Abstract
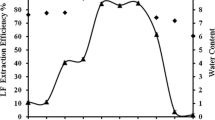
Chaotropes could significantly enhance lipase activity recovery in reverse micellar back extraction. However, the mechanism of chaotropes promoting the release of enzyme from reverse micelles was not clear. In this study, chaotropes were added in the process of lipase reverse micellar extraction, and back extraction recovery was improved. In back extraction, at 0.6 M urea in stripping solution, 94.60 % total extraction recovery was obtained. Meanwhile at 0.3 M guanidine hydrochloride, nearly 65 % lipases were released into the stripping solution. DLS and Karl Fischer method results showed that the presence of urea in stripping solution could weaken the electrostatic interaction between lipase and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide molecules, promoting lipase release from reverse micelles, and guanidine hydrochloride could stimulate lipase and free water molecules enwrapped in reverse micelle release into the stripping solution. These experimental results provide a clue for understanding the mechanism of chaotropes influencing on protein recovery in reverse micelle back extraction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mendes, A. A., & Oliveira, P. C. (2012). Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 78, 119–134.
Giovenco, S., Verheggen, F., & Laane, C. (1987). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 9, 470–473.
Noritomi, H., Hidaka, Y., Kato, S., & Nagahama, K. (1999). Biotechnology Techniques, 13, 181–183.
Shin, Y. O., Weber, M. E., & Vera, J. H. (2003). Separation Science and Technology, 38, 1733–1748.
Jarudilokkul, S., Poppenborg, L. H., & Stuckey, D. C. (1999). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 62, 593–601.
Zhang, W., Liu, H. Z., & Chen, J. Y. (2002). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 12, 1–5.
Chen, L. J., & Cao, X. J. (2007). Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 40, 511–515.
Nagayama, K., Nishimura, R., & Doi, T. (1999). Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 74, 227–230.
Naoe, K., Murata, M., One, C., & Kawagoe, M. (2002). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 10, 137–142.
Zhou, B., Wan, J. F., Wang, J. Z., & Cao, X. J. (2012). Process Biochemistry, 47, 229–233.
Stoytcheva, M., Montero, G., & Zlatev, R. (2012). Current Analytical Chemistry, 8, 400–407.
Naoe, K., Takeuchi, C., Kawagoe, M., Nagayama, K., & Imai, M. (2007). Journal of Chromatography B, 850, 277–284.
Gaikaiwari, R. P., Wagh, S. A., & Kulkarni, B. D. (2012). Bioresource Technology, 108, 224–230.
Zhou, H. T., Lin, S. S., & Xing, H. (2013). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 416, 16–22.
Calvaruso, G., Minore, A., & Liveri, V. T. (2001). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 243, 227–232.
Dias, L. G., Florenzano, F. H., & Reed, W. F. (2002). Langmuir, 18, 319–324.
Li, Q., Hu, X. L., Ma, S. Y., & Politi, M. J. (2002). Acta Chimica Sinica, 60, 438–445.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 20976052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, T., Cao, X. Effect of Chaotropes on Lipase Back Extraction Recovery in the Process of Reverse Micellar Extraction. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 3287–3296 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0738-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0738-0