardon, K. F., & Wood, T. K. (2005). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 66, 422–429.
Pathak, H., & Madamwar, D. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1616–1626.
Eaton, R. W., & Chapman, P. J. (1995). Journal of Bacteriology, 177, 6983–6988.
McClay, K., Boss, C., Keresztes, I., & Steffan, R. J. (2005). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 5476–5483.
Maugard, T., Enaud, E., Choisy, P., & Legoy, M. D. (2001). Phytochemistry, 58, 897–904.
Qu, Y. Y., Zhang, X. W., Ma, Q., Ma, F., Zhang, Q., Li, X. L., et al. (2012). Biotechnological Letters, 34, 353–357.
Lu, Y., & Mei, L. H. (2007). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 247–253.
Prakash, D., Pandey, J., Tiwary, B. N., & Jain, R. K. (2010). BMC Biotechnology, 10, 49.
Zhang, Q., Qu, Y. Y., Zhou, J. T., Zhang, X. W., Zhou, H., Ma, Q., et al. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 10553–10560.
Liu, J. F., Zhang, Z. J., Li, A. T., Pan, J., & Xu, J. H. (2011). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 665–672.
Zhang, X. W., Qu, Y. Y., Ma, Q., Zhou, H., Li, X. L., Kong, C. L., et al. (2013). Process Biochemistry, 48, 581–587.
Han, G. H., Bang, S. E., Babu, B. K., Chang, M., Shin, H. J., & Kim, S. W. (2011). Process Biochemistry, 46, 788–791.
Pan, H. F., Xie, Z. P., Bao, W. N., & Zhang, J. G. (2008). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 42, 133–138.
Ghosh, D., & Hallenbeck, P. C. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 1820–1825.
Shi, S. N., Ma, F., Sun, T. H., Li, A., Zhou, J. T., & Qu, Y. Y. (2013). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169, 1088–1097.
Shi, S. N., Ma, F., Sun, T. H., Li, A., Zhou, J. T., & Qu, Y. Y. (2013). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 170, 951–961.
Han, G. H., Shin, H. J., & Kim, S. W. (2008). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 42, 617–623.
Qu, Y. Y., Shi, S. N., Zhou, H., Ma, Q., Li, X. L., Zhang, X. W., et al. (2012). PLoS One, 7, e44313.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21176040) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-13-0077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Qu, Y., Ma, Q. et al. Production of Indirubin from Tryptophan by Recombinant Escherichia coli Containing Naphthalene Dioxygenase Genes from Comamonas sp. MQ. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 3194–3206 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0743-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0743-3